High tunnels provide an affordable, passive environment to extend the growing season by protecting crops from frost and wind while allowing natural sunlight and ventilation. Greenhouses offer more control over temperature, humidity, and pests through active heating and cooling systems, making them ideal for year-round production and sensitive plants. Choosing between the two depends on budget, climate, and the level of environmental control needed for optimal crop growth.
Table of Comparison
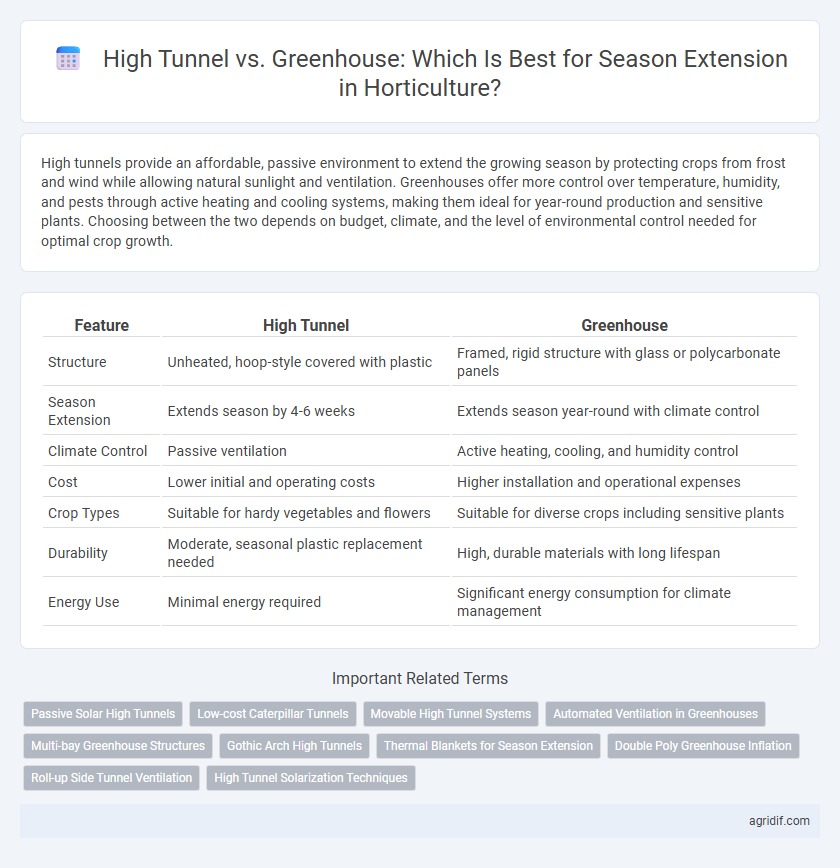
| Feature | High Tunnel | Greenhouse |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Unheated, hoop-style covered with plastic | Framed, rigid structure with glass or polycarbonate panels |
| Season Extension | Extends season by 4-6 weeks | Extends season year-round with climate control |
| Climate Control | Passive ventilation | Active heating, cooling, and humidity control |
| Cost | Lower initial and operating costs | Higher installation and operational expenses |
| Crop Types | Suitable for hardy vegetables and flowers | Suitable for diverse crops including sensitive plants |
| Durability | Moderate, seasonal plastic replacement needed | High, durable materials with long lifespan |
| Energy Use | Minimal energy required | Significant energy consumption for climate management |
Introduction to Season Extension: High Tunnels vs Greenhouses
High tunnels and greenhouses are key structures used in horticulture to extend the growing season by providing controlled environments that protect crops from adverse weather conditions. High tunnels typically offer passive solar heating with unheated, ventilated designs, making them cost-effective for enhancing early spring and late fall production. Greenhouses provide more precise climate control through heating, cooling, and ventilation systems, allowing year-round cultivation but with higher initial and operational costs compared to high tunnels.
Structural Differences Between High Tunnels and Greenhouses
High tunnels feature a simple, hoop-shaped framework covered with polyethylene film, lacking rigid walls and relying on passive ventilation, which makes them cost-effective but less climate-controlled. Greenhouses possess a rigid frame constructed from aluminum or steel combined with glass or polycarbonate panels, enabling better insulation, active climate control, and year-round crop production. The structural differences result in varied durability, environmental regulation, and initial investment costs, influencing growers' decisions based on their seasonal extension goals and crop requirements.
Climate Control Capabilities in High Tunnels and Greenhouses
High tunnels provide passive climate control through row covers and ventilation, allowing modest temperature regulation suitable for early spring and late fall cropping. Greenhouses offer advanced climate control systems, including heating, cooling, and automated ventilation, enabling precise temperature and humidity management for year-round production. The superior environmental regulation in greenhouses supports optimal plant growth and extended growing seasons compared to high tunnels.
Cost Comparison: High Tunnels Versus Greenhouses
High tunnels offer a more cost-effective solution for season extension, typically costing 50-70% less to construct and maintain than traditional greenhouses. Initial investment for high tunnels ranges from $3 to $6 per square foot, compared to $15 to $25 per square foot for greenhouses, making high tunnels ideal for small-scale and budget-conscious growers. Operating expenses for high tunnels are also significantly lower, as they rely mainly on passive solar heating and natural ventilation, whereas greenhouses often require expensive heating, cooling, and automated climate control systems.
Crop Suitability for High Tunnels and Greenhouses
High tunnels are ideal for hardy crops like leafy greens, root vegetables, and certain brassicas that tolerate cooler temperatures and benefit from passive solar heating, extending the growing season with minimal energy input. Greenhouses provide a controlled environment suited for sensitive crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers, offering precise temperature, humidity, and light management for year-round production. Crop suitability depends on the plant's temperature tolerance, light requirements, and sensitivity to environmental fluctuations, making high tunnels better for cold-hardy, low-maintenance crops and greenhouses essential for heat-loving, high-value crops.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
High tunnels require simpler installation with lightweight frames and plastic covers, making them cost-effective and easy to set up without specialized skills. Greenhouses involve more complex construction using durable materials like glass or polycarbonate panels, requiring professional installation and higher initial investment. Maintenance for high tunnels mainly includes repairing plastic covers and monitoring ventilation, while greenhouses demand regular cleaning, structural inspections, and climate control system upkeep to ensure optimal growing conditions.
Pest and Disease Management in Protected Structures
High tunnels and greenhouses offer distinct advantages for pest and disease management in horticulture season extension. High tunnels provide natural ventilation, reducing humidity and the incidence of fungal diseases, while greenhouses allow precise environmental control, enabling targeted pest management strategies and reducing pest entry. Understanding the trade-offs in airflow, temperature regulation, and structural design is essential for optimizing pest and disease control in protected crop production.
Energy Use and Sustainability Considerations
High tunnels use passive solar energy and rely on minimal supplemental heating, making them more energy-efficient and sustainable for season extension compared to greenhouses that often require active heating systems powered by electricity or fossil fuels. The reduced energy demand of high tunnels lowers carbon emissions and operational costs, aligning with sustainable horticultural practices. However, greenhouses offer greater climate control, potentially extending growing seasons further but with increased environmental impact due to higher energy consumption.
Yield Outcomes: High Tunnel vs Greenhouse Performance
High tunnels typically enhance yield by providing a controlled environment that protects crops from frost and extends the growing season by several weeks, leading to earlier and increased harvests compared to open fields. Greenhouses offer more precise climate regulation with temperature, humidity, and light control, resulting in higher yields for temperature-sensitive or high-value crops but require greater investment and operational costs. Studies show high tunnels can increase vegetable yields by 20-50%, while greenhouses may boost production by 50-100%, depending on crop type and management practices.
Choosing the Right Structure for Your Farm Operation
High tunnels offer cost-effective season extension by providing protection from frost and wind while maintaining natural ventilation, making them ideal for small to medium-scale farms emphasizing energy efficiency. Greenhouses provide a controlled environment with advanced climate regulation, allowing precise temperature, humidity, and light management critical for year-round production and high-value crops. Selecting the right structure depends on crop requirements, budget, labor availability, and intended production scale, with high tunnels suited for hardy crops and greenhouses favored for sensitive or intensive horticultural operations.
Related Important Terms
Passive Solar High Tunnels
Passive solar high tunnels maximize season extension by utilizing transparent, UV-stabilized polyethylene covers and south-facing orientation to capture solar energy, reducing heating costs compared to traditional greenhouses. These structures offer superior ventilation and simpler construction, making them ideal for sustainable, energy-efficient crop production in cooler climates.
Low-cost Caterpillar Tunnels
Low-cost caterpillar tunnels offer an affordable alternative to traditional greenhouses for season extension, providing effective frost protection and increased crop yield. These flexible high tunnels optimize sunlight exposure and ventilation while significantly reducing construction and maintenance costs compared to standard greenhouse structures.
Movable High Tunnel Systems
Movable high tunnel systems provide flexible season extension by allowing growers to reposition structures for optimal sunlight exposure and crop rotation, reducing soil-borne diseases compared to fixed greenhouses. These high tunnels offer lower construction and operational costs while maintaining microclimate control suitable for diverse horticultural crops throughout extended growing seasons.
Automated Ventilation in Greenhouses
Automated ventilation systems in greenhouses regulate temperature and humidity with precision, enhancing crop growth and extending the growing season more effectively than high tunnels. These systems use sensors and motorized vents to optimize air circulation, reducing labor and mitigating risks of heat stress and disease in horticultural production.
Multi-bay Greenhouse Structures
Multi-bay greenhouse structures offer superior season extension compared to high tunnels by providing enhanced climate control, improved insulation, and greater durability, which supports year-round crop production. These structures maximize space efficiency and enable better management of temperature, humidity, and light conditions, essential for high-value horticultural crops during off-seasons.
Gothic Arch High Tunnels
Gothic Arch High Tunnels provide effective season extension by utilizing a curved roof design that reduces snow accumulation and improves light transmission compared to traditional greenhouses. This structure optimizes temperature regulation and ventilation, resulting in enhanced crop yield and extended growing seasons with lower energy costs.
Thermal Blankets for Season Extension
Thermal blankets enhance the effectiveness of both high tunnels and greenhouses by retaining heat and extending the growing season in horticulture. These blankets reduce frost risk and stabilize soil temperatures, enabling earlier planting and later harvests in diverse climates.
Double Poly Greenhouse Inflation
Double poly greenhouse inflation efficiently extends the growing season by providing superior insulation and temperature control compared to high tunnels, reducing heat loss and frost risk during colder months. This enhanced climate management fosters earlier planting and prolonged harvests, optimizing crop yields and overall horticultural productivity.
Roll-up Side Tunnel Ventilation
Roll-up side tunnel ventilation in high tunnels enhances air circulation and temperature control, making it more energy-efficient and cost-effective than traditional greenhouses for season extension. This system reduces heat buildup and humidity, promoting optimal plant growth conditions without the need for complex mechanical ventilation.
High Tunnel Solarization Techniques
High tunnel solarization techniques utilize transparent polyethylene covers to trap solar radiation, raising soil temperatures and effectively controlling soil-borne pathogens while extending the growing season by several weeks. Compared to traditional greenhouses, high tunnels offer a cost-effective, energy-efficient solution for season extension with enhanced soil sterilization benefits that improve crop yield and quality.
High tunnel vs Greenhouse for season extension Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com