Certified organic seeds guarantee compliance with strict agricultural standards, reducing chemical exposure and promoting sustainable farming practices ideal for organic farming pets' environments. Heirloom seeds offer a diverse genetic heritage and unique flavors, preserving biodiversity while maintaining natural growth patterns beneficial for organic ecosystems. Choosing between certified organic and heirloom seeds depends on prioritizing certified purity or genetic diversity to enhance the quality of organic farming pet care.
Table of Comparison
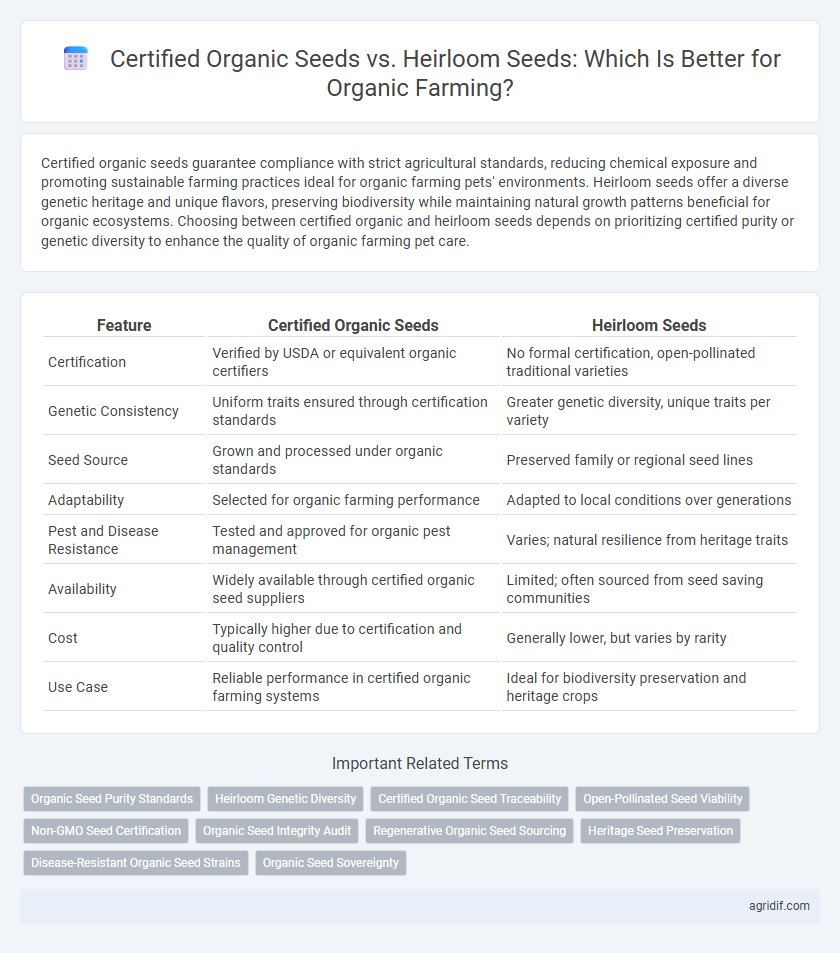
| Feature | Certified Organic Seeds | Heirloom Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Certification | Verified by USDA or equivalent organic certifiers | No formal certification, open-pollinated traditional varieties |
| Genetic Consistency | Uniform traits ensured through certification standards | Greater genetic diversity, unique traits per variety |
| Seed Source | Grown and processed under organic standards | Preserved family or regional seed lines |
| Adaptability | Selected for organic farming performance | Adapted to local conditions over generations |
| Pest and Disease Resistance | Tested and approved for organic pest management | Varies; natural resilience from heritage traits |
| Availability | Widely available through certified organic seed suppliers | Limited; often sourced from seed saving communities |
| Cost | Typically higher due to certification and quality control | Generally lower, but varies by rarity |
| Use Case | Reliable performance in certified organic farming systems | Ideal for biodiversity preservation and heritage crops |
Understanding Certified Organic Seeds
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous inspection and certification processes to ensure they are free from synthetic chemicals, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and harmful pesticides, aligning with organic farming standards. These seeds are produced on farms that comply with strict organic regulations, guaranteeing their purity, sustainability, and environmental safety for organic crop production. Using certified organic seeds supports organic integrity and promotes biodiversity while meeting consumer demand for truly organic produce.
What Are Heirloom Seeds?
Heirloom seeds are traditional plant varieties that have been passed down through generations, prized for their genetic diversity and unique flavors in organic farming. Unlike certified organic seeds, heirloom seeds are open-pollinated, allowing farmers to save and replant seeds year after year without losing their desirable traits. These seeds contribute to biodiversity and resilience in organic agriculture, preserving heritage crops that are well-adapted to local environments.
Key Differences Between Organic and Heirloom Seeds
Certified organic seeds are produced without synthetic chemicals and follow strict USDA organic guidelines, ensuring they meet organic farming standards, while heirloom seeds are traditional varieties preserved for their genetic diversity and unique traits without necessarily meeting organic certification. Organic seeds often undergo rigorous testing for purity and germination rates, whereas heirloom seeds prioritize heritage and flavor continuity over certification. Choosing between the two depends on whether a farmer prioritizes organic compliance or genetic diversity and preservation of rare plant varieties.
Benefits of Certified Organic Seeds
Certified organic seeds ensure compliance with strict USDA organic standards, guaranteeing crops free from synthetic pesticides and GMOs, which enhances overall crop health and marketability. These seeds offer higher germination rates and greater resistance to diseases due to rigorous certification processes. Using certified organic seeds supports sustainable farming practices by promoting biodiversity and soil health essential for long-term productivity.
Advantages of Planting Heirloom Seeds
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and resilience, enhancing the adaptability of crops in organic farming systems. They preserve unique flavors, colors, and nutritional profiles that are often lost in hybrid or certified organic seeds. By saving heirloom seeds year after year, farmers reduce dependency on external seed suppliers, supporting sustainable and cost-effective organic cultivation.
Seed Purity and Genetic Diversity
Certified organic seeds guarantee seed purity through rigorous testing and adherence to strict organic standards, minimizing contamination from synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms. Heirloom seeds, prized for their genetic diversity, maintain unique traits passed down through generations, supporting resilient ecosystems and crop adaptability. Choosing between certified organic and heirloom seeds depends on the balance desired between assured purity and preserving genetic variation in organic farming systems.
Adaptability to Local Growing Conditions
Certified organic seeds are specifically bred and tested to meet organic standards, ensuring they thrive in certified organic soils with minimal synthetic inputs. Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and are often better adapted to local growing conditions due to their historical cultivation in specific regions. Selecting seeds with proven adaptability to local climate and soil increases plant resilience and optimizes yield in organic farming systems.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous testing to ensure high germination rates and resistance to pests, contributing to consistent crop yield and quality in organic farming systems. Heirloom seeds, valued for their genetic diversity and unique flavors, often produce crops with superior taste but may exhibit variable yields due to less uniformity and susceptibility to environmental stress. The choice between certified organic and heirloom seeds directly impacts the balance between maximizing yield efficiency and preserving desirable crop characteristics in sustainable agriculture.
Cost Considerations for Farmers
Certified organic seeds generally come at a higher price due to rigorous testing and certification processes ensuring compliance with organic standards. Heirloom seeds, while often less expensive and preserving genetic diversity, may lack organic certification, potentially increasing the risk of contamination or lower yield in strict organic systems. Farmers must weigh initial seed costs against long-term benefits such as soil health, pest resistance, and market demand for certified organic produce.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Organic Farming
Certified organic seeds guarantee compliance with strict organic standards, free from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms, ensuring purity for organic farming. Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and resilience, preserving traditional traits and often enhancing flavor and adaptability to local conditions. Selecting the right seeds for organic farming balances certification status with seed heritage to optimize crop health, sustainability, and yield quality.
Related Important Terms
Organic Seed Purity Standards
Certified organic seeds comply with strict Organic Seed Purity Standards ensuring no synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are present, supporting authentic organic farming practices. Heirloom seeds, while prized for genetic diversity and adaptability, may not always meet these purity standards unless specifically certified organic, potentially affecting organic certification.
Heirloom Genetic Diversity
Heirloom seeds offer unparalleled genetic diversity, preserving rare and regionally adapted plant traits crucial for resilient organic farming systems. Unlike certified organic seeds that prioritize uniformity and compliance, heirloom varieties contribute to biodiversity, enhancing crop adaptability and long-term sustainability.
Certified Organic Seed Traceability
Certified organic seeds ensure traceability through rigorous documentation and certification standards, enabling farmers to verify seed origin and compliance with organic regulations. Heirloom seeds, while valued for genetic diversity and heritage preservation, often lack formal traceability, posing challenges for strict organic certification and market transparency.
Open-Pollinated Seed Viability
Certified organic seeds ensure compliance with strict USDA organic standards, offering reliable germination rates and disease resistance, while heirloom seeds, known for their open-pollinated nature, maintain genetic diversity and adaptability through natural pollination processes. Open-pollinated seed viability in heirloom varieties supports sustainable organic farming by preserving traits like flavor and resilience, although certified organic seeds provide consistency and verified organic integrity crucial for commercial production.
Non-GMO Seed Certification
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous Non-GMO Seed Certification processes ensuring they are free from genetically modified organisms and comply with strict organic standards. Heirloom seeds, while prized for preserving genetic diversity and traditional traits, do not always come with Non-GMO certification, making certified organic seeds a more reliable choice for guaranteed GMO-free planting in organic farming.
Organic Seed Integrity Audit
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous Organic Seed Integrity Audits to ensure compliance with organic standards, preventing contamination from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. Heirloom seeds, while prized for genetic diversity and preservation of heritage varieties, may lack this formal certification, posing potential risks in maintaining organic integrity throughout cultivation.
Regenerative Organic Seed Sourcing
Certified organic seeds ensure compliance with strict organic standards, promoting soil health and biodiversity essential for regenerative organic farming systems. Heirloom seeds, valued for genetic diversity and adaptation to local conditions, complement regenerative practices by preserving resilience and fostering sustainable seed sourcing.
Heritage Seed Preservation
Certified organic seeds are rigorously tested for organic compliance and provide consistent performance for sustainable farming, while heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity essential for heritage seed preservation and maintaining plant resilience. Planting heirloom seeds supports biodiversity by preserving traditional varieties adapted to local environments, ensuring the survival of rare and culturally significant crops.
Disease-Resistant Organic Seed Strains
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous testing and certification to ensure disease resistance and compatibility with organic farming standards, providing growers with reliable, pathogen-free options. Heirloom seeds, while prized for genetic diversity and heritage traits, may lack standardized disease-resistant qualities, making certified organic seed strains preferable for managing crop health in organic cultivation.
Organic Seed Sovereignty
Certified organic seeds undergo rigorous inspection and meet strict USDA organic standards, ensuring they are free from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms, which supports sustainable organic farming practices. Heirloom seeds, often open-pollinated and preserved by local communities, play a crucial role in Organic Seed Sovereignty by maintaining genetic diversity and empowering farmers to save, exchange, and cultivate seeds adapted to their regional environments.
Certified organic seeds vs heirloom seeds for planting Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com