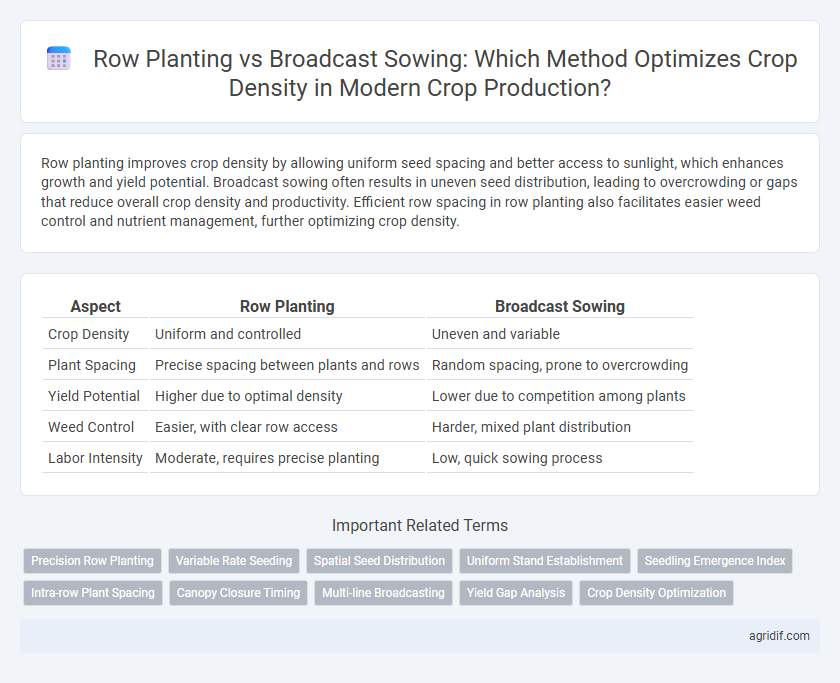
Row planting improves crop density by allowing uniform seed spacing and better access to sunlight, which enhances growth and yield potential. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven seed distribution, leading to overcrowding or gaps that reduce overall crop density and productivity. Efficient row spacing in row planting also facilitates easier weed control and nutrient management, further optimizing crop density.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Row Planting | Broadcast Sowing |
|---|---|---|
| Crop Density | Uniform and controlled | Uneven and variable |
| Plant Spacing | Precise spacing between plants and rows | Random spacing, prone to overcrowding |
| Yield Potential | Higher due to optimal density | Lower due to competition among plants |
| Weed Control | Easier, with clear row access | Harder, mixed plant distribution |
| Labor Intensity | Moderate, requires precise planting | Low, quick sowing process |
Introduction to Row Planting and Broadcast Sowing
Row planting arranges seeds in uniform rows, optimizing crop density by providing adequate space for root expansion and nutrient absorption, which enhances air circulation and reduces pest infestations. Broadcast sowing disperses seeds indiscriminately over the soil surface, often resulting in uneven seed distribution and varied plant density, potentially leading to overcrowding or gaps that impair growth efficiency. This fundamental difference in seed placement impacts overall crop health, yield uniformity, and ease of crop management practices.
Defining Crop Density in Modern Agriculture
Crop density in modern agriculture refers to the number of plants per unit area, directly influencing crop yield and resource efficiency. Row planting enables precise control over crop density by spacing seeds uniformly, optimizing sunlight exposure, nutrient uptake, and air circulation. Broadcast sowing typically results in uneven crop density, leading to competition among plants and potential yield reduction due to overcrowding or sparse distribution.
Efficiency of Seed Use in Row Planting vs Broadcast Sowing
Row planting enhances seed use efficiency by ensuring precise spacing and uniform depth, reducing seed wastage and promoting optimal plant density for higher yields. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven seed distribution, leading to overcrowding or gaps, which decreases overall crop density efficiency and increases seed consumption. Efficient seed utilization in row planting supports better resource management and cost-effectiveness in crop production.
Impact on Crop Growth and Uniformity
Row planting enhances crop density by allowing precise seed placement, which promotes optimal spacing and reduces competition among plants, leading to better growth and higher uniformity. Broadcast sowing results in uneven seed distribution, causing irregular germination and inconsistent plant density that negatively affects crop growth and uniformity. Efficient crop management and yield improvement are strongly linked to the adoption of row planting techniques over broadcast sowing for precise crop density control.
Weed Control: Advantages of Row Arrangement
Row planting enhances weed control by allowing easier identification and removal of weeds between rows, leading to reduced competition for nutrients and sunlight. The organized spacing in row arrangement facilitates mechanical or manual weeding, improving overall crop health and yield. In contrast, broadcast sowing results in dense, uneven plant distribution that complicates effective weed management and increases crop vulnerability.
Effects on Soil Health and Compaction
Row planting ensures uniform seed spacing, promoting better root development and improved soil aeration, which reduces soil compaction and enhances microbial activity. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven seed distribution, leading to patchy crop density and increased soil compaction due to overlapping root zones and limited air flow. Consistent crop density achieved through row planting supports healthier soil structure and minimizes the risk of soil degradation.
Implications for Irrigation and Water Management
Row planting improves crop density control by enabling uniform spacing, which enhances water distribution efficiency and reduces irrigation water wastage. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven crop stands, complicating water management and increasing evaporation losses due to irregular canopy cover. Efficient irrigation scheduling and water conservation are more achievable with row planting, supporting sustainable water management in crop production systems.
Harvesting Efficiency in Different Planting Methods
Row planting enhances harvesting efficiency by providing uniform crop spacing, which facilitates easier access for machinery and reduces crop damage during collection. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven plant distribution, leading to lower crop density and increased labor requirements for selective harvesting. Optimized crop density in row planting maximizes yield per area and improves the precision of harvesting operations.
Suitability for Various Crop Types
Row planting optimizes crop density by allowing precise spacing, making it suitable for crops like maize, soybean, and cotton that require adequate airflow and sunlight for optimal growth. Broadcast sowing suits small-seeded crops such as wheat, rice, and millet, enabling quick coverage but often resulting in uneven plant distribution and competition for nutrients. Selecting the planting method depends on the crop's growth habits, seed size, and nutrient needs to achieve efficient space utilization and yield potential.
Yield Outcomes: Row Planting versus Broadcast Sowing
Row planting enhances crop density by allowing precise spacing between plants, promoting better air circulation and sunlight penetration, which leads to higher yield outcomes compared to broadcast sowing. Broadcast sowing results in uneven seed distribution and competition among seedlings, often reducing overall crop yield due to overcrowding and nutrient deficiency. Studies indicate that row planting can increase yield by up to 30% in crops like maize and wheat, emphasizing its advantage in maximizing production efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Precision Row Planting
Precision row planting enhances crop density by ensuring optimal spacing between plants, which improves light penetration, nutrient uptake, and reduces competition compared to broadcast sowing. This method increases yield potential and resource efficiency by placing seeds at uniform depths and intervals, enabling better weed control and mechanization.
Variable Rate Seeding
Row planting enables precise control over crop density through Variable Rate Seeding (VRS), optimizing seed placement and enhancing yield potential by adapting to soil variability. Broadcast sowing lacks uniform seed distribution, resulting in uneven plant populations and inefficiencies compared to the targeted precision of VRS in row planting systems.
Spatial Seed Distribution
Row planting ensures precise spatial seed distribution, optimizing crop density by allowing uniform plant spacing and better access to sunlight, nutrients, and water. Broadcast sowing results in random seed placement, often causing uneven plant density and increased competition, which can reduce overall crop yield.
Uniform Stand Establishment
Row planting ensures uniform stand establishment by maintaining consistent crop spacing, which optimizes light interception and nutrient distribution. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven crop density, leading to competition among plants and reduced overall yield potential.
Seedling Emergence Index
Row planting enhances Seedling Emergence Index by ensuring optimal spacing and uniform seed distribution, which leads to higher crop density and improved seedling vigor. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven seed placement, reducing seedling emergence rates and causing lower overall crop density.
Intra-row Plant Spacing
Row planting enhances crop density control by allowing precise intra-row plant spacing, which improves nutrient distribution and air circulation compared to broadcast sowing. Broadcast sowing often leads to uneven plant spacing, resulting in competition for resources and reduced overall yield.
Canopy Closure Timing
Row planting enhances uniform crop density by ensuring optimal spacing, which accelerates canopy closure and maximizes light interception for higher photosynthetic efficiency. Broadcast sowing often results in uneven plant distribution, delaying canopy closure and reducing overall crop productivity due to increased weed competition and suboptimal resource utilization.
Multi-line Broadcasting
Multi-line broadcasting enhances crop density by evenly distributing seeds across multiple rows, minimizing seed wastage and promoting uniform plant growth compared to traditional broadcast sowing. This method improves soil aeration and nutrient absorption, resulting in higher yield potential and better crop stand establishment than conventional row planting techniques.
Yield Gap Analysis
Row planting enhances crop density by ensuring uniform seed spacing, which improves resource utilization and reduces competition among plants, leading to higher yield efficiency compared to broadcast sowing. Yield gap analysis reveals that row planting narrows the gap between potential and actual yields by optimizing plant population and facilitating better management practices.
Crop Density Optimization
Row planting optimizes crop density by ensuring uniform spacing, which enhances sunlight penetration, nutrient uptake, and airflow compared to broadcast sowing. This precise arrangement reduces competition among plants, leading to higher yield efficiency and improved crop health.
Row planting vs Broadcast sowing for crop density Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com