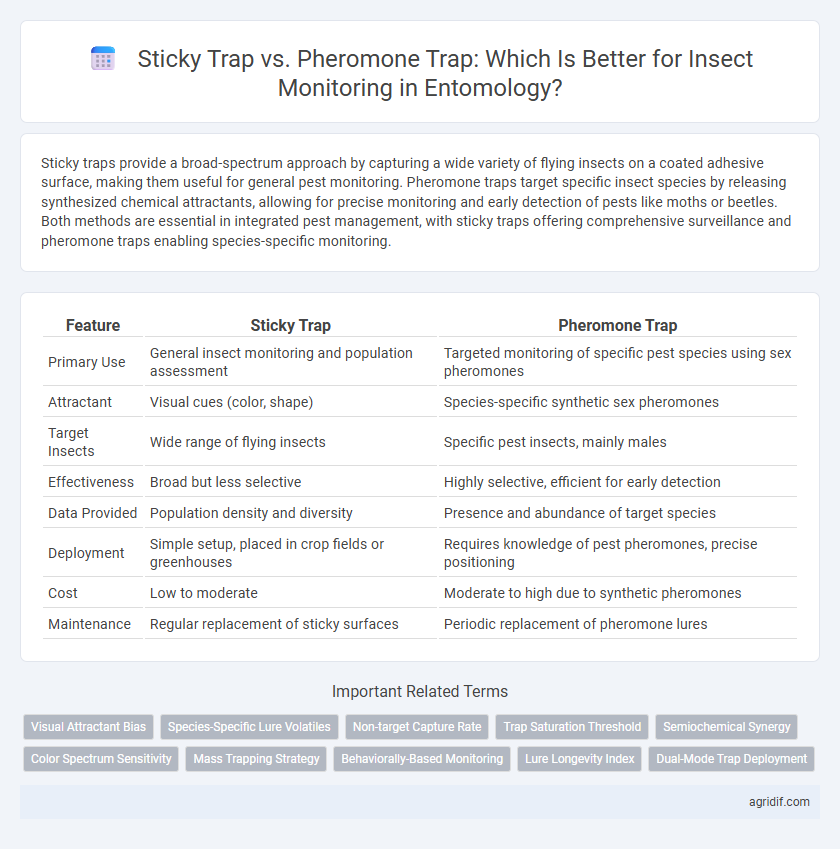
Sticky traps provide a broad-spectrum approach by capturing a wide variety of flying insects on a coated adhesive surface, making them useful for general pest monitoring. Pheromone traps target specific insect species by releasing synthesized chemical attractants, allowing for precise monitoring and early detection of pests like moths or beetles. Both methods are essential in integrated pest management, with sticky traps offering comprehensive surveillance and pheromone traps enabling species-specific monitoring.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sticky Trap | Pheromone Trap |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | General insect monitoring and population assessment | Targeted monitoring of specific pest species using sex pheromones |
| Attractant | Visual cues (color, shape) | Species-specific synthetic sex pheromones |
| Target Insects | Wide range of flying insects | Specific pest insects, mainly males |
| Effectiveness | Broad but less selective | Highly selective, efficient for early detection |
| Data Provided | Population density and diversity | Presence and abundance of target species |
| Deployment | Simple setup, placed in crop fields or greenhouses | Requires knowledge of pest pheromones, precise positioning |
| Cost | Low to moderate | Moderate to high due to synthetic pheromones |
| Maintenance | Regular replacement of sticky surfaces | Periodic replacement of pheromone lures |
Overview of Insect Monitoring in Agriculture
Sticky traps provide a broad-spectrum approach by capturing various flying insects through adhesive surfaces, effectively monitoring pest populations in agricultural fields. Pheromone traps utilize species-specific chemical lures to attract targeted insect pests, enabling precise monitoring of key pest species and their population dynamics. Combining both trapping methods enhances accuracy in assessing pest diversity and density, facilitating timely and informed pest management decisions in crop production.
Introduction to Sticky Traps
Sticky traps are adhesive-coated cards or surfaces used to capture flying insects for monitoring pest populations in agricultural and horticultural settings. These traps provide continuous, passive sampling by attracting insects through color or light, effectively capturing a broad range of species without using chemical lures. Their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and ability to monitor both adult insect presence and population fluctuations make sticky traps essential tools in integrated pest management (IPM) programs.
Introduction to Pheromone Traps
Pheromone traps utilize species-specific chemical signals to attract target insects, enabling precise monitoring of pest populations. These traps offer selective detection, reducing non-target captures compared to sticky traps that rely on physical adhesion and attract a broader range of insects. The use of pheromone traps enhances integrated pest management by providing early warning of infestations and aiding in population dynamics studies.
Mechanisms of Action: Sticky vs Pheromone Traps
Sticky traps capture insects by physically adhering them to a coated surface, preventing escape through a strong adhesive layer. Pheromone traps utilize species-specific chemical lures that mimic insect mating signals, attracting target insects into a confined space for monitoring or control. The effectiveness of pheromone traps depends on the precise chemical composition and release rate, while sticky traps rely on passive trapping without species discrimination.
Target Pest Range and Specificity
Sticky traps capture a broad spectrum of flying insects, making them suitable for monitoring multiple pest species simultaneously but often resulting in non-target captures. Pheromone traps utilize species-specific chemical signals, providing high specificity by attracting only the target pest, which enhances monitoring accuracy for particular insect populations. The choice between the two depends on whether wide-range surveillance or precise pest targeting is required for effective pest management.
Trap Placement and Maintenance Requirements
Sticky traps require placement in well-lit areas near foliage to maximize insect capture, while pheromone traps should be positioned at crop canopy height to effectively lure target species. Maintenance for sticky traps involves frequent replacement to prevent surface saturation and ensure trap adhesiveness, whereas pheromone traps need periodic renewal of lures and cleaning to sustain pheromone emission and trap efficiency. Proper placement and consistent maintenance significantly influence data accuracy and pest management outcomes in integrated pest monitoring programs.
Effectiveness Under Field Conditions
Sticky traps provide continuous passive monitoring by capturing various insect species indiscriminately, making them effective in identifying population diversity under field conditions. Pheromone traps selectively attract target species using specific chemical signals, offering higher specificity and sensitivity for pest population monitoring. Field studies indicate pheromone traps often yield more accurate data on target insect abundance, crucial for timely pest management decisions.
Data Accuracy and Monitoring Reliability
Sticky traps capture a broad range of insect species, offering diverse data but sometimes leading to non-target catches that can reduce monitoring precision. Pheromone traps target specific pest species by emitting chemical signals, enhancing data accuracy and improving reliability for monitoring population dynamics. Combining both trap types can optimize insect monitoring by balancing comprehensive sampling with species-specific accuracy.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Trap Types
Sticky traps offer a cost-effective solution for monitoring a wide range of insect species due to their low production and maintenance expenses, making them suitable for large-scale deployment. Pheromone traps, while generally more expensive because of synthetic lure development and specialized deployment, provide higher specificity and sensitivity by attracting target insect species, enabling more precise population assessments. Evaluating cost-benefit involves balancing the inexpensive, broad-spectrum utility of sticky traps against the targeted efficiency and early detection advantages provided by pheromone traps, depending on monitoring goals and pest management strategies.
Choosing the Right Trap for Integrated Pest Management
Sticky traps capture a wide range of flying insects by adhesion, making them effective for general monitoring but less selective in pest identification. Pheromone traps use species-specific chemical signals to attract target pests, providing precise data for population monitoring and timing control measures. Selecting the right trap depends on pest species, monitoring goals, and integration with broader pest management strategies to optimize accuracy and effectiveness.
Related Important Terms
Visual Attractant Bias
Sticky traps rely on visual attractant bias by exploiting insects' attraction to bright colors and reflective surfaces, making them effective for monitoring species drawn to such cues. Pheromone traps circumvent this bias by targeting species-specific chemical signals, providing a more selective and accurate method for monitoring pheromone-responsive insects.
Species-Specific Lure Volatiles
Sticky traps capture a broad spectrum of insects using visual cues and adhesive surfaces, while pheromone traps utilize species-specific lure volatiles to selectively attract target insect populations, enhancing monitoring accuracy. Pheromone traps exploit chemical signals unique to each species, enabling precise detection and population assessment crucial for integrated pest management strategies.
Non-target Capture Rate
Sticky traps often exhibit higher non-target capture rates compared to pheromone traps, which are designed to attract specific insect species using species-specific chemical signals. Pheromone traps minimize bycatch by selectively luring target pests, thereby reducing ecological disturbance and improving monitoring accuracy in entomological studies.
Trap Saturation Threshold
Sticky traps often reach saturation thresholds faster due to their adhesive surface capturing a broad range of insects, which can reduce monitoring accuracy for target species. Pheromone traps selectively attract specific insects using species-specific chemical lures, maintaining effectiveness and lower saturation levels for precise population assessments.
Semiochemical Synergy
Sticky traps provide a broad-spectrum approach by capturing diverse insect species through adhesive surfaces, while pheromone traps utilize species-specific semiochemicals to selectively attract target pests. Combining sticky traps with pheromone lures leverages semiochemical synergy, enhancing monitoring accuracy by increasing capture rates and enabling precise population assessments in integrated pest management programs.
Color Spectrum Sensitivity
Sticky traps utilize broad-spectrum yellow coloration to attract a wide range of phototactic insects, leveraging their sensitivity to wavelengths around 570 nm, whereas pheromone traps target species-specific olfactory receptors with minimal reliance on color spectrum sensitivity, optimizing selective insect monitoring. Color spectrum sensitivity in sticky traps enhances capture rates by exploiting visual stimuli, while pheromone traps depend primarily on chemical cues for precision in detecting particular insect populations.
Mass Trapping Strategy
Sticky traps capture a wide range of insect species by physically entrapping them on adhesive surfaces, making them effective for general monitoring but less selective for target pests in mass trapping strategies. Pheromone traps utilize species-specific sex or aggregation pheromones to attract and capture targeted insect populations, enhancing control efficiency and reducing non-target captures in integrated pest management programs.
Behaviorally-Based Monitoring
Sticky traps capture a broad range of insects by physically intercepting them, while pheromone traps specifically attract target species using sex or aggregation pheromones, enhancing monitoring accuracy through behaviorally-based lures. Pheromone traps provide precise data on insect population dynamics and mating behaviors, crucial for integrated pest management programs.
Lure Longevity Index
Sticky traps offer consistent capture rates but typically exhibit a lower Lure Longevity Index compared to pheromone traps, which maintain attractant potency for extended periods, enhancing monitoring accuracy in entomological studies. The higher Lure Longevity Index of pheromone traps reduces replacement frequency and improves long-term surveillance of target insect populations.
Dual-Mode Trap Deployment
Dual-mode trap deployment combining sticky traps and pheromone traps enhances insect monitoring accuracy by capturing a broader range of insect species and behaviors, improving pest population assessment in entomological studies. Sticky traps provide visual capture for various flying insects, while pheromone traps specifically attract target species through chemical signaling, enabling comprehensive data collection and more effective integrated pest management strategies.
Sticky trap vs pheromone trap for insect monitoring Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com