Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for conserving water in crop production. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a larger area, simulating natural rainfall, but often results in higher water loss through evaporation and wind drift. Choosing between drip and sprinkler irrigation depends on crop type, soil conditions, and water availability, with drip systems favored for precise water management and sprinkler systems for broader coverage.
Table of Comparison
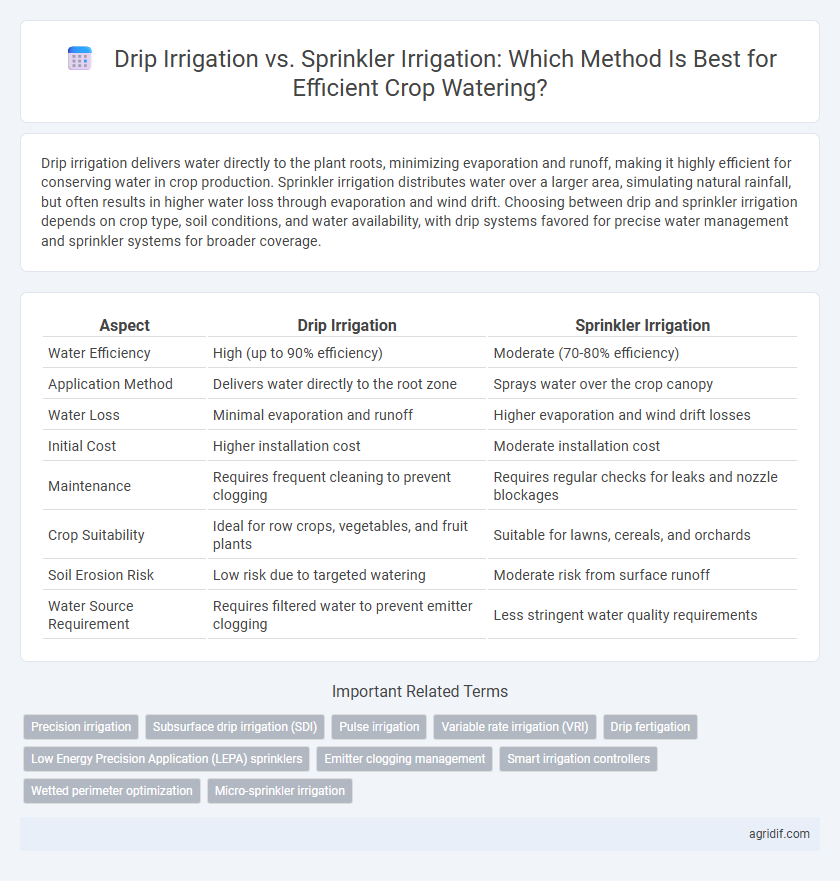
| Aspect | Drip Irrigation | Sprinkler Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High (up to 90% efficiency) | Moderate (70-80% efficiency) |
| Application Method | Delivers water directly to the root zone | Sprays water over the crop canopy |
| Water Loss | Minimal evaporation and runoff | Higher evaporation and wind drift losses |
| Initial Cost | Higher installation cost | Moderate installation cost |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent cleaning to prevent clogging | Requires regular checks for leaks and nozzle blockages |
| Crop Suitability | Ideal for row crops, vegetables, and fruit plants | Suitable for lawns, cereals, and orchards |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Low risk due to targeted watering | Moderate risk from surface runoff |
| Water Source Requirement | Requires filtered water to prevent emitter clogging | Less stringent water quality requirements |
Introduction to Irrigation Methods in Crop Production
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of crops through a network of valves, pipes, and emitters, maximizing water efficiency and reducing evaporation losses. Sprinkler irrigation simulates rainfall by distributing water over the crop canopy via overhead nozzles, suitable for various field sizes but often resulting in higher water consumption due to runoff and evaporation. Selecting the appropriate irrigation method depends on factors such as crop type, soil texture, water availability, and overall farm management goals.
Overview of Drip Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems deliver water directly to the root zone through a network of tubes, emitters, and valves, minimizing evaporation and runoff while maximizing water efficiency. These systems are highly effective in sandy soils and for crops requiring precise moisture control, such as vegetables and fruits. Compared to sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation reduces water use by up to 50% and enhances crop yield by maintaining consistent soil moisture levels.
Overview of Sprinkler Irrigation Systems
Sprinkler irrigation systems distribute water through a network of pipes and spray it over crops in a controlled manner, mimicking natural rainfall. These systems are highly efficient for uniform water application across varying topographies and soil types, reducing water runoff and erosion. Sprinkler irrigation is suitable for a wide range of crops, promoting better growth by maintaining consistent moisture levels in the root zone.
Water Efficiency: Drip vs Sprinkler Irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, resulting in up to 90% water-use efficiency compared to sprinkler systems. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over larger areas but can lose 30-50% due to wind drift and evaporation. Studies show drip irrigation can reduce water consumption by 30-60% while improving crop yield, making it ideal for water-scarce regions.
Cost Analysis: Installation and Operation
Drip irrigation systems generally have higher initial installation costs due to their complex tubing and emitter setup but offer lower operational expenses by minimizing water waste and energy consumption. Sprinkler irrigation typically involves lower upfront investment with simpler equipment but incurs higher operational costs through greater water usage and increased power requirements for pumping. Evaluating long-term cost efficiency, drip irrigation provides substantial savings in water bills and maintenance, making it more cost-effective for sustainable crop production.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, promoting higher crop yields and improved quality by minimizing water wastage and reducing soil erosion. Sprinkler irrigation provides uniform water distribution but can lead to higher evaporation losses and increased risk of disease due to wet foliage. Studies show drip irrigation can increase crop yield by up to 30% and enhance fruit quality through better nutrient retention compared to sprinkler systems.
Suitability for Different Crops and Soils
Drip irrigation is highly suitable for row crops, fruits, and vegetables, especially in sandy or loamy soils where precision water delivery minimizes evaporation and runoff. Sprinkler irrigation works well for cereals and pasture crops on clay or silty soils, providing uniform coverage and helping control soil erosion. Crop water requirements and soil infiltration rates critically determine the optimal irrigation method for maximizing yield efficiency.
Maintenance and Longevity of Irrigation Systems
Drip irrigation systems require regular inspection for clogged emitters and filter cleaning to maintain optimal performance, offering greater longevity with proper upkeep due to their lower susceptibility to damage and reduced water pressure strain. In contrast, sprinkler irrigation systems demand frequent maintenance of nozzles and pumps, and their exposed components are more vulnerable to wear from weather and mechanical impact, potentially shortening system lifespan. Efficient maintenance schedules and quality materials significantly affect the durability and operational cost-effectiveness of both irrigation types in crop production.
Environmental Impact and Water Conservation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, thereby enhancing water conservation and reducing soil erosion. Sprinkler irrigation often results in higher water usage due to evaporation and wind drift, leading to increased environmental strain. Implementing drip systems significantly lowers water waste and conserves groundwater, benefiting sustainable crop production and ecosystem health.
Choosing the Right Irrigation Method for Your Farm
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to plant roots, maximizing water efficiency and reducing evaporation, making it ideal for high-value crops and arid regions. Sprinkler irrigation covers larger areas uniformly, suitable for row crops and varied terrains but may result in higher water loss through evaporation and wind drift. Analyze soil type, crop water requirements, and farm size to select the irrigation system that optimizes water use and enhances crop yield.
Related Important Terms
Precision irrigation
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for precision irrigation in crop production. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a larger area but may lead to higher water loss due to evaporation and wind drift, reducing its precision and efficiency compared to drip systems.
Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface drip irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to the root zone, enhancing water use efficiency by reducing evaporation and runoff compared to sprinkler irrigation systems. SDI is particularly effective in crop production, as it promotes deeper root growth and minimizes weed growth by keeping the soil surface dry.
Pulse irrigation
Pulse irrigation delivers water in controlled, intermittent bursts, optimizing soil moisture levels and reducing water wastage compared to continuous sprinkler irrigation. This method enhances crop yield efficiency by promoting deeper water infiltration and minimizing evaporation losses, making it highly suitable for water-sensitive crops in arid regions.
Variable rate irrigation (VRI)
Variable rate irrigation (VRI) enhances both drip and sprinkler irrigation systems by precisely adjusting water application based on soil moisture and crop needs, improving water use efficiency and crop yield. VRI technology in drip irrigation delivers targeted water directly to root zones, while VRI-integrated sprinklers optimize spray patterns and rates, minimizing runoff and evaporation losses.
Drip fertigation
Drip fertigation delivers nutrients and water directly to the root zone with precision, enhancing crop yield and reducing water usage by up to 50% compared to traditional sprinkler irrigation. This method minimizes nutrient leaching and evaporation losses, making it ideal for efficient crop production in arid and semi-arid regions.
Low Energy Precision Application (LEPA) sprinklers
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone with high efficiency, reducing evaporation and runoff, while LEPA sprinklers optimize water use by applying low-energy, precise droplets close to the soil surface, minimizing wind drift and evaporation. LEPA systems enhance crop yield and water conservation, especially in arid regions, by combining precision application with efficient energy use.
Emitter clogging management
Drip irrigation systems require regular maintenance to prevent emitter clogging caused by sediment, algae, or mineral deposits, ensuring uniform water distribution and optimal crop growth. In contrast, sprinkler irrigation faces less frequent clogging issues but demands monitoring of nozzle blockages and pressure fluctuations to maintain effective water application.
Smart irrigation controllers
Smart irrigation controllers optimize water use in drip irrigation by delivering precise moisture levels directly to plant roots, reducing water waste and enhancing crop yield efficiency. In sprinkler irrigation, these controllers adjust spray patterns and timing based on real-time weather data, minimizing evaporation and runoff for improved water conservation in crop production.
Wetted perimeter optimization
Drip irrigation maximizes the wetted perimeter by delivering water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, thereby enhancing water use efficiency in crop production. In contrast, sprinkler irrigation distributes water over a broader area with less precise wetting patterns, often resulting in higher water loss and reduced wetted perimeter optimization.
Micro-sprinkler irrigation
Micro-sprinkler irrigation offers precise water delivery with reduced evaporation and runoff compared to traditional sprinkler systems, enhancing water use efficiency in crop production. This method improves soil moisture uniformity and root zone coverage, promoting healthier crop growth and higher yields.
Drip Irrigation vs Sprinkler Irrigation for Watering Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com