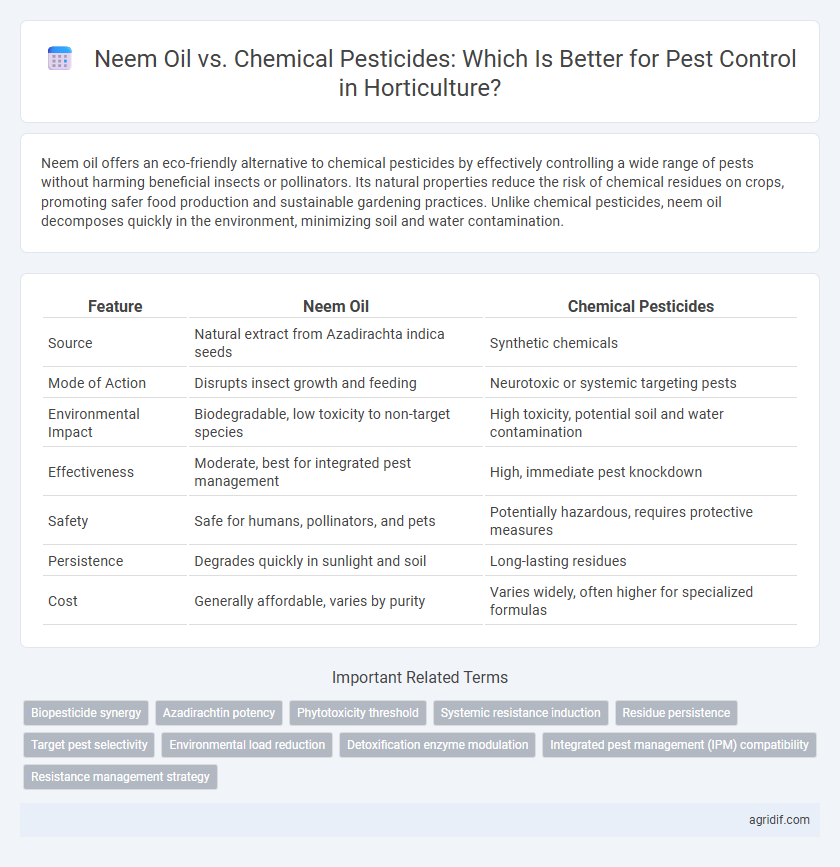
Neem oil offers an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides by effectively controlling a wide range of pests without harming beneficial insects or pollinators. Its natural properties reduce the risk of chemical residues on crops, promoting safer food production and sustainable gardening practices. Unlike chemical pesticides, neem oil decomposes quickly in the environment, minimizing soil and water contamination.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Neem Oil | Chemical Pesticides |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural extract from Azadirachta indica seeds | Synthetic chemicals |
| Mode of Action | Disrupts insect growth and feeding | Neurotoxic or systemic targeting pests |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity to non-target species | High toxicity, potential soil and water contamination |
| Effectiveness | Moderate, best for integrated pest management | High, immediate pest knockdown |
| Safety | Safe for humans, pollinators, and pets | Potentially hazardous, requires protective measures |
| Persistence | Degrades quickly in sunlight and soil | Long-lasting residues |
| Cost | Generally affordable, varies by purity | Varies widely, often higher for specialized formulas |
Introduction to Neem Oil and Chemical Pesticides in Horticulture
Neem oil, derived from the seeds of the Azadirachta indica tree, is a natural pesticide widely used in horticulture for its broad-spectrum pest control and eco-friendly properties. Chemical pesticides, synthesized from various chemical compounds, offer potent and fast-acting solutions for targeting specific pests but often pose environmental and health risks due to their residual toxicity. The choice between neem oil and chemical pesticides impacts pest resistance, soil health, and overall sustainability in horticultural practices.
Mechanisms of Action: Neem Oil vs Chemical Pesticides
Neem oil acts primarily through azadirachtin, disrupting insect hormone systems, inhibiting feeding, growth, and reproduction, leading to targeted pest mortality with minimal environmental impact. Chemical pesticides typically function by neurotoxins or metabolic inhibitors that cause immediate pest death but often result in broader ecological damage and resistance development. The sustainable mode of action and biodegradability of neem oil make it a preferred alternative for integrated pest management in horticulture.
Efficacy Against Common Horticultural Pests
Neem oil exhibits high efficacy against common horticultural pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites by disrupting their life cycles and acting as a natural insect repellent. Chemical pesticides often provide rapid and broad-spectrum pest elimination but may lead to pesticide resistance and harm beneficial insects such as pollinators and predators. Integrated pest management strategies combining neem oil's botanical properties with selective chemical use can optimize pest control while minimizing environmental impact.
Safety Profile for Humans, Pets, and Pollinators
Neem oil offers a superior safety profile compared to chemical pesticides, posing minimal toxicity risks to humans, pets, and beneficial pollinators such as bees and butterflies. Its natural compounds degrade quickly in the environment, reducing long-term exposure and contamination. Chemical pesticides often contain synthetic toxins linked to health hazards and pollinator decline, making neem oil a safer alternative for sustainable horticulture pest management.
Impact on Soil Health and Microbial Activity
Neem oil supports soil health by promoting beneficial microbial activity and enhancing nutrient cycling, whereas chemical pesticides often disrupt soil ecosystems and reduce microbial diversity. The natural antifungal and antibacterial properties of neem oil improve soil fertility without harmful residues. In contrast, chemical pesticides can lead to soil toxicity, impair microorganism populations, and decrease long-term soil productivity.
Environmental Sustainability and Eco-Friendly Practices
Neem oil offers an environmentally sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides by biodegrading rapidly and exhibiting low toxicity to beneficial insects such as pollinators and predators. Its natural active compounds, like azadirachtin, disrupt pest growth and reproduction without contaminating soil or water ecosystems. Chemical pesticides often persist in the environment, causing bioaccumulation and harming biodiversity, whereas neem oil supports eco-friendly pest control in horticulture by minimizing ecological disruption.
Resistance Development: Chemical vs Botanical Solutions
Neem oil offers a sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides by reducing the risk of resistance development in pests due to its complex mixture of bioactive compounds. Chemical pesticides often target specific biochemical pathways, leading to rapid resistance buildup in pest populations and requiring higher doses or new chemicals. Botanical solutions like neem oil promote integrated pest management by enhancing pest control effectiveness while minimizing environmental impact and resistance issues.
Application Methods and Best Practices
Neem oil is applied primarily through foliar sprays or soil drenching to target pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites, making it an eco-friendly alternative that enhances plant immunity without harming beneficial insects. Chemical pesticides often require precise timing and dosage applications to prevent phytotoxicity and resistance development, with methods including seed treatments, foliar sprays, and systemic injections. Best practices recommend integrating neem oil in pest management programs due to its biodegradability and lower environmental impact, while chemical pesticides should be used judiciously with appropriate personal protective equipment and adherence to legal guidelines.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Neem oil offers a cost-effective alternative to chemical pesticides, with lower application rates and reduced environmental cleanup expenses. While chemical pesticides may provide immediate pest knockdown, their long-term economic impact includes potential crop loss from resistance and health-related costs. Incorporating neem oil into pest management can enhance sustainability and reduce overall expenditure in horticultural operations.
Regulatory Guidelines and Organic Certification
Neem oil is widely accepted in organic horticulture due to its natural origin and compliance with strict organic certification standards set by organizations such as USDA Organic and OMRI. Chemical pesticides often face stringent regulatory restrictions and lengthy approval processes under agencies like the EPA, limiting their use in certified organic farming. Choosing neem oil supports sustainable pest control practices that align with global organic regulations, promoting environmental safety and marketability of organic produce.
Related Important Terms
Biopesticide synergy
Neem oil, rich in azadirachtin, offers a biopesticide synergy by disrupting pest feeding and reproduction while enhancing plant immunity, contrasting with chemical pesticides that often cause resistance and environmental harm. Integrating neem oil with selective chemical agents can optimize pest control efficiency, reducing chemical residues and promoting sustainable horticulture practices.
Azadirachtin potency
Neem oil, rich in azadirachtin, acts as a potent natural insect repellent and growth inhibitor targeting over 200 insect species, offering an eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides that often lead to resistance and environmental harm. Azadirachtin disrupts insect hormonal systems causing reduced feeding, molting, and reproduction, ensuring effective pest control with minimal toxicity to beneficial organisms and humans.
Phytotoxicity threshold
Neem oil exhibits a higher phytotoxicity threshold compared to many chemical pesticides, allowing safer application on sensitive plants without damaging foliage. Its natural bioactive compounds degrade more rapidly in the environment, reducing risks of harmful residue accumulation while effectively controlling a broad spectrum of horticultural pests.
Systemic resistance induction
Neem oil enhances systemic resistance in plants by activating their innate defense mechanisms through bioactive compounds like azadirachtin, promoting long-term pest suppression without harming beneficial insects. Chemical pesticides typically provide immediate pest eradication but often fail to induce systemic resistance, leading to potential pest resurgence and environmental toxicity concerns.
Residue persistence
Neem oil, derived from Azadirachta indica, exhibits rapid biodegradation in soil and on crops, resulting in minimal residue persistence and reduced environmental impact compared to synthetic chemical pesticides, which often leave harmful residues that persist for weeks or months. This shorter residue persistence of neem oil enhances its safety for beneficial insects and reduces the risk of contamination in food products and surrounding ecosystems.
Target pest selectivity
Neem oil demonstrates high target pest selectivity by disrupting the life cycle of specific insects such as aphids, whiteflies, and mites while minimizing harm to beneficial pollinators and predatory insects. Chemical pesticides often exhibit broad-spectrum toxicity, affecting non-target organisms including natural pest predators and soil microorganisms, which can lead to ecosystem imbalances and pest resistance.
Environmental load reduction
Neem oil, derived from the Azadirachta indica tree, offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, significantly reducing soil and water contamination while preserving beneficial insect populations. Its use in pest control minimizes toxic residue buildup and lowers the environmental load compared to synthetic chemicals known for persistence and bioaccumulation.
Detoxification enzyme modulation
Neem oil influences detoxification enzyme modulation by enhancing glutathione S-transferase activity, promoting effective biotransformation of toxins and reducing pest resistance. Chemical pesticides often disrupt detoxification enzymes, leading to accumulation of toxic metabolites and increased environmental hazards in horticultural pest management.
Integrated pest management (IPM) compatibility
Neem oil offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to chemical pesticides, effectively targeting a wide range of pests while preserving beneficial insects essential to Integrated Pest Management (IPM) systems. Its compatibility with IPM strategies supports sustainable pest control by minimizing environmental impact and reducing pest resistance development compared to synthetic chemical pesticides.
Resistance management strategy
Neem oil acts as a natural resistance management strategy by disrupting pest life cycles and reducing the development of pesticide-resistant populations through its complex mix of bioactive compounds. Chemical pesticides often lead to rapid resistance buildup due to their singular mode of action, making neem oil a sustainable alternative for long-term pest control in horticulture.
Neem oil vs Chemical pesticides for pest control Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com