AI breeding enhances dairy farming pet productivity by enabling precise genetic selection and reducing disease risks compared to natural service. Natural service offers advantages in low-cost management and can improve fertility outcomes in certain herd conditions. Choosing between AI and natural service depends on specific farm goals, herd size, and resource availability.
Table of Comparison
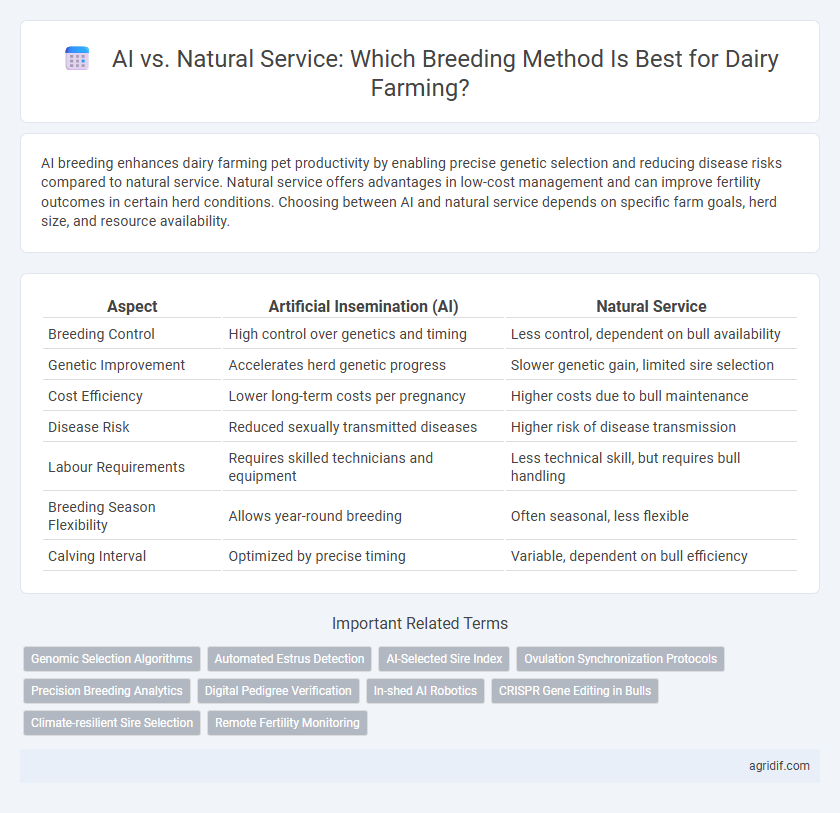
| Aspect | Artificial Insemination (AI) | Natural Service |
|---|---|---|
| Breeding Control | High control over genetics and timing | Less control, dependent on bull availability |
| Genetic Improvement | Accelerates herd genetic progress | Slower genetic gain, limited sire selection |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower long-term costs per pregnancy | Higher costs due to bull maintenance |
| Disease Risk | Reduced sexually transmitted diseases | Higher risk of disease transmission |
| Labour Requirements | Requires skilled technicians and equipment | Less technical skill, but requires bull handling |
| Breeding Season Flexibility | Allows year-round breeding | Often seasonal, less flexible |
| Calving Interval | Optimized by precise timing | Variable, dependent on bull efficiency |
Introduction to Dairy Cattle Breeding Methods
Dairy cattle breeding methods primarily include Artificial Insemination (AI) and Natural Service, each offering distinct advantages for herd improvement. AI allows precise genetic selection, enhanced disease control, and faster genetic progress by using semen from superior sires worldwide. Natural Service, involving live bulls, provides simpler management and natural mating behavior but carries higher risks of disease and slower genetic gains compared to AI.
Understanding AI (Artificial Insemination) in Dairy Farming
Artificial Insemination (AI) in dairy farming enhances genetic improvement by allowing precise selection of superior sires, increasing herd productivity and disease control. This method reduces the risks associated with natural service, such as injury and transmission of venereal diseases, while enabling widespread use of elite genetics at a lower cost. AI requires skilled technicians and strict heat detection for maximizing conception rates, ultimately driving sustainable herd improvement.
Natural Service: The Traditional Breeding Approach
Natural service remains the traditional breeding approach in dairy farming, relying on a bull to mate naturally with cows, ensuring instinctive selection and fertility cues. This method promotes natural behaviors, reduces technological reliance, and can be cost-effective for small-scale farms with limited resources. Despite advances in AI (artificial insemination), natural service offers benefits such as improved detection of heat and reduced need for specialized equipment.
Genetic Improvement: AI vs Natural Service
Artificial insemination (AI) offers significant advantages for genetic improvement in dairy farming by enabling selective breeding from superior sires worldwide, enhancing traits such as milk yield, disease resistance, and fertility. Natural service relies on the genetic quality of local bulls, which may limit the rate of genetic progress due to a smaller and less diverse gene pool. Implementing AI accelerates genetic gain through precise sire selection, contributing to increased herd productivity and long-term profitability.
Cost and Labor Considerations in Breeding Methods
AI breeding in dairy farming reduces labor costs by eliminating the need for bull maintenance and allows for precise timing and genetic selection, optimizing overall expenses. Natural service requires continuous bull upkeep, including feeding, housing, and health care, leading to higher recurring costs and increased labor demands. While AI technology involves upfront investment in equipment and training, its efficiency often results in lower long-term expenses compared to the resource-intensive nature of natural service.
Disease Control and Biosecurity in Breeding
AI (Artificial Insemination) in dairy farming significantly enhances disease control and biosecurity compared to natural service by minimizing direct contact between animals, thus reducing the risk of transmitting sexually transmitted infections such as Brucella abortus and Leptospira spp. Controlled use of semen from disease-screened bulls in AI programs helps maintain herd health and supports biosecurity protocols by preventing the introduction of pathogens. Effective implementation of AI also facilitates traceability and monitoring of genetic material, strengthening disease surveillance and overall biosecurity in breeding management.
Fertility Rates: AI Compared to Natural Service
Artificial Insemination (AI) in dairy farming typically achieves higher fertility rates compared to natural service, with conception rates averaging around 60-70% versus 50-60% for natural breeding. AI allows for precise timing of insemination, leveraging estrus detection technologies to optimize conception chances and reduce calving intervals. Genetic selection through AI also enhances herd fertility by enabling access to superior bull semen, improving overall reproductive efficiency.
Practical Challenges in Implementing AI
Implementing artificial insemination (AI) in dairy farming faces practical challenges such as precise heat detection, requiring skilled labor and technology for optimal timing. In contrast, natural service depends on bull availability and handling but demands less technical expertise. The cost of AI equipment and potential for lower conception rates in suboptimal conditions can limit its adoption compared to natural service breeding methods.
Environmental and Management Factors
AI breeding in dairy farming offers precise control over genetics and reduces the spread of diseases compared to natural service, enhancing herd health and productivity. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and housing conditions significantly affect the success rates of artificial insemination, requiring optimized management practices for maximum efficiency. Natural service, while less controllable, adapts better to variable environmental conditions and lower labor input but may increase risks of pathogen transmission and genetic inconsistency.
Choosing the Right Breeding Method for Your Dairy Farm
Choosing the right breeding method for your dairy farm involves evaluating the efficiency and accuracy of AI (Artificial Insemination) versus the natural service approach. AI allows for genetic improvement through selective breeding, reduces disease transmission, and offers cost-effective semen from high-quality sires, while natural service provides ease of management and ensures conception in challenging fertility conditions. An optimal breeding strategy considers herd size, reproduction goals, labor availability, and the health profile of the animals to maximize productivity and profitability.
Related Important Terms
Genomic Selection Algorithms
Genomic selection algorithms enhance AI breeding accuracy by analyzing vast genomic data to predict offspring traits, outperforming traditional natural service methods in genetic gain and herd improvement. Implementing AI-driven genomic tools accelerates dairy cattle genetic progress, optimizing productivity and disease resistance beyond conventional breeding limitations.
Automated Estrus Detection
Automated estrus detection systems using AI technology significantly increase breeding accuracy by continuously monitoring behavioral and physiological indicators, reducing missed heats and improving conception rates in dairy cows. Natural service, while traditional, often leads to lower detection efficiency and higher labor costs compared to AI-driven monitoring tools that enhance herd reproductive management.
AI-Selected Sire Index
AI-selected sire index leverages genomic data and predictive analytics to identify bulls with superior genetic traits, significantly improving breeding accuracy and herd productivity in dairy farming. Compared to natural service, AI enables precise selection for traits like milk yield, fertility, and disease resistance, accelerating genetic progress and enhancing overall herd performance.
Ovulation Synchronization Protocols
Ovulation synchronization protocols using AI in dairy farming enhance breeding efficiency by precisely timing artificial insemination, increasing conception rates and genetic improvements compared to natural service. These protocols reduce heat detection errors, optimize herd reproductive performance, and enable better management of calving intervals for higher milk production.
Precision Breeding Analytics
Precision Breeding Analytics leverages AI algorithms to analyze vast datasets from dairy herd genetics, reproductive performance, and environmental factors, enabling optimized mating decisions with higher accuracy than Natural Service. This technology enhances fertility rates and genetic gain by predicting optimal breeding windows and matching superior sires, reducing reliance on traditional bull service while improving overall herd productivity.
Digital Pedigree Verification
AI breeding enhances genetic selection through precise Digital Pedigree Verification, allowing accurate monitoring of lineage and improving herd quality. Natural Service lacks standardized digital records, limiting traceability and reducing the efficiency of pedigree data management in dairy farming.
In-shed AI Robotics
In-shed AI robotics for dairy breeding enhance conception rates by enabling precise timing and monitoring of artificial insemination compared to traditional natural service methods, reducing labor costs and improving genetic progress. Automated systems use real-time data analytics on cow health and estrus detection, increasing breeding efficiency and herd productivity.
CRISPR Gene Editing in Bulls
CRISPR gene editing in bulls offers precision and accelerated genetic improvements compared to natural service, enabling targeted enhancements in traits such as disease resistance and milk production efficiency. This artificial approach complements traditional breeding by reducing generational intervals and increasing overall herd productivity in dairy farming.
Climate-resilient Sire Selection
AI breeding enables precise climate-resilient sire selection by integrating genetic data and environmental adaptability, enhancing herd productivity under changing climate conditions. Natural service lacks this targeted approach, making it less effective in selecting sires that withstand heat stress and other climate challenges.
Remote Fertility Monitoring
Remote fertility monitoring leverages AI-driven sensors and data analytics to detect optimal breeding periods, improving conception rates and reducing reliance on traditional natural service methods. This technology enhances herd reproductive efficiency by providing real-time insights into cow fertility cycles, minimizing missed heat events and supporting timely artificial insemination decisions.
AI vs Natural Service for breeding Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com