Optimal plant spacing is crucial for effective population control in crop production, as it influences resource availability and reduces competition among plants. Dense planting may lead to overcrowding, resulting in stunted growth, lower yields, and higher susceptibility to diseases due to restricted air circulation. Balancing adequate spacing ensures healthy root development, maximizes sunlight exposure, and enhances overall crop productivity.
Table of Comparison
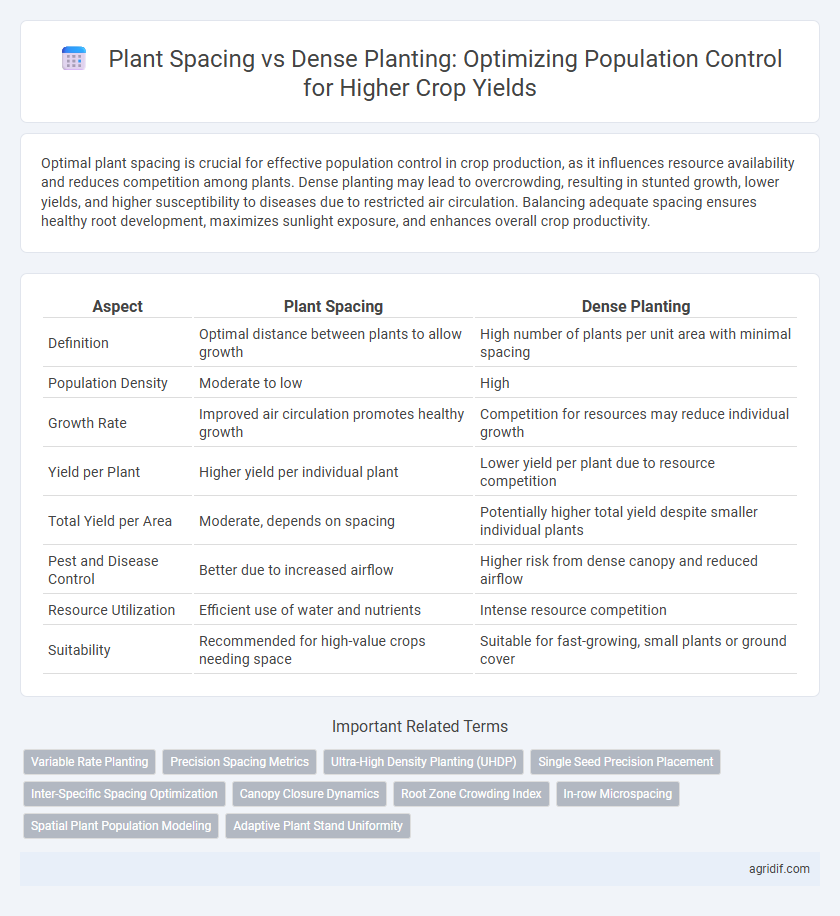
| Aspect | Plant Spacing | Dense Planting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimal distance between plants to allow growth | High number of plants per unit area with minimal spacing |
| Population Density | Moderate to low | High |
| Growth Rate | Improved air circulation promotes healthy growth | Competition for resources may reduce individual growth |
| Yield per Plant | Higher yield per individual plant | Lower yield per plant due to resource competition |
| Total Yield per Area | Moderate, depends on spacing | Potentially higher total yield despite smaller individual plants |
| Pest and Disease Control | Better due to increased airflow | Higher risk from dense canopy and reduced airflow |
| Resource Utilization | Efficient use of water and nutrients | Intense resource competition |
| Suitability | Recommended for high-value crops needing space | Suitable for fast-growing, small plants or ground cover |
Introduction to Plant Population Management
Effective plant population management is crucial for optimizing crop yield and resource utilization. Proper plant spacing reduces competition for nutrients, water, and light, promoting healthier growth and higher productivity. Dense planting increases crop density but often leads to stress and lower individual plant performance, making population control essential for balanced growth.
Understanding Plant Spacing in Crop Production
Optimal plant spacing in crop production directly influences plant population density, affecting resource availability such as sunlight, water, and nutrients for each plant. Understanding the balance between adequate spacing and dense planting helps prevent overcrowding, which can lead to competition stress, reduced photosynthesis, and lower yields. Strategic spacing promotes healthy root development and air circulation, enhancing crop growth and disease resistance.
Dense Planting: Definition and Rationale
Dense planting refers to the agricultural practice of cultivating crops at closer intervals than traditional spacing to maximize land use efficiency and increase yield per unit area. This method aims to enhance competition among plants for light, nutrients, and water, which induces stronger growth patterns and optimizes resource allocation. Dense planting supports population control by managing plant density to balance between maximizing output and minimizing issues like overcrowding and disease spread.
Plant Spacing vs Dense Planting: Key Differences
Plant spacing involves arranging crops at optimal intervals to maximize air circulation, sunlight exposure, and nutrient availability, promoting healthy growth and reducing disease risk. Dense planting increases plant population per unit area, enhancing yield potential but often leading to competition for resources, higher humidity, and greater vulnerability to pests and diseases. Balancing plant spacing and density is crucial for effective population control, influencing overall crop productivity and resource efficiency.
Effects on Crop Yield and Productivity
Optimal plant spacing ensures adequate light penetration, nutrient availability, and airflow, directly enhancing photosynthesis and reducing disease incidence, which boosts overall crop yield and productivity. Dense planting increases competition among plants for resources, often leading to stunted growth, lower individual plant yield, and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. Balancing population density through appropriate spacing maximizes biomass production, improves resource use efficiency, and ultimately results in higher aggregate crop output.
Impact on Pest and Disease Incidence
Optimized plant spacing reduces pest and disease incidence by improving air circulation and sunlight penetration, which inhibit pathogen growth. Dense planting increases humidity and creates microenvironments conducive to pest proliferation and fungal infections. Research shows that proper spacing decreases crop losses and promotes healthier plant populations by limiting pest habitat and disease spread.
Influence on Soil Health and Nutrient Uptake
Proper plant spacing enhances soil aeration, promoting microbial activity crucial for nutrient cycling and organic matter decomposition. Dense planting often leads to competition for nutrients and water, reducing individual plant uptake efficiency and accelerating soil nutrient depletion. Optimizing spacing balances population density to maintain soil health while maximizing nutrient availability and uptake for sustainable crop production.
Water Usage and Irrigation Considerations
Proper plant spacing significantly reduces water usage by minimizing competition for soil moisture and improving irrigation efficiency, while dense planting often leads to higher water demand due to increased transpiration rates and limited root expansion. Efficient irrigation techniques such as drip or micro-sprinkler systems are more effective in spaced planting scenarios, ensuring targeted water delivery and reducing wastage. Balancing plant population with appropriate spacing optimizes water resources, enhances crop yield, and supports sustainable water management practices in agriculture.
Economic Benefits and Cost Implications
Optimal plant spacing enhances crop yield by reducing competition for nutrients, light, and water, thereby maximizing economic returns through efficient resource use. Dense planting can increase initial seed costs and elevate risk of disease, resulting in higher management expenses and potential yield loss. Balancing plant population density is crucial for minimizing input costs while ensuring sustainable crop productivity and profit margins.
Choosing the Optimal Plant Density for Your Crop
Selecting the optimal plant density involves balancing adequate space for root development and access to sunlight while maximizing yield per unit area. Overcrowding through dense planting can lead to nutrient competition, increased susceptibility to pests, and reduced air circulation, negatively impacting crop health and productivity. Tailoring plant spacing to specific crop varieties and local environmental conditions enhances growth efficiency, disease resistance, and overall harvest quality.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Planting
Variable rate planting enhances crop yield by optimizing plant spacing according to soil variability and resource availability, outperforming dense planting methods that often lead to competition for nutrients and reduced growth uniformity. Precise plant population control through variable rate technology increases resource use efficiency, promoting healthier crop stands and higher productivity.
Precision Spacing Metrics
Precision spacing metrics optimize crop yield by ensuring optimal plant population density, reducing competition for light, water, and nutrients. Implementing exact intra- and inter-row distances maximizes resource use efficiency and improves overall plant health in dense planting systems.
Ultra-High Density Planting (UHDP)
Ultra-High Density Planting (UHDP) maximizes crop yields per unit area by reducing plant spacing significantly, enhancing light interception and resource use efficiency. This approach requires precise population control to prevent competition stress while promoting uniform growth and maximizing overall productivity.
Single Seed Precision Placement
Single seed precision placement optimizes plant spacing by ensuring uniform seed distribution, which enhances population control and improves crop yield efficiency. This method reduces competition for nutrients, water, and sunlight compared to dense planting, leading to healthier plant development and higher productivity.
Inter-Specific Spacing Optimization
Optimizing inter-specific plant spacing enhances resource allocation by reducing competition for sunlight, water, and nutrients, leading to improved crop yield and pest resistance. Precise spacing tailored to species growth patterns supports healthy population control, minimizes disease spread, and maximizes photosynthetic efficiency.
Canopy Closure Dynamics
Optimizing plant spacing directly influences canopy closure dynamics, balancing light interception and airflow to enhance photosynthetic efficiency while minimizing disease risk. Dense planting accelerates canopy closure, reducing weed growth but may increase competition for nutrients and water, impacting overall crop yield and health.
Root Zone Crowding Index
Optimal plant spacing is crucial to managing the Root Zone Crowding Index, as dense planting increases competition for nutrients and water, reducing overall crop yield and health. Properly calibrated spacing improves root development and enhances resource efficiency, leading to better population control and sustainable crop production.
In-row Microspacing
In-row microspacing optimizes plant population by maintaining precise distances between seedlings, enhancing nutrient uptake and reducing competition for resources in dense planting systems. Controlled spacing improves airflow and light penetration, resulting in healthier crop growth and increased yield efficiency.
Spatial Plant Population Modeling
Spatial plant population modeling reveals that optimal plant spacing enhances resource allocation, reduces intra-species competition, and maximizes yield efficiency in crop production. Dense planting increases plant density but often leads to diminished individual plant growth and escalated disease risk, underscoring the importance of precise spatial configuration for effective population control.
Adaptive Plant Stand Uniformity
Adaptive plant stand uniformity enhances crop yield by optimizing spacing to balance light interception and nutrient availability, minimizing competition among plants. Maintaining ideal plant spacing rather than dense planting improves resource allocation, reduces disease spread, and supports consistent growth for uniform crop populations.
Plant Spacing vs Dense Planting for Population Control Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com