Hand weeding in onion beds preserves soil health and reduces chemical residue, promoting organic growth and minimizing environmental impact. Chemical weeding offers faster weed control and labor efficiency but may lead to herbicide resistance and potential toxicity. Balancing both methods can optimize onion yield while maintaining sustainable horticultural practices.
Table of Comparison
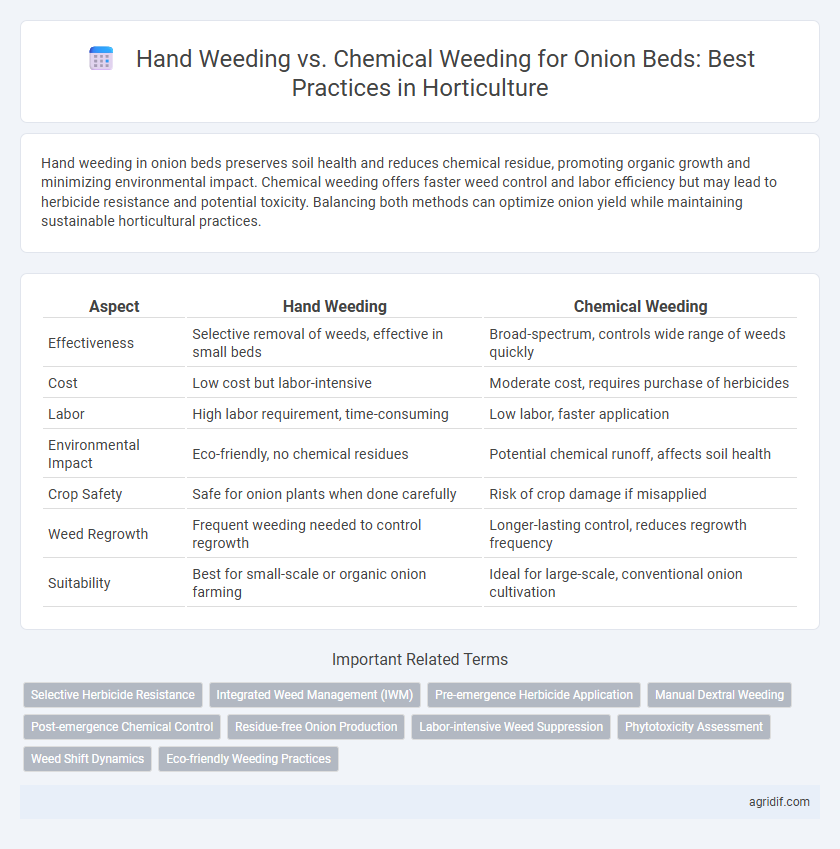
| Aspect | Hand Weeding | Chemical Weeding |
|---|---|---|
| Effectiveness | Selective removal of weeds, effective in small beds | Broad-spectrum, controls wide range of weeds quickly |
| Cost | Low cost but labor-intensive | Moderate cost, requires purchase of herbicides |
| Labor | High labor requirement, time-consuming | Low labor, faster application |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, no chemical residues | Potential chemical runoff, affects soil health |
| Crop Safety | Safe for onion plants when done carefully | Risk of crop damage if misapplied |
| Weed Regrowth | Frequent weeding needed to control regrowth | Longer-lasting control, reduces regrowth frequency |
| Suitability | Best for small-scale or organic onion farming | Ideal for large-scale, conventional onion cultivation |
Introduction to Weed Management in Onion Cultivation
Hand weeding in onion cultivation offers precise removal of weeds without harming onion plants, preserving soil structure and reducing chemical residues. Chemical weeding employs selective herbicides to control weed populations efficiently but requires careful management to avoid herbicide resistance and potential environmental impact. Effective weed management combines timely hand weeding and targeted chemical application to optimize onion crop yield and quality.
Overview of Hand Weeding Techniques
Hand weeding in onion beds involves manual removal of weeds using tools such as hoes, knives, or by hand to minimize damage to onion bulbs and roots. This technique allows selective targeting of weeds, preserving soil structure and promoting better aeration compared to chemical methods. Regular hand weeding significantly reduces weed competition, enhancing onion growth and yield in sustainable horticultural practices.
Chemical Weeding: Methods and Herbicides Used
Chemical weeding in onion beds primarily involves selective herbicides such as oxyfluorfen and pendimethalin, which target broadleaf weeds and grasses without harming the onion bulbs. Application methods include pre-emergence spraying to prevent weed seed germination and post-emergence treatments to control actively growing weeds. Proper timing and dosage are crucial to maximize efficacy and minimize herbicide resistance in the horticultural management of onions.
Efficiency of Hand Weeding vs Chemical Weeding
Hand weeding in onion beds provides precise removal of weeds, minimizing damage to onion plants and reducing herbicide resistance. Chemical weeding offers rapid coverage and labor efficiency, significantly decreasing manual labor requirements and time expenditure. The choice between methods balances cost, environmental impact, and weed control effectiveness in sustainable horticulture practices.
Impact on Onion Crop Yield and Quality
Hand weeding in onion beds preserves crop yield and quality by minimizing soil disturbance and preventing chemical residues, promoting healthier bulb development with fewer impurities. Chemical weeding can increase the risk of phytotoxicity and chemical residue accumulation, potentially reducing onion bulb size and consumer acceptability. Research indicates that integrated hand weeding combined with selective herbicide use optimizes onion yield and maintains high quality standards.
Labor and Cost Analysis: Manual vs Chemical Approaches
Hand weeding onion beds requires intensive labor, with average costs ranging from $150 to $300 per acre due to the need for skilled workers and time-consuming processes. Chemical weeding, using selective herbicides such as oxyfluorfen or pendimethalin, reduces labor expenses by up to 70%, with chemical costs varying between $20 and $50 per acre. Efficient chemical application minimizes manual intervention, offering a cost-effective alternative that balances labor input and weed control efficacy in commercial onion cultivation.
Environmental Effects of Chemical Weed Control
Chemical weed control in onion beds often relies on herbicides that can persist in soil and water, leading to contamination and harm to beneficial soil microorganisms. These chemicals may cause runoff, polluting nearby water bodies and affecting aquatic ecosystems. Compared to hand weeding, which is labor-intensive but environmentally benign, chemical methods pose significant risks of creating resistant weed species and reducing biodiversity in agricultural landscapes.
Health and Safety Considerations in Weeding Practices
Hand weeding in onion beds minimizes exposure to harmful chemicals, reducing risks of skin irritation, respiratory issues, and long-term health problems for workers. Chemical weeding, while effective in controlling weeds, poses potential hazards such as pesticide poisoning, environmental contamination, and the need for protective equipment and training. Choosing hand weeding prioritizes worker safety and environmental health, crucial factors in sustainable horticulture practices.
Integrated Weed Management for Onion Beds
Hand weeding in onion beds offers precise removal of weeds without damaging the crop, preserving soil health and minimizing chemical residues. Chemical weeding provides broad-spectrum control but risks developing herbicide resistance and environmental contamination if overused. Integrated Weed Management combines hand weeding and targeted herbicide application to optimize weed control, enhance onion yield, and promote sustainable horticultural practices.
Recommendations for Sustainable Weed Control in Onion Farming
Hand weeding in onion beds offers precise weed removal without harming crops, promoting soil health and reducing chemical residues. Chemical weeding provides rapid and broad-spectrum control but risks environmental contamination and herbicide resistance. Sustainable weed control in onion farming favors integrated approaches combining minimal, targeted herbicide use with regular hand weeding to balance efficacy and ecological safety.
Related Important Terms
Selective Herbicide Resistance
Selective herbicide resistance in onion beds allows chemical weeding to target broadleaf weeds without damaging the crop, offering efficient weed control compared to labor-intensive hand weeding. However, integrating hand weeding remains essential to manage resistant weed populations and prevent resistance buildup in herbicide-tolerant onion varieties.
Integrated Weed Management (IWM)
Hand weeding in onion beds offers precise removal of weeds without chemical residues, enhancing soil health, while chemical weeding provides rapid and broad-spectrum control of invasive species. Combining these approaches within an Integrated Weed Management (IWM) framework optimizes weed suppression, reduces herbicide resistance, and promotes sustainable onion crop productivity.
Pre-emergence Herbicide Application
Pre-emergence herbicide application in onion beds offers targeted weed control by inhibiting seed germination, reducing labor costs and soil disturbance compared to hand weeding. This method enhances crop yield and minimizes crop damage risk, ensuring efficient weed management in early growth stages.
Manual Dextral Weeding
Manual dextral weeding in onion beds enhances precision by selectively removing weeds while preserving bulb integrity, reducing soil disturbance compared to chemical herbicides. This practice supports sustainable horticulture by minimizing chemical residues and promoting healthy onion growth through targeted weed management.
Post-emergence Chemical Control
Post-emergence chemical control in onion beds offers efficient management of broadleaf and grass weeds, minimizing crop damage compared to hand weeding, which is labor-intensive and less timely. Selective herbicides such as oxyfluorfen and quizalofop provide targeted weed suppression, improving yield and reducing the risk of weed resistance in sustainable horticultural practices.
Residue-free Onion Production
Hand weeding in onion beds ensures residue-free production by eliminating the risk of chemical contamination, preserving soil health and crop safety. Chemical weeding, while efficient for large-scale weed control, often leaves pesticide residues that compromise the purity and marketability of onions.
Labor-intensive Weed Suppression
Hand weeding in onion beds offers precise weed suppression but demands high labor intensity and time commitment, making it less efficient for large-scale operations. Chemical weeding reduces manual labor by targeting weeds systemically, enhancing productivity but requires careful management to prevent herbicide resistance and environmental impact.
Phytotoxicity Assessment
Hand weeding in onion beds eliminates the risk of phytotoxicity, preserving bulb quality and growth integrity, whereas chemical weeding with selective herbicides requires rigorous phytotoxicity assessment to prevent damage such as leaf chlorosis or stunted development. Detailed evaluation of herbicide residues and their impact on onion tissue is critical to ensure effective weed management without compromising crop health.
Weed Shift Dynamics
Hand weeding in onion beds allows for targeted removal of specific weed species, promoting a dynamic shift in the weed community toward less competitive plants and reducing herbicide resistance development. Chemical weeding, while efficient in controlling broad-spectrum weeds, can lead to a dominance shift favoring herbicide-resistant weed populations, altering the overall weed shift dynamics detrimentally over time.
Eco-friendly Weeding Practices
Hand weeding in onion beds preserves soil health and biodiversity by avoiding synthetic chemicals, promoting sustainable horticulture practices. Chemical weeding, while efficient, risks soil contamination and harms beneficial organisms, making hand weeding the preferred eco-friendly method for long-term crop resilience.
Hand weeding vs Chemical weeding for onion beds Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com