Heirloom varieties offer organic farmers seeds with deep genetic diversity and rich flavor profiles, preserving heritage traits that thrive in natural growing conditions without synthetic inputs. Hybrid varieties provide consistent yields and disease resistance, but may lack the resilience and unique characteristics favored in organic systems. Selecting heirloom seeds supports biodiversity and sustainable practices essential for long-term soil health in organic pet food cultivation.
Table of Comparison
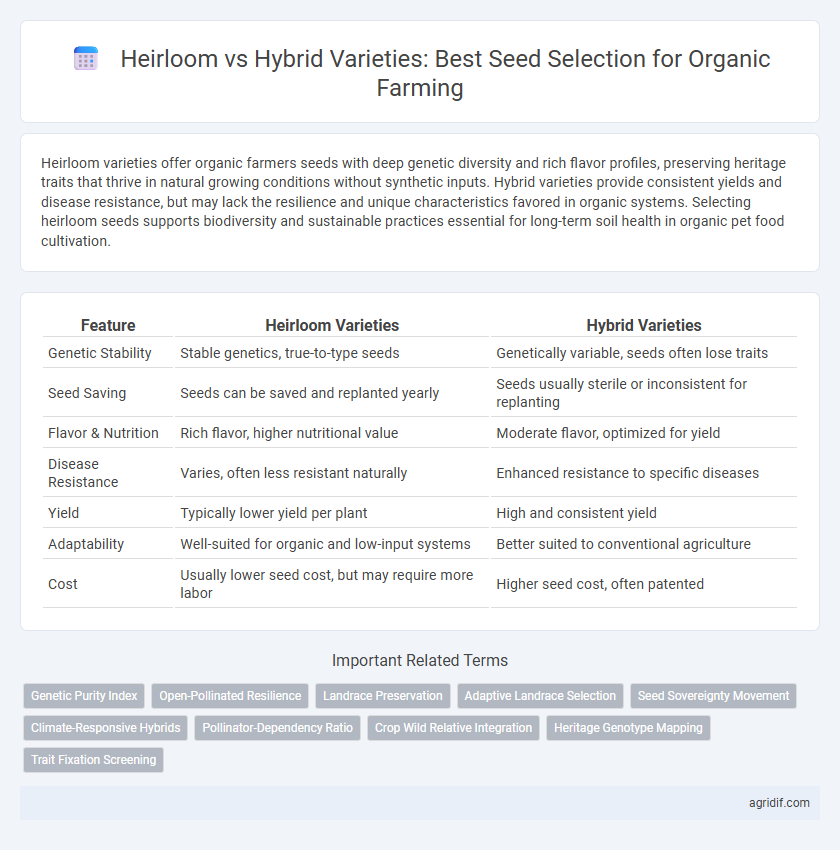
| Feature | Heirloom Varieties | Hybrid Varieties |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Stability | Stable genetics, true-to-type seeds | Genetically variable, seeds often lose traits |
| Seed Saving | Seeds can be saved and replanted yearly | Seeds usually sterile or inconsistent for replanting |
| Flavor & Nutrition | Rich flavor, higher nutritional value | Moderate flavor, optimized for yield |
| Disease Resistance | Varies, often less resistant naturally | Enhanced resistance to specific diseases |
| Yield | Typically lower yield per plant | High and consistent yield |
| Adaptability | Well-suited for organic and low-input systems | Better suited to conventional agriculture |
| Cost | Usually lower seed cost, but may require more labor | Higher seed cost, often patented |
Introduction to Heirloom and Hybrid Varieties
Heirloom seed varieties are traditional, open-pollinated plants passed down through generations, valued for their genetic diversity, flavor, and adaptability to local environmental conditions in organic farming. Hybrid seed varieties are created by crossbreeding two distinct parent plants to produce offspring with specific desired traits such as increased yield, disease resistance, and uniformity. Organic farmers often select heirloom seeds to preserve biodiversity and maintain natural genetics, while hybrids may be used selectively for their performance advantages under organic management.
Historical Significance of Heirloom Seeds
Heirloom seeds possess a rich historical significance, representing plant varieties passed down through generations with preservation of unique genetic traits and flavors. These seeds offer genetic diversity crucial for sustainable organic farming, in contrast to hybrid varieties bred primarily for uniformity and commercial yield. Cultivating heirloom plants supports biodiversity and helps maintain agricultural heritage while enhancing resilience against pests and environmental changes.
The Science Behind Hybrid Varieties
Hybrid varieties result from crossbreeding two distinct parent plants to combine desirable traits such as disease resistance, higher yield, and uniform growth. This genetic technique enhances vigor and adaptability but often sacrifices seed-saving viability, requiring farmers to purchase new seeds each season. Unlike heirloom varieties, hybrids rely on controlled pollination methods to maintain specific hybrid characteristics, backed by extensive scientific research in genetics and plant breeding.
Genetic Diversity in Seed Selection
Heirloom varieties preserve genetic diversity by maintaining unique traits passed down through generations, supporting resilience against pests and changing environmental conditions in organic farming. Hybrid varieties, created through controlled crossbreeding, often prioritize higher yields but lack the genetic variability found in heirlooms, potentially reducing adaptability. Selecting heirloom seeds in organic farming enhances biodiversity and strengthens ecosystem stability, essential for sustainable agricultural practices.
Flavor and Nutritional Differences
Heirloom varieties offer superior flavor and higher nutritional content due to their genetic diversity and natural adaptation over time, making them prized in organic farming for quality produce. Hybrid varieties, while often bred for yield and disease resistance, may sacrifice some flavor complexity and nutrient density compared to heirlooms. Selecting heirloom seeds supports organic principles by enhancing taste and nutrient profiles, aligning with consumer demand for natural and wholesome food.
Adaptability to Local Growing Conditions
Heirloom varieties exhibit superior adaptability to local growing conditions due to their long-term natural selection in specific environments, enhancing resilience to regional pests and climate variations. Hybrid varieties, while often engineered for higher yields and uniformity, may lack the genetic diversity needed to thrive under diverse or changing local conditions. Selecting heirloom seeds supports sustainable organic farming by promoting biodiversity and maintaining crop stability in specific agro-ecosystems.
Seed Saving and Sustainability Practices
Heirloom varieties retain genetic diversity and allow farmers to save seeds that reliably reproduce true-to-type plants, supporting long-term sustainability in organic farming. Hybrid varieties often fail to produce viable seeds for replanting, making seed saving impractical and increasing dependence on commercial seed suppliers. Prioritizing heirloom seeds promotes biodiversity, preserves unique plant traits, and aligns with sustainable organic practices by reducing external inputs and maintaining ecosystem resilience.
Pest and Disease Resistance Comparison
Heirloom varieties often exhibit unique genetic traits that provide diverse but sometimes limited pest and disease resistance compared to hybrids, which are bred specifically for enhanced resilience. Hybrid varieties tend to demonstrate stronger, targeted resistance to common pests and diseases due to controlled crossbreeding processes enhancing their defensive traits. Seed selection in organic farming requires balancing the natural genetic diversity of heirlooms with the superior, specific resistance profiles found in hybrid seeds to optimize crop health and yield.
Economic Considerations for Farmers
Heirloom varieties often demand higher market prices due to their unique flavors and heritage appeal, offering farmers enhanced profit margins despite lower yields. Hybrid varieties provide increased disease resistance and higher productivity, reducing input costs and improving overall economic efficiency on the farm. Selecting between heirloom and hybrid seeds requires balancing market niche opportunities against production cost savings for sustainable financial returns.
Choosing the Right Variety for Your Organic Farm
Heirloom varieties offer genetic diversity and superior flavor profiles, making them ideal for maintaining biodiversity and traditional taste in organic farming. Hybrid varieties provide higher yields and disease resistance, beneficial for maximizing productivity under organic practices. Selecting the right seed depends on balancing heritage traits and crop performance to suit specific organic farm conditions and market demands.
Related Important Terms
Genetic Purity Index
Heirloom varieties maintain a high Genetic Purity Index due to their stable, open-pollinated traits, ensuring true-to-type seeds generation after generation. In contrast, hybrid varieties often exhibit lower genetic purity because their seeds may segregate, resulting in inconsistent traits and reduced uniformity in subsequent plantings.
Open-Pollinated Resilience
Heirloom varieties, often open-pollinated, exhibit greater genetic diversity and resilience, making them ideal for organic farming systems aiming to maintain seed sovereignty and adapt to local environmental stresses. In contrast, hybrid varieties offer uniformity and higher short-term yields but lack the genetic stability and adaptability crucial for sustainable, resilient organic seed selection.
Landrace Preservation
Heirloom varieties play a crucial role in landrace preservation by maintaining genetic diversity and adapting locally to environmental conditions, unlike hybrid varieties which often prioritize uniformity and yield over genetic resilience. Preserving heirloom seeds ensures the continuation of region-specific traits essential for organic farming systems, supporting biodiversity and long-term agricultural sustainability.
Adaptive Landrace Selection
Heirloom varieties exhibit superior adaptability in organic farming through adaptive landrace selection, maintaining genetic diversity that enhances resilience to local pests and climatic conditions. Hybrid varieties often lack this intrinsic adaptability due to their uniform genetics, making heirloom seeds a strategic choice for sustainable, site-specific organic cultivation.
Seed Sovereignty Movement
Heirloom varieties preserve genetic diversity and cultural heritage within the Seed Sovereignty Movement by offering open-pollinated seeds that can be saved and replanted year after year, fostering farmer independence. Hybrid varieties, while often higher yielding, produce sterile seeds that undermine traditional seed-saving practices and threaten the autonomy central to organic farming communities.
Climate-Responsive Hybrids
Climate-responsive hybrid varieties in organic farming offer enhanced resilience to unpredictable weather patterns and diseases, ensuring consistent yields without synthetic inputs. Heirloom varieties, while valued for genetic diversity and flavor, often lack the adaptive traits necessary for thriving under rapidly changing climatic conditions.
Pollinator-Dependency Ratio
Heirloom varieties exhibit a higher pollinator-dependency ratio compared to hybrid varieties, promoting biodiversity by supporting native pollinators such as bees and butterflies in organic farming systems. Hybrid varieties, often bred for self-pollination or reduced pollinator reliance, may limit ecosystem services critical for sustainable seed selection and crop resilience.
Crop Wild Relative Integration
Heirloom varieties preserve genetic diversity crucial for integrating Crop Wild Relatives (CWR) into organic farming, enhancing resilience and adaptation to local environments. Hybrid varieties often lack this genetic variability, limiting successful CWR integration and reducing long-term sustainability in organic seed selection.
Heritage Genotype Mapping
Heirloom varieties, characterized by their stable genetic traits passed through generations, provide a rich source for heritage genotype mapping essential in organic farming seed selection. In contrast, hybrid varieties exhibit heterosis but lack the genetic consistency required for preserving biodiversity and adapting to organic cultivation systems.
Trait Fixation Screening
Heirloom varieties exhibit stable trait fixation through generations, preserving genetic diversity and adapting well to organic farming conditions, whereas hybrid varieties often require continuous seed purchase due to unstable trait segregation and inconsistent performance. Trait fixation screening in organic seed selection prioritizes heirloom seeds for their predictable phenotypic traits and resilience, supporting sustainable crop production without synthetic inputs.
Heirloom varieties vs hybrid varieties for seed selection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com