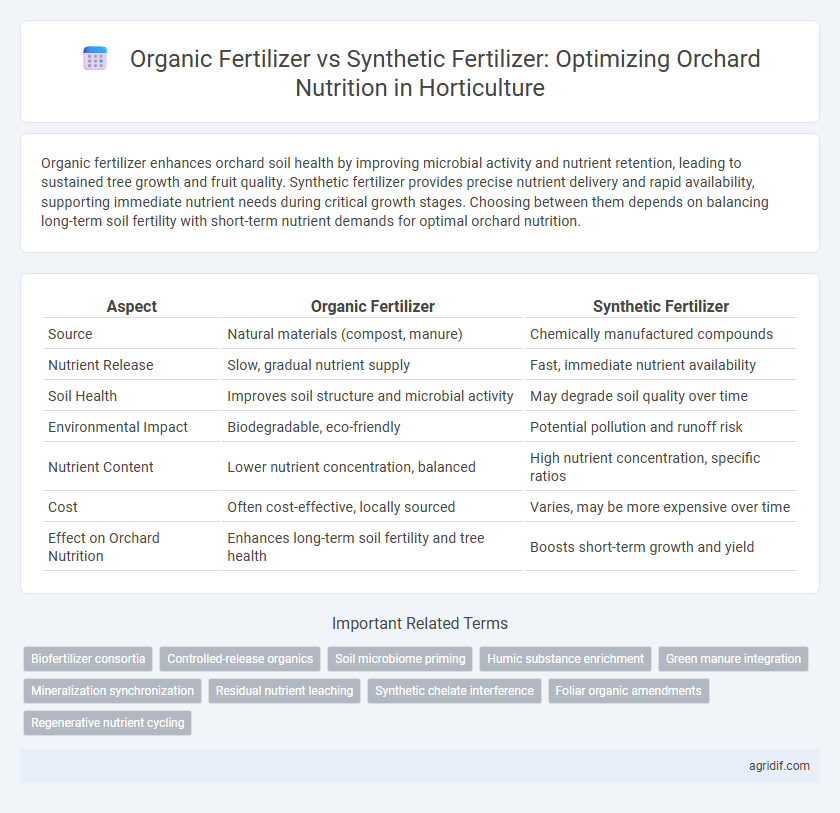
Organic fertilizer enhances orchard soil health by improving microbial activity and nutrient retention, leading to sustained tree growth and fruit quality. Synthetic fertilizer provides precise nutrient delivery and rapid availability, supporting immediate nutrient needs during critical growth stages. Choosing between them depends on balancing long-term soil fertility with short-term nutrient demands for optimal orchard nutrition.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Organic Fertilizer | Synthetic Fertilizer |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural materials (compost, manure) | Chemically manufactured compounds |
| Nutrient Release | Slow, gradual nutrient supply | Fast, immediate nutrient availability |
| Soil Health | Improves soil structure and microbial activity | May degrade soil quality over time |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly | Potential pollution and runoff risk |
| Nutrient Content | Lower nutrient concentration, balanced | High nutrient concentration, specific ratios |
| Cost | Often cost-effective, locally sourced | Varies, may be more expensive over time |
| Effect on Orchard Nutrition | Enhances long-term soil fertility and tree health | Boosts short-term growth and yield |
Overview of Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers in Orchard Nutrition
Organic fertilizers in orchard nutrition provide slow-release nutrients derived from natural sources such as compost, manure, and bone meal, enhancing soil structure, microbial activity, and long-term fertility. Synthetic fertilizers offer precise, concentrated nutrient delivery with immediate availability, enabling targeted correction of deficiencies in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for fruit tree growth. Balancing organic and synthetic fertilizers optimizes nutrient uptake efficiency, promotes sustainable soil health, and supports high orchard productivity.
Key Nutrient Sources: Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers provide essential nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium through natural sources like compost, manure, and bone meal, enhancing soil microbial activity and nutrient availability over time. Synthetic fertilizers deliver concentrated and readily available forms of these key nutrients, ensuring rapid uptake and targeted nourishment for orchard crops. The choice between organic and synthetic fertilizers influences soil health, nutrient release rates, and long-term orchard productivity.
Soil Health Impact in Orchards
Organic fertilizers enhance soil health in orchards by improving microbial activity, increasing organic matter content, and promoting nutrient cycling, which leads to better soil structure and water retention. In contrast, synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but can degrade soil quality over time by reducing microbial diversity and causing nutrient imbalances. Long-term orchard productivity benefits more from organic fertilization due to its positive impact on soil biology and sustainability.
Fertilizer Application Methods for Fruit Trees
Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, release nutrients slowly through microbial activity, enhancing soil structure and providing long-term nutrition for fruit trees when applied as surface mulch or buried near root zones. Synthetic fertilizers offer precise nutrient ratios and rapid availability, often applied via fertigation or soil injection to target immediate nutritional needs and promote faster growth in orchards. Combining application methods, tailored to specific orchard conditions, maximizes nutrient efficiency and tree health for optimal fruit production.
Nutrient Release and Availability to Orchard Crops
Organic fertilizers release nutrients slowly through microbial activity, enhancing long-term soil health and sustained nutrient availability for orchard crops. Synthetic fertilizers provide a rapid and concentrated nutrient supply, allowing immediate uptake but posing risks of leaching and nutrient imbalances. Optimizing orchard nutrition requires balancing the controlled nutrient release from organic fertilizers with the quick availability of synthetic inputs to meet crop demands efficiently.
Environmental Consequences: Organic vs Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers enhance soil biodiversity and improve long-term soil structure by releasing nutrients slowly, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching and water pollution. Synthetic fertilizers, while providing immediate nutrient availability, often lead to soil acidification, nutrient runoff, and increased greenhouse gas emissions. The environmental consequences of synthetic fertilizer overuse include eutrophication of water bodies and decreased microbial activity, whereas organic alternatives promote sustainable orchard nutrition through improved ecosystem health.
Orchard Crop Yield and Fruit Quality Differences
Organic fertilizers improve orchard crop yield by enhancing soil microbial activity and nutrient retention, leading to better root development and consistent fruit growth. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability, resulting in rapid growth but may cause nutrient imbalances and reduced fruit quality over time. Studies show orchards using organic fertilizers produce fruits with higher sugar content, better texture, and longer shelf life compared to those treated with synthetic alternatives.
Cost Comparison for Commercial Orchard Management
Organic fertilizers typically incur higher upfront costs due to processing and transportation but offer long-term soil health benefits that can reduce future input expenses in commercial orchard management. Synthetic fertilizers are generally more cost-effective initially, providing targeted nutrient delivery that promotes rapid tree growth and fruit production. However, dependence on synthetic inputs may lead to increased costs over time from soil degradation and the need for additional amendments to sustain orchard productivity.
Long-term Sustainability in Orchard Fertilization
Organic fertilizers improve soil structure and enhance microbial activity, promoting long-term sustainability in orchard nutrition by maintaining nutrient balance and reducing dependency on chemical inputs. Synthetic fertilizers offer immediate nutrient availability, but their overuse can degrade soil health and lead to nutrient runoff, harming orchard ecosystems. Sustainable orchard fertilization prioritizes organic amendments to support soil fertility and resilience over successive growing seasons.
Choosing the Right Fertilizer Strategy for Orchards
Organic fertilizers improve soil structure and microbial activity by providing slow-release nutrients crucial for long-term orchard health. Synthetic fertilizers deliver precise nutrient formulations for rapid nutrient availability, supporting immediate growth and higher yields. Selecting the right fertilizer strategy depends on soil conditions, orchard crop requirements, and environmental sustainability goals.
Related Important Terms
Biofertilizer consortia
Biofertilizer consortia enhance orchard nutrition by promoting natural nutrient cycles and improving soil microbial diversity, outperforming synthetic fertilizers that may cause nutrient imbalances and long-term soil degradation. Integrating organic biofertilizer consortia supports sustainable orchard productivity through nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilization, and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria activities critical for orchard health.
Controlled-release organics
Controlled-release organic fertilizers enhance orchard nutrition by gradually supplying essential nutrients, improving soil microbial activity and reducing nutrient leaching compared to synthetic fertilizers. Their sustained nutrient release aligns with tree uptake patterns, promoting healthier growth and minimizing environmental impact.
Soil microbiome priming
Organic fertilizers enhance orchard nutrition by stimulating diverse soil microbiomes, increasing microbial activity, and improving nutrient cycling, which supports sustainable plant growth. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but often disrupt soil microbial communities, potentially reducing long-term soil health and microbiome priming essential for orchard resilience.
Humic substance enrichment
Organic fertilizers enhance orchard nutrition by providing rich humic substances that improve soil structure, increase microbial activity, and promote nutrient availability, leading to healthier root systems and better fruit yield. Synthetic fertilizers lack these humic compounds, often resulting in quicker nutrient release but limited long-term soil health benefits and reduced microbial diversity.
Green manure integration
Green manure integration enhances organic fertilizer's ability to improve soil structure, boost microbial activity, and increase nutrient availability for orchard nutrition, promoting long-term sustainability. Synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient supply but lack the soil-enriching benefits of green manure, often leading to nutrient leaching and reduced soil fertility over time.
Mineralization synchronization
Organic fertilizers release nutrients through slow mineralization processes that align with the orchard's nutrient uptake patterns, enhancing long-term soil fertility and microbial activity. Synthetic fertilizers provide readily available nutrients but often cause nutrient leaching and imbalanced mineralization rates, potentially disrupting orchard nutrient synchronization and reducing overall soil health.
Residual nutrient leaching
Organic fertilizers reduce residual nutrient leaching in orchards by releasing nutrients slowly through microbial decomposition, enhancing soil structure and nutrient retention. Synthetic fertilizers often cause higher residual nutrient leaching due to their water-soluble nature, leading to increased nutrient runoff and groundwater contamination.
Synthetic chelate interference
Synthetic fertilizers offer precise nutrient delivery but synthetic chelates in orchard nutrition can interfere with micronutrient availability by forming stable complexes that hinder plant uptake, potentially causing nutrient imbalances. Organic fertilizers improve soil structure and microbial activity, which enhance natural nutrient cycling and reduce the risks of chelate-related micronutrient deficiencies in orchards.
Foliar organic amendments
Foliar organic amendments in orchard nutrition enhance nutrient uptake efficiency by supplying readily absorbable micronutrients and promoting beneficial microbial activity on leaf surfaces. Compared to synthetic fertilizers, organic foliar sprays improve tree health and fruit quality through natural nutrient release and reduced chemical residues.
Regenerative nutrient cycling
Organic fertilizers enhance regenerative nutrient cycling in orchards by promoting soil microbial activity and improving soil structure, which supports long-term soil fertility and plant health. In contrast, synthetic fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability but may disrupt natural nutrient cycles, potentially leading to soil degradation and reduced microbial diversity over time.
Organic fertilizer vs Synthetic fertilizer for orchard nutrition Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com