Deep litter systems in poultry farming offer a natural environment that promotes better foot health and allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors, enhancing overall welfare. Cage systems, while space-efficient and easier for waste management, often restrict movement and can lead to stress and physical deformities in birds. Choosing between deep litter and cage systems depends on balancing animal welfare with operational efficiency and space constraints.
Table of Comparison
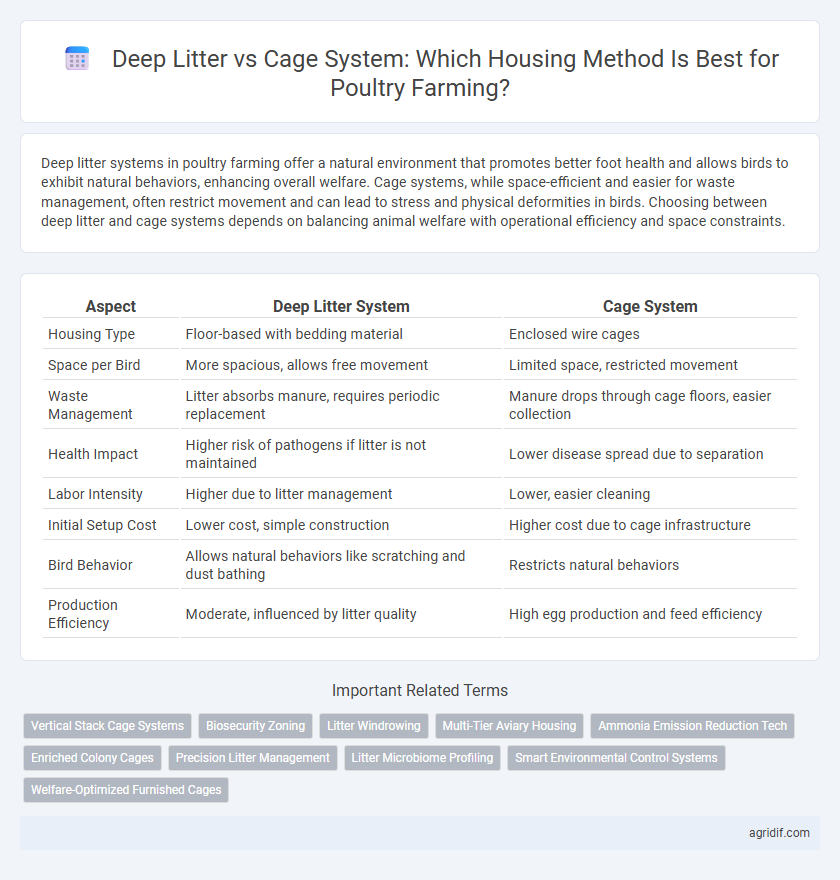
| Aspect | Deep Litter System | Cage System |
|---|---|---|
| Housing Type | Floor-based with bedding material | Enclosed wire cages |
| Space per Bird | More spacious, allows free movement | Limited space, restricted movement |
| Waste Management | Litter absorbs manure, requires periodic replacement | Manure drops through cage floors, easier collection |
| Health Impact | Higher risk of pathogens if litter is not maintained | Lower disease spread due to separation |
| Labor Intensity | Higher due to litter management | Lower, easier cleaning |
| Initial Setup Cost | Lower cost, simple construction | Higher cost due to cage infrastructure |
| Bird Behavior | Allows natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing | Restricts natural behaviors |
| Production Efficiency | Moderate, influenced by litter quality | High egg production and feed efficiency |
Overview of Deep Litter and Cage Systems
Deep litter system in poultry farming involves housing birds on a deep layer of absorbent material that accumulates over time, promoting natural behaviors like scratching and dust bathing while facilitating manure decomposition. Cage systems confine poultry in wire enclosures designed for efficient space utilization, easier disease control, and simplified management of feeding and waste but often limit movement and natural behaviors. Each housing method impacts bird welfare, environmental management, and production efficiency differently, influencing the choice based on farm goals and resources.
Key Differences Between Deep Litter and Cage Housing
Deep litter housing allows poultry to move freely on a bedding material that accumulates manure, promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress, while cage systems confine birds in individual or small groups, limiting movement and increasing ease of management. Deep litter systems require regular maintenance to control moisture and ammonia levels, whereas cage systems enable better control of hygiene and disease but may raise ethical concerns regarding animal welfare. The choice between these systems impacts welfare, productivity, and environmental management in poultry farming.
Advantages of Deep Litter System in Poultry Farming
The deep litter system in poultry farming offers advantages such as improved bird welfare through increased movement and natural behaviors, reducing stress levels. This housing method enhances biosecurity by allowing easier waste management and promoting beneficial microbial activity in the litter. Additionally, it reduces construction and maintenance costs compared to cage systems while supporting better thermal insulation and moisture control.
Benefits of Cage System in Poultry Production
The cage system in poultry production maximizes space utilization, enabling higher stocking densities and improved flock management. It reduces disease outbreaks by limiting bird contact with feces and minimizes cannibalism through controlled environments. Enhanced egg quality and cleaner eggs are also significant benefits due to better hygiene and reduced contamination risks.
Health and Welfare Considerations for Poultry
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors, enabling birds to forage and dust bathe, which enhances their overall welfare and reduces stress-related illnesses. Cage systems, while efficient in space utilization, often restrict movement, leading to increased risks of skeletal deformities and behavioral problems such as feather pecking. Health concerns in cage environments include higher incidences of foot lesions and respiratory issues due to limited ventilation and waste accumulation, making litter-based housing preferable for maintaining poultry health.
Cost Analysis: Deep Litter vs Cage System
The cost analysis of poultry housing reveals that the deep litter system generally involves lower initial investment compared to the cage system due to reduced infrastructure requirements. Operational expenses in the deep litter method include bedding materials and frequent cleaning, whereas the cage system demands higher maintenance costs linked to equipment and ventilation. Long-term profitability depends on factors such as flock density, labor costs, and biosecurity measures, with deep litter favoring small to medium-scale farms while cage systems suit large-scale commercial operations.
Impact on Egg Production and Quality
Deep litter housing in poultry farming promotes natural behaviors, leading to improved egg shell quality and higher egg weight due to reduced stress levels. Cage systems offer controlled environments that enhance feed efficiency and consistent egg production but may result in thinner shells and increased incidence of cracked eggs. Studies show that deep litter systems favor overall egg quality, while cage systems optimize quantity and uniformity in commercial egg production.
Environmental Considerations and Waste Management
Deep litter systems promote natural decomposition of poultry waste within bedding material, reducing ammonia emissions and enhancing soil fertility through composting. Cage systems concentrate waste beneath birds, facilitating easier manure collection but increasing risks of localized pollution and nutrient runoff if not properly managed. Efficient waste management in deep litter setups supports sustainable nutrient recycling, while cage systems demand rigorous environmental controls to mitigate air and water contamination.
Labor and Management Requirements
Deep litter systems in poultry farming demand higher labor input for regular bedding maintenance, litter turning, and moisture control to prevent disease, while cage systems require less frequent cleaning but necessitate meticulous monitoring of bird health and equipment functionality. Cage systems benefit from streamlined management due to easier access for feeding, watering, and egg collection, reducing manual labor but increasing reliance on mechanical systems and technical maintenance. Efficient labor deployment in deep litter housing often involves more physical work and vigilant environmental management, contrasting with the cage system's focus on technical oversight and system reliability.
Choosing the Best System for Your Poultry Farm
Deep litter systems promote natural behaviors by providing bedding materials that absorb moisture and reduce ammonia, enhancing bird welfare and potentially lowering overall maintenance costs. Cage systems offer higher stocking densities and easier health monitoring, leading to improved feed efficiency and disease control in large-scale operations. Selecting the best housing depends on balancing welfare priorities, farm size, cost constraints, and production goals to maximize productivity and sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Vertical Stack Cage Systems
Vertical stack cage systems in poultry farming optimize space utilization by housing multiple bird tiers within a compact footprint, enhancing biosecurity and ease of manure management. These systems increase bird density per square meter compared to deep litter houses, reducing labor costs but may limit natural behaviors and require careful ventilation control to maintain bird welfare.
Biosecurity Zoning
Deep litter systems promote improved biosecurity zoning by reducing direct contact between birds and contaminated surfaces through layered bedding that absorbs waste, minimizing pathogen spread. Cage systems allow for stricter zoning controls with isolated compartments limiting cross-contamination but require rigorous cleaning protocols to prevent disease buildup in confined spaces.
Litter Windrowing
Litter windrowing in deep litter poultry housing enhances manure management by promoting microbial decomposition, reducing ammonia emissions, and improving bird health compared to cage systems. This method maintains drier and more aerated bedding, which lowers pathogen load and supports sustainable waste recycling practices.
Multi-Tier Aviary Housing
Multi-tier aviary housing in poultry farming offers a dynamic alternative to traditional deep litter and cage systems by maximizing vertical space and enhancing bird welfare, allowing natural behaviors such as perching and nesting. This system improves manure management and reduces disease risk compared to deep litter floors, while providing better mobility and social interaction than conventional cages.
Ammonia Emission Reduction Tech
Deep litter systems reduce ammonia emissions by promoting microbial breakdown of poultry waste within the bedding, enhancing nitrogen retention and minimizing harmful gas release. In contrast, cage systems often require frequent manure removal and rely on ventilation technologies to control ammonia levels, but typically result in higher localized ammonia concentrations compared to deep litter environments.
Enriched Colony Cages
Enriched colony cages in poultry farming enhance bird welfare by providing perches, nesting areas, and litter, combining benefits of deep litter comfort with cage system efficiency. This housing method optimizes space utilization and improves behavioral expression compared to traditional cage systems, promoting higher productivity and health outcomes.
Precision Litter Management
Precision litter management in deep litter systems enhances ammonia control and bird welfare by maintaining optimal moisture levels and microbial balance, reducing respiratory issues common in poultry housing. Cage systems offer ease of waste removal but lack the environmental benefits of deep litter setups, which promote natural behaviors and improve manure nutrient recycling when managed with precision.
Litter Microbiome Profiling
Deep litter systems promote diverse litter microbiomes with beneficial bacterial communities that enhance poultry health and reduce pathogenic load, whereas cage systems exhibit limited microbial diversity due to restricted waste accumulation and reduced environmental exposure. Microbiome profiling reveals that the complex microbial ecosystems in deep litter housing contribute to improved nutrient cycling and pathogen resistance, highlighting its advantage over conventional cage systems in sustaining flock welfare.
Smart Environmental Control Systems
Smart Environmental Control Systems in poultry farming enhance both Deep Litter and Cage Systems by optimizing temperature, humidity, ventilation, and lighting to improve bird health and productivity. These systems leverage sensors and automated adjustments to maintain ideal conditions, reducing disease risk and energy consumption regardless of the housing method.
Welfare-Optimized Furnished Cages
Welfare-optimized furnished cages in poultry farming enhance bird comfort and natural behaviors by providing perches, nesting areas, and ample space, reducing stress and feather pecking compared to traditional cage systems. These enriched environments improve overall health and productivity, bridging welfare benefits of deep litter systems with the efficiency of caged housing.
Deep Litter vs Cage System for Housing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com