Trellising provides structured support for climbing plants, maximizing vertical space and improving air circulation, which reduces disease risk. Staking is ideal for individual plants requiring sturdy upright support to prevent bending or breakage during strong winds. Choosing between trellising and staking depends on plant type, growth habit, and garden layout to optimize yield and health.
Table of Comparison
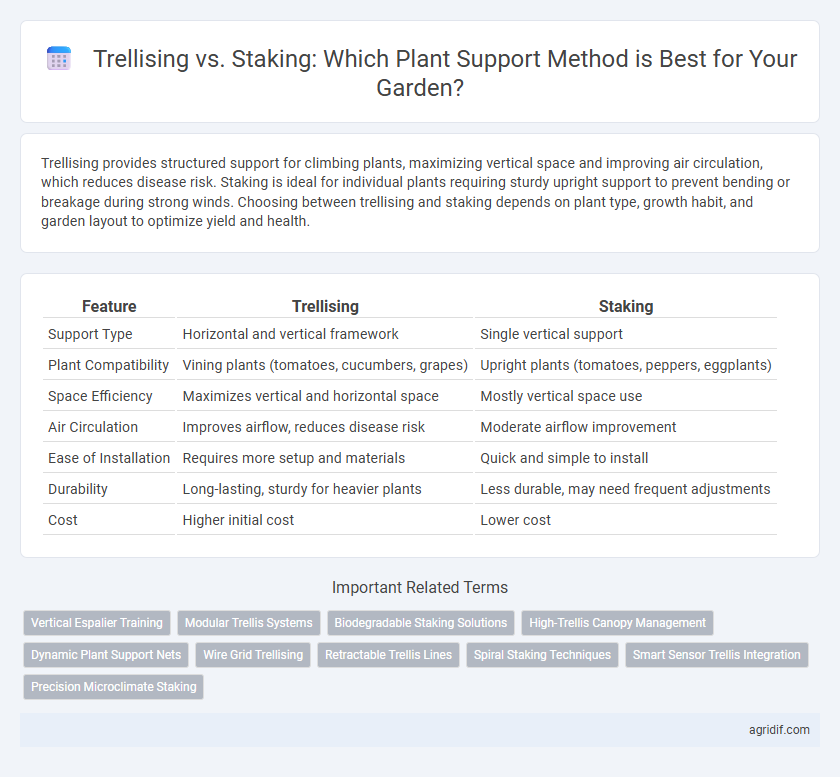
| Feature | Trellising | Staking |
|---|---|---|
| Support Type | Horizontal and vertical framework | Single vertical support |
| Plant Compatibility | Vining plants (tomatoes, cucumbers, grapes) | Upright plants (tomatoes, peppers, eggplants) |
| Space Efficiency | Maximizes vertical and horizontal space | Mostly vertical space use |
| Air Circulation | Improves airflow, reduces disease risk | Moderate airflow improvement |
| Ease of Installation | Requires more setup and materials | Quick and simple to install |
| Durability | Long-lasting, sturdy for heavier plants | Less durable, may need frequent adjustments |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower cost |
Understanding Trellising and Staking in Horticulture
Trellising and staking are essential horticultural techniques used to support plant growth by preventing damage and promoting air circulation. Trellising involves training plants to grow vertically along a framework, optimizing space and increasing exposure to sunlight, while staking provides individual support by anchoring plants with poles or stakes to maintain upright growth. Selecting the appropriate method depends on plant species, growth habits, and garden design, ensuring healthy development and higher yields.
Key Differences Between Trellising and Staking
Trellising involves supporting plants by training them to grow vertically along a framework of wires, lattices, or grids, ideal for climbing vegetables like beans and cucumbers. Staking uses single or multiple stakes driven into the soil to support individual plants such as tomatoes or peppers, preventing bending or breaking. The key difference lies in trellising providing a structured pathway for plant growth and improving air circulation, while staking offers direct, localized support to maintain plant uprightness.
Benefits of Trellising for Crop Growth
Trellising enhances crop growth by improving air circulation and sunlight exposure, which reduces disease incidence and promotes healthier plants. This support method maximizes space efficiency, allowing vertical growth that increases yield per square foot. Crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and beans benefit from trellising as it prevents fruit rot and simplifies harvesting, leading to higher-quality produce.
Advantages of Staking in Small-Scale Gardens
Staking offers precise support for individual plants, making it ideal for small-scale gardens where space and plant variety are limited. It enhances air circulation around the plant, reducing the risk of fungal diseases and promoting healthier growth. The ease of installation and flexibility in adjusting stakes accommodate plant growth stages effectively, ensuring optimal support for vegetables like tomatoes, peppers, and beans.
Suitable Crops for Trellising and Staking
Trellising is ideal for vine crops like tomatoes, cucumbers, and pole beans, providing vertical support that enhances air circulation and fruit exposure to sunlight. Staking suits crops such as peppers, eggplants, and determinate tomatoes, offering sturdy, individual plant support that prevents lodging and simplifies harvesting. Selecting the appropriate support method depends on plant growth habits and space availability, optimizing yield and crop health.
Installation Techniques: Trellising vs Staking
Trellising installation involves securing plants to vertical or angled frameworks using ties, clips, or knots, ensuring even support and maximizing sun exposure. Staking requires driving individual stakes into the soil near each plant and fastening stems with soft ties to prevent damage and allow growth flexibility. Both methods demand proper spacing and anchoring techniques to maintain plant health and structural stability throughout the growing season.
Cost Analysis: Trellis Systems vs Stakes
Trellis systems generally involve higher initial costs due to materials like wood, metal, or durable plastic and require more labor for installation compared to stakes. However, trellising can offer better long-term value by improving plant health and yield, potentially reducing replacement and maintenance expenses. Stakes are cheaper upfront and easier to install but may need frequent replacement and provide less structural support for heavy or sprawling plants, impacting overall cost-effectiveness.
Maintenance Requirements for Trellising and Staking
Trellising requires periodic inspection to ensure ties and supports remain secure, with occasional adjustments as plants grow and spread. Staking demands regular tightening and repositioning of ties to prevent damage from wind and plant weight, often needing more frequent attention than trellising. Both methods benefit from routine pruning to maintain plant health and promote optimal growth.
Impact on Plant Health and Yield
Trellising provides superior air circulation and sunlight exposure, reducing disease incidence and promoting robust plant health compared to staking. Plants supported by trellises exhibit higher yields due to improved structural support, allowing fruit to develop evenly and reducing damage from soil contact. Staking may be easier for small plants but often limits growth potential and increases vulnerability to pests and rot.
Choosing the Best Support Method for Your Garden
Selecting the ideal plant support method depends on crop type, garden layout, and growth habits; trellising suits vining plants like tomatoes and cucumbers by promoting vertical growth and improving air circulation. Staking works well for individual plants such as peppers and eggplants, providing sturdy support and easier access for maintenance. Efficient plant support maximizes sunlight exposure, reduces disease risk, and enhances yield quality in horticultural practice.
Related Important Terms
Vertical Espalier Training
Vertical espalier training maximizes space efficiency by guiding plants to grow flat against a trellis, improving air circulation and sunlight exposure essential for fruit production. Compared to staking, trellising provides stronger structural support for espaliered branches, reducing breakage and facilitating easier pruning and harvesting.
Modular Trellis Systems
Modular trellis systems offer flexible, reusable, and customizable plant support solutions that enhance vertical growth and improve air circulation for horticultural crops such as tomatoes, cucumbers, and beans. These systems outperform traditional staking by providing greater stability, reducing plant stress, and facilitating easier maintenance and harvesting.
Biodegradable Staking Solutions
Biodegradable staking solutions in horticulture offer sustainable plant support by decomposing naturally, reducing environmental impact while providing necessary stability to plants like tomatoes and peppers. Compared to trellising, biodegradable stakes simplify installation and minimize plastic waste, aligning with eco-friendly gardening practices and promoting healthy plant growth.
High-Trellis Canopy Management
High-trellis canopy management enhances airflow and light penetration in horticultural crops, promoting healthier growth and higher yields compared to traditional staking methods. Utilizing vertical space efficiently, high trellises support vigorous vine development and improve disease resistance by reducing ground contact.
Dynamic Plant Support Nets
Dynamic plant support nets enhance growth by providing flexible, adjustable trellising that accommodates plant expansion and reduces stem damage, unlike rigid staking methods. These nets optimize air circulation and light exposure, promoting healthier crops and higher yields in horticultural systems.
Wire Grid Trellising
Wire grid trellising provides durable, space-efficient support for climbing plants by allowing vertical growth and improved air circulation, which reduces disease risk and enhances fruit exposure to sunlight. Unlike staking, wire grids facilitate better crop management and harvest efficiency, making them ideal for tomatoes, cucumbers, and peas in commercial horticulture.
Retractable Trellis Lines
Retractable trellis lines offer versatile, space-saving plant support by allowing gardeners to easily adjust tension and height, promoting optimal growth for climbing plants like tomatoes and cucumbers. This system enhances air circulation and sunlight exposure while reducing damage risk compared to traditional staking methods.
Spiral Staking Techniques
Spiral staking techniques provide enhanced support and airflow for vine crops and tall plants, promoting healthier growth and easier maintenance compared to traditional trellising. This method reduces stem damage by allowing natural plant movement while maximizing vertical space and exposure to sunlight.
Smart Sensor Trellis Integration
Smart sensor trellis integration enhances traditional trellising by providing real-time monitoring of plant health, growth patterns, and environmental conditions, optimizing support structures for maximum yield. Unlike staking, which offers limited feedback, sensor-equipped trellises enable precision irrigation, pest detection, and adaptive structural adjustments through IoT connectivity, revolutionizing plant support in modern horticulture.
Precision Microclimate Staking
Precision Microclimate Staking enhances plant support by tailoring stake placement and height to optimize airflow, sunlight exposure, and humidity levels around individual crops, promoting healthier growth and reducing disease risk. This method offers superior control over microenvironments compared to traditional trellising, enabling precise adjustments to meet specific horticultural needs.
Trellising vs Staking for Plant Support Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com