Micro-irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, enhancing water efficiency and reducing evaporation losses compared to traditional irrigation methods. This targeted approach promotes healthier tree growth and increases fruit yield by providing consistent moisture levels tailored to orchard needs. Traditional irrigation often leads to water wastage and uneven distribution, making micro-irrigation a sustainable choice for orchard water management.
Table of Comparison
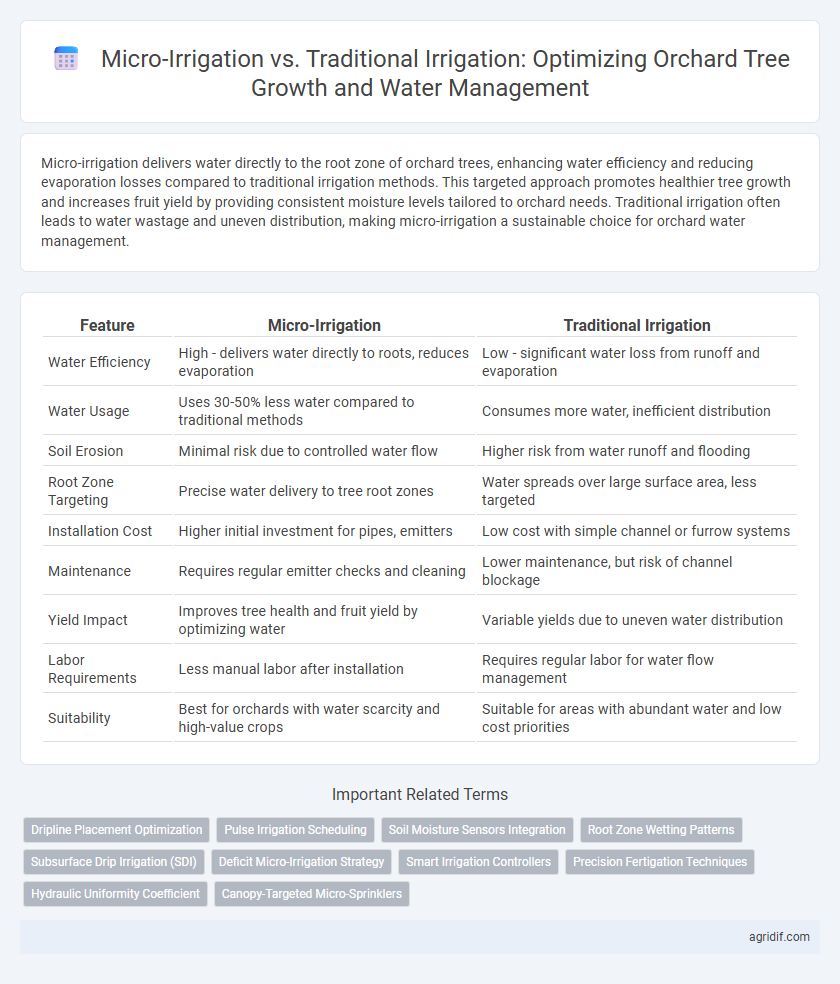
| Feature | Micro-Irrigation | Traditional Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High - delivers water directly to roots, reduces evaporation | Low - significant water loss from runoff and evaporation |
| Water Usage | Uses 30-50% less water compared to traditional methods | Consumes more water, inefficient distribution |
| Soil Erosion | Minimal risk due to controlled water flow | Higher risk from water runoff and flooding |
| Root Zone Targeting | Precise water delivery to tree root zones | Water spreads over large surface area, less targeted |
| Installation Cost | Higher initial investment for pipes, emitters | Low cost with simple channel or furrow systems |
| Maintenance | Requires regular emitter checks and cleaning | Lower maintenance, but risk of channel blockage |
| Yield Impact | Improves tree health and fruit yield by optimizing water | Variable yields due to uneven water distribution |
| Labor Requirements | Less manual labor after installation | Requires regular labor for water flow management |
| Suitability | Best for orchards with water scarcity and high-value crops | Suitable for areas with abundant water and low cost priorities |
Introduction to Orchard Irrigation Methods
Micro-irrigation systems, such as drip and micro-sprinkler irrigation, deliver water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, enhancing water use efficiency by reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. Traditional irrigation often leads to uneven water distribution and higher water consumption, making it less sustainable in water-scarce regions. Implementing micro-irrigation in orchards supports precise water management, improves tree health, and increases crop yield while conserving vital water resources.
Overview of Micro-Irrigation Systems
Micro-irrigation systems, such as drip and micro-sprinkler irrigation, deliver water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, significantly reducing water wastage compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. These systems enhance water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff, leading to improved soil moisture control and healthier tree growth. Studies show micro-irrigation can increase yield by up to 30% while conserving up to 50% of water resources in orchard management.
Traditional Irrigation Techniques in Orchards
Traditional irrigation techniques in orchards primarily include flood irrigation, furrow irrigation, and basin irrigation, which rely heavily on surface water distribution. These methods, while simpler and often less costly initially, frequently result in uneven water application, higher water loss through evaporation and runoff, and increased labor requirements. Despite these inefficiencies, traditional irrigation remains widely used in many orchard systems due to established infrastructure and familiarity among farmers.
Water Use Efficiency Comparison
Micro-irrigation systems, such as drip and micro-sprinkler irrigation, deliver water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, enhancing water use efficiency by reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. Studies indicate micro-irrigation can improve water use efficiency by 30-50%, enabling precise control over irrigation scheduling and volume, which minimizes water waste and promotes uniform soil moisture distribution. Traditional irrigation often results in significant water loss, with efficiencies ranging from 40-60%, whereas micro-irrigation optimizes water utilization, supporting sustainable orchard management and conserving critical water resources.
Impact on Orchard Tree Health and Productivity
Micro-irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, reducing water wastage and promoting deeper root growth, which enhances tree health and resilience. Traditional irrigation methods, such as flood or furrow irrigation, often result in uneven water distribution, increasing the risk of root diseases and water stress that can lower fruit yield and quality. Studies show that micro-irrigation improves orchard productivity by up to 30% due to more efficient water use and stable soil moisture levels.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Micro-irrigation systems for orchard trees demand precise installation involving drip emitters or micro-sprinklers positioned at the root zones, requiring initial investment in filtration and pressure regulation equipment. Maintenance emphasizes regular inspection for emitter blockages, system flushing, and seasonal adjustments to flow rates to prevent clogging and ensure uniform water distribution. Traditional irrigation methods, such as flood or furrow irrigation, have simpler installation but entail higher water loss, soil erosion risks, and frequent channel maintenance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Micro-irrigation systems for orchard trees require higher initial investment costs, typically ranging from $800 to $1,500 per acre, compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation, which may cost around $200 to $400 per acre. Despite the upfront expense, micro-irrigation offers significant long-term savings by reducing water use by 30-50%, lowering energy costs, and minimizing fertilizer runoff, leading to enhanced crop yield and soil health. Over a 5-10 year period, these efficiency gains often result in a return on investment that offsets the initial setup costs, making micro-irrigation a economically viable choice for sustainable orchard management.
Soil Moisture Distribution and Management
Micro-irrigation provides precise soil moisture distribution by delivering water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This targeted water application promotes uniform soil moisture levels, enhancing root development and reducing water wastage in orchards. Efficient soil moisture management through micro-irrigation leads to improved tree health and higher fruit yield by maintaining optimal hydration without oversaturation.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Micro-irrigation systems deliver water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, significantly reducing water wastage and minimizing soil erosion compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This targeted approach enhances water-use efficiency by up to 90%, conserving groundwater resources and mitigating nutrient leaching into surrounding ecosystems. Implementing micro-irrigation supports sustainable orchard management by lowering energy consumption for water pumping and reducing greenhouse gas emissions associated with excess water application.
Selecting the Right Irrigation Method for Your Orchard
Micro-irrigation enhances water efficiency by delivering precise moisture directly to orchard tree roots, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This targeted approach supports consistent soil moisture, promoting healthier root systems and improving fruit yield and quality. Selecting micro-irrigation aligns with sustainable water management goals, especially in regions facing water scarcity or regulations on water usage.
Related Important Terms
Dripline Placement Optimization
Optimizing dripline placement in micro-irrigation systems for orchard trees significantly enhances water use efficiency by delivering precise moisture directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff typical in traditional irrigation. Strategic emitter spacing and depth placement tailored to root architecture promote uniform water distribution, improving tree health and fruit yield while conserving water resources.
Pulse Irrigation Scheduling
Pulse irrigation scheduling enhances water efficiency in micro-irrigation systems by delivering short, frequent watering intervals tailored to orchard trees' root zones, reducing runoff and deep percolation compared to traditional irrigation methods. This approach optimizes soil moisture retention and promotes healthier tree growth while conserving water resources critical for sustainable orchard management.
Soil Moisture Sensors Integration
Integrating soil moisture sensors with micro-irrigation systems for orchard trees enables precise water delivery, reducing water waste and enhancing root zone moisture uniformity compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This technology optimizes irrigation scheduling by providing real-time soil moisture data, improving water use efficiency and promoting healthier tree growth in orchard management.
Root Zone Wetting Patterns
Micro-irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, creating precise wetting patterns that optimize moisture availability and minimize evaporation losses compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This targeted approach enhances root development, improves water use efficiency, and reduces runoff, leading to healthier orchard trees and sustainable water management.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to the root zone of orchard trees, significantly enhancing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation losses compared to traditional surface irrigation methods. This micro-irrigation technique improves tree health and yield by maintaining optimal soil moisture levels, minimizing nutrient leaching, and reducing weed growth.
Deficit Micro-Irrigation Strategy
Deficit micro-irrigation strategically applies water below full crop evapotranspiration, optimizing water use efficiency and sustaining orchard tree yield by carefully managing moisture stress. Compared to traditional irrigation, this method reduces water consumption by up to 40% while maintaining fruit quality and minimizing runoff and deep percolation losses.
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers enhance micro-irrigation efficiency for orchard trees by delivering precise water volumes tailored to soil moisture and tree water needs, reducing water waste compared to traditional irrigation methods. These controllers integrate weather data and soil sensors to optimize irrigation schedules, promoting healthier tree growth and conserving water resources.
Precision Fertigation Techniques
Micro-irrigation systems deliver water and nutrients directly to the root zone of orchard trees, optimizing water use efficiency and promoting healthier growth through precise fertigation techniques that minimize nutrient runoff and leaching. Traditional irrigation methods often result in uneven water distribution and nutrient application, leading to higher water consumption and reduced fertilizer use efficiency compared to the targeted delivery in micro-irrigation.
Hydraulic Uniformity Coefficient
Micro-irrigation systems for orchard trees achieve a higher Hydraulic Uniformity Coefficient (HUC) typically above 90%, ensuring consistent water distribution across the root zone, which reduces water stress and improves yield efficiency. In contrast, traditional irrigation methods often exhibit lower HUC values, around 60-75%, leading to uneven water application, increased runoff, and potential over-irrigation in some areas of the orchard.
Canopy-Targeted Micro-Sprinklers
Canopy-targeted micro-sprinklers in micro-irrigation deliver precise water application directly to the tree canopy, enhancing water use efficiency and reducing soil evaporation compared to traditional flood or furrow irrigation methods. This targeted approach improves tree health, fruit quality, and yield by maintaining optimal moisture levels in the root zone and minimizing water runoff and deep percolation losses.
Micro-Irrigation vs Traditional Irrigation for Orchard Trees Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com