Compost tea and fish emulsion both offer nutrient-rich options for foliar feeding in organic farming, enhancing plant health and growth effectively. Compost tea provides beneficial microorganisms that improve soil structure and nutrient uptake, while fish emulsion supplies a quick boost of nitrogen and trace minerals essential for leaf development. Choosing between these depends on the specific nutrient needs and microbial benefits desired for the crops.
Table of Comparison
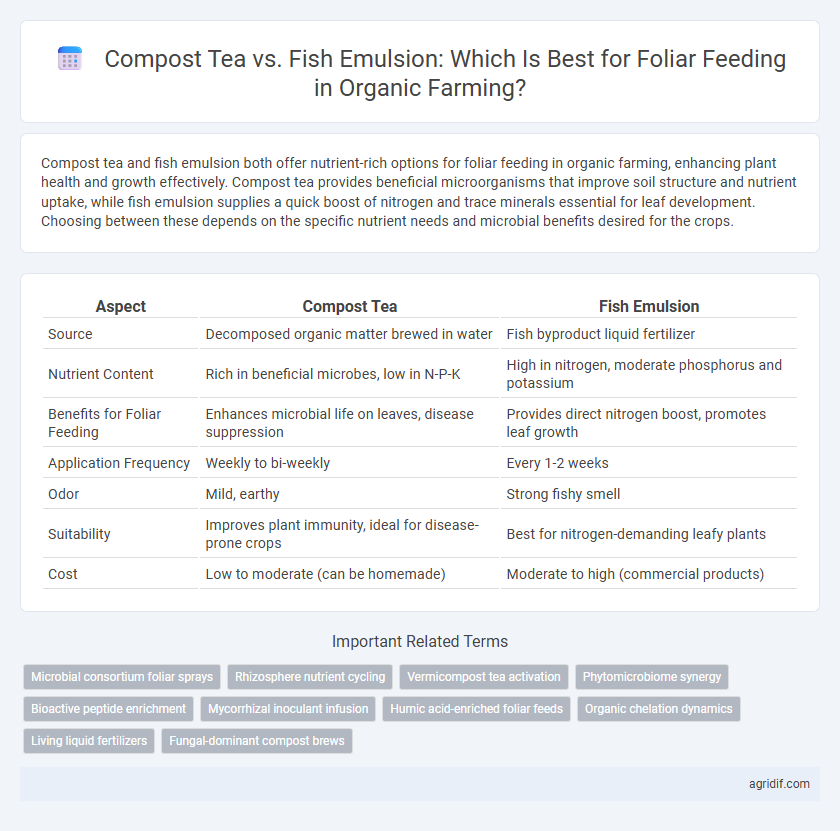
| Aspect | Compost Tea | Fish Emulsion |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Decomposed organic matter brewed in water | Fish byproduct liquid fertilizer |
| Nutrient Content | Rich in beneficial microbes, low in N-P-K | High in nitrogen, moderate phosphorus and potassium |
| Benefits for Foliar Feeding | Enhances microbial life on leaves, disease suppression | Provides direct nitrogen boost, promotes leaf growth |
| Application Frequency | Weekly to bi-weekly | Every 1-2 weeks |
| Odor | Mild, earthy | Strong fishy smell |
| Suitability | Improves plant immunity, ideal for disease-prone crops | Best for nitrogen-demanding leafy plants |
| Cost | Low to moderate (can be homemade) | Moderate to high (commercial products) |
Introduction to Foliar Feeding in Organic Farming
Foliar feeding in organic farming involves applying nutrient-rich solutions directly to plant leaves, enhancing nutrient uptake and promoting faster growth. Compost tea, a biological stimulant brewed from aerated compost, provides beneficial microbes and micronutrients that improve plant health and soil biology. Fish emulsion, derived from decomposed fish, delivers a rich source of nitrogen and trace minerals, making it effective for rapid nutrient supplementation in organic crops.
What is Compost Tea?
Compost tea is a liquid solution brewed by steeping compost in water, rich in beneficial microorganisms and nutrients that enhance plant health and soil vitality. It acts as a natural foliar feed, supplying plants with essential minerals and boosting their immune systems against pests and diseases. Unlike fish emulsion, compost tea provides a diverse microbial population that improves nutrient uptake and promotes sustainable soil ecology.
What is Fish Emulsion?
Fish emulsion is a nutrient-rich organic fertilizer derived from the byproducts of fish processing, containing high levels of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium essential for plant growth. It is commonly used in foliar feeding to rapidly supply plants with easily absorbed nutrients, promoting vigorous leaf and root development. Compared to compost tea, fish emulsion offers a more concentrated and immediately available source of nutrients, making it ideal for correcting specific nutrient deficiencies in organic farming.
Nutrient Composition: Compost Tea vs Fish Emulsion
Compost tea contains a balanced mix of micronutrients and beneficial microorganisms that enhance plant health and nutrient uptake during foliar feeding. Fish emulsion provides a rich source of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting rapid leaf growth and greening. Comparing nutrient composition, compost tea offers broader microbial diversity, while fish emulsion delivers higher primary macronutrient concentrations essential for immediate plant nutrition.
Application Methods: How to Use Each for Foliar Feeding
Compost tea for foliar feeding is applied as a diluted spray, typically using a fine mist to ensure even coverage on plant leaves, maximizing nutrient absorption and beneficial microbial contact. Fish emulsion requires dilution in water, usually at a 1:10 ratio, and is sprayed directly onto foliage to supply a rapid nutrient boost, particularly nitrogen. Both methods benefit from early morning or late afternoon application to reduce evaporation and enhance uptake efficiency.
Benefits of Compost Tea for Plants
Compost tea enhances plant growth by delivering a rich blend of beneficial microorganisms that improve nutrient uptake and disease resistance. It promotes a balanced soil microbiome, boosting plant immunity and increasing chlorophyll content for healthier foliage. Unlike fish emulsion, compost tea reduces the risk of nutrient burn and unpleasant odors while providing sustained foliar nourishment.
Benefits of Fish Emulsion for Plants
Fish emulsion is a nutrient-rich foliar feed that provides plants with an immediate boost of essential macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, promoting robust growth and vibrant foliage. Its organic origin contains micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and trace minerals that enhance plant immunity and resilience against pests and diseases. This natural fertilizer improves soil microbial activity, encouraging healthy root development and overall plant vitality in organic farming systems.
Potential Risks and Limitations
Compost tea may harbor harmful pathogens if not properly brewed and handled, posing risks of plant diseases and contamination during foliar feeding. Fish emulsion can cause leaf burn or odor issues due to its high nitrogen content and strong smell, with potential for attracting pests. Both require careful dilution and application timing to minimize risks and maximize nutrient absorption in organic farming practices.
Cost and Availability Comparison
Compost tea and fish emulsion differ significantly in cost, with compost tea generally being more affordable due to homemade production, while fish emulsion often comes at a higher price from commercial suppliers. Availability of compost tea depends on access to quality compost and brewing equipment, making it more accessible for small-scale farmers, whereas fish emulsion is widely available in agricultural supply stores, offering convenience for larger operations. Considering budget constraints and ease of access, organic farmers often choose compost tea for cost savings, while fish emulsion remains a popular option for its consistent nutrient content.
Choosing the Right Foliar Feed for Your Organic Farm
Compost tea and fish emulsion both serve as effective foliar feeds, with compost tea offering a rich diversity of beneficial microbes that enhance plant disease resistance and nutrient uptake, while fish emulsion provides a high nitrogen content promoting vigorous growth. Choosing the right foliar feed depends on your crop's specific nutrient requirements and soil microbial health, as compost tea supports soil ecology whereas fish emulsion delivers a quick nutrient boost. Regular application of compost tea improves overall soil fertility and plant resilience, making it ideal for long-term organic farm productivity.
Related Important Terms
Microbial consortium foliar sprays
Compost tea offers a diverse microbial consortium that enhances nutrient uptake and disease resistance in plants during foliar feeding, while fish emulsion primarily provides readily available nitrogen and trace minerals without the broad spectrum of beneficial microbes. Microbial consortium foliar sprays like compost tea can improve plant health by promoting beneficial microbial interactions on leaf surfaces, which fish emulsion lacks due to its nutrient-focused composition.
Rhizosphere nutrient cycling
Compost tea enhances rhizosphere nutrient cycling by introducing diverse microbial populations that break down organic matter and improve nutrient availability for foliar uptake, while fish emulsion provides a concentrated source of nitrogen and trace minerals directly absorbed by leaves. The microbial activity stimulated by compost tea supports long-term soil health, whereas fish emulsion offers immediate nutrient supply but lacks the biological complexity to sustain nutrient cycling in the rhizosphere.
Vermicompost tea activation
Vermicompost tea activation enhances nutrient bioavailability and microbial diversity, making it more effective than fish emulsion for foliar feeding in organic farming by improving plant nutrient uptake and disease resistance. Activated vermicompost tea provides a balanced supply of macro and micronutrients along with beneficial microorganisms, promoting healthier plant growth without the risk of phytotoxicity often associated with fish emulsion.
Phytomicrobiome synergy
Compost tea enhances foliar feeding by promoting a diverse and beneficial phytomicrobiome synergy that boosts plant immunity and nutrient uptake, whereas fish emulsion primarily provides immediate nitrogen-rich nutrients but lacks the microbial complexity to support long-term soil and leaf surface microbial communities. Leveraging compost tea in organic farming optimizes microbial interactions critical for plant health, outperforming fish emulsion's singular nutrient focus.
Bioactive peptide enrichment
Compost tea enhances foliar feeding by providing a rich source of bioactive peptides and beneficial microorganisms that promote nutrient absorption and plant immunity. Fish emulsion supplies a concentrated dose of nitrogen and bioactive peptides, improving chlorophyll synthesis and overall plant vigor in organic farming systems.
Mycorrhizal inoculant infusion
Compost tea enriched with mycorrhizal inoculants promotes symbiotic fungal networks on plant roots, enhancing nutrient uptake and disease resistance more effectively than fish emulsion for foliar feeding. Unlike fish emulsion, which provides quick nitrogen-rich nutrients, the mycorrhizal infusion in compost tea supports long-term soil health and plant vitality through microbial diversity.
Humic acid-enriched foliar feeds
Humic acid-enriched foliar feeds, derived from compost tea, enhance nutrient uptake and microbial activity more effectively than fish emulsion, promoting healthier plant growth and improved stress resistance. Compost tea provides a balanced profile of humic substances and beneficial microbes, whereas fish emulsion primarily supplies nitrogen with limited humic content, making compost tea superior for foliar applications targeting soil and plant vitality.
Organic chelation dynamics
Compost tea enhances organic chelation dynamics by supplying a diverse array of microbial populations that mobilize micronutrients for foliar uptake, improving nutrient bioavailability. Fish emulsion provides readily available nitrogen and trace minerals but offers less complex chelation, making compost tea more effective for sustained nutrient absorption in organic foliar feeding.
Living liquid fertilizers
Compost tea and fish emulsion are both potent living liquid fertilizers used in organic farming for foliar feeding, with compost tea rich in beneficial microbes that enhance soil and plant health, while fish emulsion provides a high concentration of readily available nitrogen and trace minerals. The microbial diversity in compost tea supports nutrient uptake and disease resistance, whereas fish emulsion acts as an immediate nutrient source, making their combined use effective for balanced plant nutrition and improved crop yields.
Fungal-dominant compost brews
Fungal-dominant compost brews provide a rich source of beneficial microbes and nutrients that enhance plant resistance to foliar diseases and improve nutrient uptake more effectively than fish emulsion. Unlike fish emulsion, which primarily supplies nitrogen and micronutrients, compost tea supports a balanced microbial ecosystem on leaf surfaces, promoting healthier plant growth and mitigating pathogen colonization.
Compost tea vs fish emulsion for foliar feeding Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com