Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and preserve traditional plant varieties, making them ideal for organic farming pet gardens due to their natural resilience and flavor. Hybrid seeds are bred for higher yields and disease resistance but may not produce true-to-type plants in subsequent generations, limiting seed saving practices. Choosing heirloom seeds supports sustainability and biodiversity, essential for maintaining healthy soil and ecosystem balance in organic pet gardening.
Table of Comparison
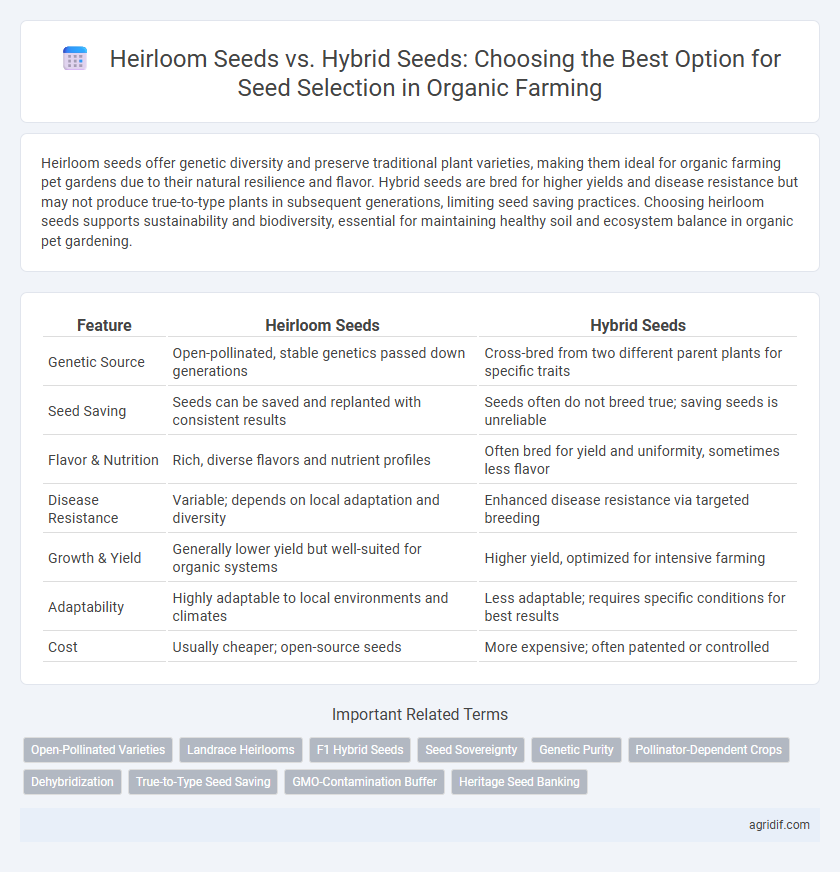
| Feature | Heirloom Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Source | Open-pollinated, stable genetics passed down generations | Cross-bred from two different parent plants for specific traits |
| Seed Saving | Seeds can be saved and replanted with consistent results | Seeds often do not breed true; saving seeds is unreliable |
| Flavor & Nutrition | Rich, diverse flavors and nutrient profiles | Often bred for yield and uniformity, sometimes less flavor |
| Disease Resistance | Variable; depends on local adaptation and diversity | Enhanced disease resistance via targeted breeding |
| Growth & Yield | Generally lower yield but well-suited for organic systems | Higher yield, optimized for intensive farming |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable to local environments and climates | Less adaptable; requires specific conditions for best results |
| Cost | Usually cheaper; open-source seeds | More expensive; often patented or controlled |
Introduction to Seed Types in Organic Farming
Heirloom seeds, known for their genetic diversity and preservation of traditional plant varieties, play a crucial role in organic farming by enhancing crop resilience and flavor profiles. Hybrid seeds, created through the controlled crossbreeding of parent plants, offer higher yields and uniformity but may lack the genetic stability needed for long-term organic sustainability. Understanding the differences between heirloom and hybrid seeds is essential for organic farmers aiming to optimize seed selection for biodiversity, soil health, and environmental impact.
Defining Heirloom Seeds: Characteristics and Origins
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties that have been passed down through generations, often for at least 50 years, preserving genetic diversity and unique traits. These seeds maintain their original characteristics, such as flavor, color, and growth habits, making them ideal for organic farming focused on natural biodiversity. Unlike hybrids, heirloom seeds originate from traditional agricultural practices without genetic modification or crossbreeding interventions.
Understanding Hybrid Seeds: Features and Development
Hybrid seeds are created through controlled cross-pollination of two genetically distinct parent plants, combining desirable traits such as disease resistance, higher yield, and uniform growth. These seeds often exhibit hybrid vigor (heterosis), resulting in stronger plants with improved performance under specific environmental conditions. Understanding the development process of hybrid seeds helps organic farmers select varieties optimized for resilience and productivity, although these seeds typically do not breed true in subsequent generations.
Genetic Diversity: Heirloom vs Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds preserve extensive genetic diversity due to their open-pollinated nature, allowing plants to adapt over generations to local environments and resist pests and diseases naturally. Hybrid seeds result from controlled crosses between specific parent plants, reducing genetic variability but enhancing uniformity, yield, and disease resistance. Farmers seeking sustainability and resilience in organic farming often prefer heirloom seeds for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem balance.
Adaptability to Local Conditions
Heirloom seeds possess strong adaptability to local conditions due to their open-pollinated nature and genetic diversity, making them ideal for organic farming in specific regions. Hybrid seeds often offer uniformity and higher yields but may lack resilience against local pests, diseases, and climate variations. Selecting heirloom seeds enhances sustainable organic practices by preserving regional plant traits and promoting ecological balance.
Yield and Performance Comparisons
Heirloom seeds offer rich genetic diversity and unique flavors but typically produce lower yields compared to hybrid seeds, which are bred for enhanced yield, disease resistance, and uniform performance. Hybrid seeds often perform better under varied environmental conditions, delivering consistent, robust harvests ideal for commercial organic farming. Organic farmers prioritize heirloom seeds for their adaptability and seed-saving potential despite hybrid seeds' superior yield advantages in large-scale production.
Seed Saving and Sustainability
Heirloom seeds support seed saving by producing plants that reliably reproduce true to type, preserving genetic diversity essential for sustainable organic farming. Hybrid seeds often yield higher initial productivity but do not breed true in subsequent generations, limiting farmers' ability to save seeds and increasing dependence on commercial seed suppliers. Choosing heirloom varieties enhances long-term sustainability by maintaining resilient, locally adapted crops and reducing input costs.
Flavor, Nutrition, and Crop Quality
Heirloom seeds offer superior flavor and nutrition due to their open-pollinated nature, preserving diverse genetic traits that enhance crop quality in organic farming. Hybrid seeds often prioritize yield and disease resistance but can compromise taste and nutrient density. Selecting heirloom seeds promotes rich flavors and higher nutrient content, aligning with organic farming goals of sustainability and food quality.
Cost and Accessibility for Organic Growers
Heirloom seeds generally cost more upfront but offer organic growers sustainable access to diverse, open-pollinated varieties that can be saved and replanted annually, reducing long-term expenses. Hybrid seeds often come at a lower initial price but require repeated purchases due to their sterile or inconsistent offspring, increasing costs over time for organic farmers. Accessibility to heirloom seeds is typically through specialized suppliers or seed exchanges, while hybrid seeds are widely available from commercial retailers, influencing choice based on grower priorities and budget.
Choosing the Right Seeds for Your Organic Farm
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and preserve traditional plant varieties essential for maintaining organic farm biodiversity, while hybrid seeds provide higher yields and disease resistance beneficial for commercial-scale production. Selecting the right seeds depends on farm goals: heirlooms support sustainability and unique flavors, hybrids enhance productivity and uniformity under organic management. Understanding seed origin, adaptability, and organic certification ensures compatibility with organic farming principles and long-term soil health.
Related Important Terms
Open-Pollinated Varieties
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties prized in organic farming for their genetic diversity, adaptability, and ability to produce true-to-type plants season after season without genetic modification. Hybrid seeds result from controlled cross-pollination to enhance specific traits but often lose their effectiveness if seeds are saved and replanted, making heirlooms preferable for sustainable seed saving and maintaining biodiversity in organic gardens.
Landrace Heirlooms
Landrace heirlooms offer superior genetic diversity and adaptability compared to hybrid seeds, promoting resilience in organic farming systems. Their open-pollinated nature preserves unique regional traits, enhancing soil health and ecosystem balance through natural seed saving and crop rotation practices.
F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds are produced by crossbreeding two genetically distinct parent plants, resulting in offspring with enhanced vigor, uniformity, and disease resistance compared to heirloom seeds. Although heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and traditional traits, F1 hybrids offer higher yield potential and improved stress tolerance, making them a preferred choice in organic farming for maximizing productivity.
Seed Sovereignty
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and empower farmers with seed sovereignty by allowing them to save and exchange seeds freely, unlike hybrid seeds, which are often patented and require purchase each season, limiting farmer control. Choosing heirloom varieties supports sustainable organic farming practices and strengthens local ecosystems through adaptation to regional conditions.
Genetic Purity
Heirloom seeds maintain genetic purity by preserving original plant traits through open-pollination, ensuring consistent seed quality and adaptability across generations. Hybrid seeds result from controlled crossbreeding, sacrificing genetic uniformity for specific traits, which can limit seed saving and long-term genetic stability.
Pollinator-Dependent Crops
Heirloom seeds, known for their genetic diversity and adaptability, are preferred for pollinator-dependent crops because they support biodiversity and enhance pollination efficiency. Hybrid seeds, while often higher-yielding, may reduce genetic variation and pollinator attraction, potentially impacting crop resilience in organic farming systems.
Dehybridization
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by enabling dehybridization, allowing farmers to save seeds that produce consistent traits over generations, unlike hybrid seeds that often lose desired characteristics when replanted. Dehybridization supports organic farming principles by fostering plant resilience and adaptability without reliance on synthetic inputs or repeated hybrid seed purchases.
True-to-Type Seed Saving
Heirloom seeds offer true-to-type seed saving, preserving genetic integrity and allowing farmers to harvest seeds that reliably produce plants identical to the parent, essential for maintaining biodiversity in organic farming. Hybrid seeds, while often higher yielding, do not reliably produce true-to-type offspring due to genetic segregation, making them less suitable for seed saving in organic systems.
GMO-Contamination Buffer
Heirloom seeds offer a natural genetic lineage free from GMO contamination, making them ideal for maintaining organic farming integrity and ensuring biodiversity. In contrast, hybrid seeds, often bred for yield and disease resistance, carry a higher risk of GMO contamination, necessitating larger buffer zones to prevent genetic drift and protect organic certification.
Heritage Seed Banking
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and traditional traits essential for heritage seed banking, ensuring resilience and authenticity in organic farming systems. Hybrid seeds, while offering improved yield and uniformity, often lack the genetic stability needed for long-term seed saving and maintaining heirloom biodiversity.
Heirloom Seeds vs Hybrid Seeds for Seed Selection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com