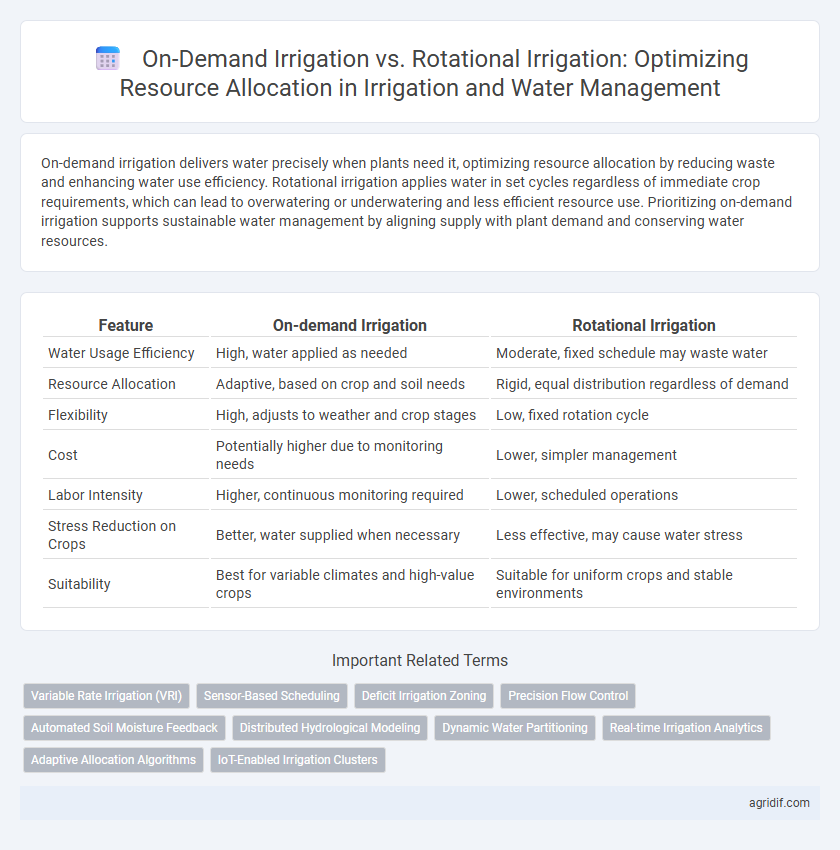
On-demand irrigation delivers water precisely when plants need it, optimizing resource allocation by reducing waste and enhancing water use efficiency. Rotational irrigation applies water in set cycles regardless of immediate crop requirements, which can lead to overwatering or underwatering and less efficient resource use. Prioritizing on-demand irrigation supports sustainable water management by aligning supply with plant demand and conserving water resources.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | On-demand Irrigation | Rotational Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Usage Efficiency | High, water applied as needed | Moderate, fixed schedule may waste water |
| Resource Allocation | Adaptive, based on crop and soil needs | Rigid, equal distribution regardless of demand |
| Flexibility | High, adjusts to weather and crop stages | Low, fixed rotation cycle |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to monitoring needs | Lower, simpler management |
| Labor Intensity | Higher, continuous monitoring required | Lower, scheduled operations |
| Stress Reduction on Crops | Better, water supplied when necessary | Less effective, may cause water stress |
| Suitability | Best for variable climates and high-value crops | Suitable for uniform crops and stable environments |
Introduction to On-Demand and Rotational Irrigation
On-demand irrigation allocates water precisely when crops show signs of need, optimizing water use efficiency and reducing wastage by responding directly to soil moisture conditions. Rotational irrigation follows a fixed schedule, distributing water uniformly across fields regardless of immediate crop requirements, which can lead to over or under-watering in different zones. Balancing these methods enhances resource allocation by combining the responsiveness of on-demand irrigation with the predictability of rotational scheduling.
Defining On-Demand Irrigation Systems
On-demand irrigation systems operate by delivering water precisely when and where crops need it, optimizing water use efficiency and minimizing waste. These systems utilize real-time data from soil moisture sensors and weather forecasts to tailor irrigation scheduling, enhancing resource allocation compared to rotational irrigation methods. This targeted approach reduces water consumption and energy costs, improving crop yield and sustainability in diverse agricultural settings.
Understanding Rotational Irrigation Methods
Rotational irrigation methods allocate water resources by scheduling watering cycles for specific zones, optimizing water use based on crop needs and soil moisture levels. This approach reduces water waste and promotes sustainable irrigation compared to on-demand irrigation, which applies water immediately in response to moisture deficits but may lead to inefficient resource use. Understanding the timing and sequence in rotational irrigation enhances water conservation and improves overall crop health.
Water Resource Allocation Challenges
On-demand irrigation delivers water precisely based on crop needs, reducing water wastage and improving efficiency in water-scarce regions. Rotational irrigation allocates water in scheduled cycles, which can lead to uneven distribution and potential overuse during allocation periods. Managing water resource allocation challenges requires balancing the precision of on-demand systems with the operational simplicity of rotational methods to optimize water use in agriculture.
Efficiency of Water Use in On-Demand vs Rotational Irrigation
On-demand irrigation optimizes water use efficiency by delivering precise amounts of water based on real-time crop and soil needs, reducing losses due to evaporation and runoff. Rotational irrigation applies water at set intervals regardless of immediate crop requirements, often leading to over-irrigation and higher water wastage. Studies show on-demand systems can improve water use efficiency by up to 30% compared to traditional rotational methods, making them more sustainable for resource allocation.
Impact on Crop Yield and Productivity
On-demand irrigation optimizes water use by delivering moisture precisely when crops need it, leading to improved crop yield and enhanced productivity through efficient resource allocation. In contrast, rotational irrigation applies water at fixed intervals regardless of crop water stress, which can result in overwatering or underwatering, negatively impacting crop growth and reducing yield potential. Employing on-demand systems leverages real-time soil moisture data, maximizing water-use efficiency and supporting sustainable agricultural practices.
Infrastructure Requirements and Costs
On-demand irrigation requires advanced sensors and automated control systems to deliver precise water quantities, often increasing initial infrastructure costs but optimizing water use efficiency. Rotational irrigation relies on predefined schedules and simpler infrastructure, resulting in lower upfront expenses but potentially higher water wastage and less flexibility in resource allocation. Investing in on-demand systems can reduce long-term water and energy costs despite higher installation expenditures compared to the more traditional and cost-effective rotational setups.
Flexibility and Scalability in Water Management
On-demand irrigation offers enhanced flexibility by delivering water precisely when and where crops require it, minimizing waste and adapting to variable weather conditions. Rotational irrigation provides scalability by systematically allocating water across large fields or multiple crops, ensuring consistent distribution but with less real-time responsiveness. Integrating these methods optimizes resource allocation, balancing water conservation with crop demands for efficient irrigation management.
Environmental Implications of Both Approaches
On-demand irrigation minimizes water waste by delivering precise amounts only when plants need it, reducing runoff and soil erosion. Rotational irrigation may lead to overwatering in some areas, increasing nutrient leaching and greenhouse gas emissions from waterlogged soils. Choosing on-demand systems enhances water use efficiency and mitigates negative environmental impacts associated with excessive water application.
Choosing the Optimal Irrigation Strategy for Sustainable Agriculture
On-demand irrigation delivers water precisely when crops need it, minimizing water waste and improving efficiency in resource allocation. Rotational irrigation schedules watering based on fixed intervals, which can lead to over-irrigation or water stress depending on environmental conditions. Selecting the optimal irrigation strategy requires analyzing crop water requirements, soil type, and climate data to enhance sustainability and maximize agricultural productivity.
Related Important Terms
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
On-demand irrigation enables precise water application based on real-time soil moisture data, maximizing resource efficiency and crop yield, while rotational irrigation applies water in systematic cycles regardless of immediate field conditions, potentially leading to over- or under-irrigation. Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) technology integrates GPS and soil sensors to adjust water flow rates within on-demand irrigation systems, optimizing water allocation by targeting specific zones and reducing waste compared to uniform rotational methods.
Sensor-Based Scheduling
Sensor-based scheduling in on-demand irrigation optimizes water use by delivering precise amounts based on real-time soil moisture data, reducing wastage compared to rotational irrigation's fixed intervals. This method enhances resource allocation efficiency by dynamically adjusting irrigation timing, improving crop yield and conserving water resources.
Deficit Irrigation Zoning
On-demand irrigation enables precise water application in deficit irrigation zoning by targeting crop water needs in real time, optimizing resource allocation and reducing waste. Rotational irrigation schedules may lead to uneven water distribution, making on-demand systems more efficient for maximizing yields under limited water availability.
Precision Flow Control
On-demand irrigation leverages precision flow control to allocate water dynamically based on real-time soil moisture data, optimizing resource use and minimizing waste. Rotational irrigation distributes water at fixed intervals, often leading to less efficient resource allocation and potential over- or under-irrigation.
Automated Soil Moisture Feedback
On-demand irrigation leverages automated soil moisture feedback systems to precisely allocate water based on real-time soil hydration levels, optimizing resource use and reducing waste. Rotational irrigation schedules apply water to predefined zones regardless of current soil moisture conditions, often leading to less efficient water distribution and higher consumption.
Distributed Hydrological Modeling
On-demand irrigation optimizes water use by delivering precise amounts based on real-time soil moisture data, reducing waste and enhancing crop yield efficiency. Distributed hydrological modeling supports this by simulating spatially variable soil moisture and runoff patterns, enabling targeted resource allocation compared to rotational irrigation's fixed scheduling.
Dynamic Water Partitioning
Dynamic Water Partitioning enhances on-demand irrigation by allocating precise water volumes based on real-time crop needs and soil moisture levels, optimizing water use efficiency and reducing wastage. Unlike rotational irrigation, this method adjusts water distribution dynamically, ensuring targeted resource allocation that supports sustainable water management and maximizes crop yield.
Real-time Irrigation Analytics
On-demand irrigation leverages real-time irrigation analytics to allocate water resources precisely based on current crop needs and soil moisture levels, enhancing water use efficiency and reducing waste. Rotational irrigation, while simpler to manage, lacks the dynamic data-driven responsiveness provided by real-time monitoring, often resulting in less optimal resource distribution.
Adaptive Allocation Algorithms
Adaptive allocation algorithms enhance resource efficiency by dynamically adjusting water distribution based on real-time soil moisture and crop water stress levels in on-demand irrigation systems. These algorithms outperform rotational irrigation by minimizing water waste and optimizing crop yield through precise, site-specific irrigation scheduling.
IoT-Enabled Irrigation Clusters
IoT-enabled irrigation clusters optimize resource allocation by enabling on-demand irrigation, which delivers water precisely when and where crops need it, reducing wastage compared to traditional rotational irrigation schedules. This technology leverages soil moisture sensors and real-time data analytics to dynamically adjust water distribution, enhancing water use efficiency and crop yield.
On-demand irrigation vs rotational irrigation for resource allocation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com