Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional varieties passed down through generations, offering resilience against pests and climate changes. GMOs often prioritize uniformity and specific traits, which can reduce genetic variation in crops. Choosing heirloom seeds supports biodiversity and safeguards adaptive traits crucial for sustainable agriculture.
Table of Comparison
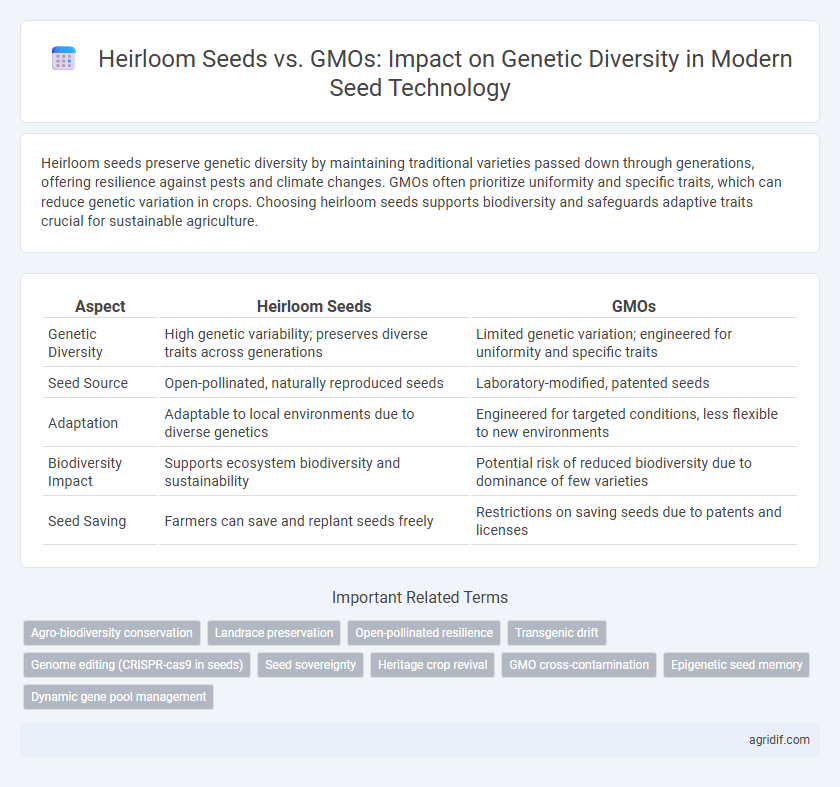
| Aspect | Heirloom Seeds | GMOs |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Diversity | High genetic variability; preserves diverse traits across generations | Limited genetic variation; engineered for uniformity and specific traits |
| Seed Source | Open-pollinated, naturally reproduced seeds | Laboratory-modified, patented seeds |
| Adaptation | Adaptable to local environments due to diverse genetics | Engineered for targeted conditions, less flexible to new environments |
| Biodiversity Impact | Supports ecosystem biodiversity and sustainability | Potential risk of reduced biodiversity due to dominance of few varieties |
| Seed Saving | Farmers can save and replant seeds freely | Restrictions on saving seeds due to patents and licenses |
Understanding Heirloom Seeds: Definition and Importance
Heirloom seeds are traditional plant varieties preserved and passed down through generations, known for their stable genetic traits and adaptability. Unlike GMOs, which are genetically modified for specific characteristics, heirloom seeds maintain natural genetic diversity crucial for ecological resilience and food security. Preserving heirloom seeds supports biodiversity, promotes sustainable agriculture, and safeguards unique flavors and cultural heritage.
What Are GMOs? Overview and Application in Agriculture
GMOs, or genetically modified organisms, involve altering an organism's DNA using biotechnology to introduce specific traits such as pest resistance or increased yield. In agriculture, GMOs are engineered to enhance crop productivity, improve nutritional content, and reduce dependency on chemical pesticides. This technology contrasts with heirloom seeds, which preserve natural genetic diversity by maintaining traditional, non-modified seed varieties through open-pollination and seed saving practices.
Genetic Diversity: Why It Matters in Crop Production
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining a wide array of unique traits and adaptations critical for resilience against pests, diseases, and climate change. Unlike GMOs, which often focus on uniformity and specific engineered traits, heirlooms contribute to a broader genetic pool essential for sustaining crop health and long-term food security. Genetic diversity in crop production supports ecosystem stability, enhances soil health, and ensures adaptability in evolving environmental conditions.
Heirloom Seeds and Their Role in Preserving Biodiversity
Heirloom seeds are vital for preserving genetic diversity as they represent traditional, open-pollinated plant varieties passed down through generations without genetic modification. These seeds contribute to biodiversity by maintaining unique traits adapted to specific local environments, enhancing resilience to pests, diseases, and climate variability. Unlike GMOs, heirloom seeds foster ecological balance and sustain agricultural heritage, supporting sustainable farming practices worldwide.
GMOs and Genetic Uniformity: Risks and Rewards
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) contribute to genetic uniformity by introducing specific traits across large seed populations, enhancing crop yield and pest resistance. This uniformity reduces genetic diversity, increasing vulnerability to pests, diseases, and environmental changes, which poses significant agricultural risks. However, GMOs offer rewards such as improved food security and reduced chemical use, balancing the challenges of genetic uniformity in seed technology.
Comparing Genetic Variation in Heirloom and GMO Crops
Heirloom seeds exhibit greater genetic variation compared to GMO crops, which are engineered for uniformity and specific traits. This enhanced genetic diversity in heirlooms contributes to increased resilience against pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. In contrast, GMO crops often have a narrow genetic base, potentially limiting adaptability in changing climates.
Impact of Heirloom Seed Saving on Future Generations
Heirloom seed saving preserves genetic diversity by maintaining a broad spectrum of plant traits that GMOs often lack due to their uniformity. This practice enhances resilience in future crops against environmental changes and diseases, ensuring sustainable agricultural ecosystems. Prioritizing heirloom seeds fosters adaptation and food security for generations to come.
GMOs and the Loss of Traditional Crop Varieties
GMOs often dominate agricultural production by prioritizing uniform traits like pest resistance, leading to the decline of heirloom seeds and traditional crop varieties. This shift reduces genetic diversity, weakening resilience to pests, diseases, and climate change. Preserving heirloom seeds is crucial for maintaining a broad genetic pool essential for sustainable agriculture and food security.
Sustainable Agriculture: Heirloom Seeds vs GMO Approaches
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional, open-pollinated varieties that adapt naturally to local environments, enhancing resilience and sustainability in agriculture. GMOs, engineered with specific traits, offer uniformity and high yields but may reduce genetic diversity, posing risks to ecosystem stability. Sustainable agriculture benefits from integrating heirloom seeds to promote biodiversity while using GMO innovations selectively for targeted improvements in crop resilience.
Policy and Regulation: Protecting Genetic Diversity in Seed Systems
Policy frameworks play a critical role in preserving genetic diversity by promoting the use of heirloom seeds and imposing strict regulations on genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Many countries implement seed laws that prioritize conserving traditional varieties, supporting farmers' rights to save, use, and exchange heirloom seeds without legal restrictions. Regulatory agencies also enforce biosafety protocols to assess GMO impacts, ensuring the protection of biodiversity within seed systems while balancing innovation and ecological sustainability.
Related Important Terms
Agro-biodiversity conservation
Heirloom seeds play a crucial role in agro-biodiversity conservation by preserving diverse genetic traits that are often lost in genetically modified organisms (GMOs), which typically emphasize uniformity and high yield. Maintaining heirloom seed varieties ensures the survival of unique plant genetics essential for resilient ecosystems and sustainable agriculture.
Landrace preservation
Heirloom seeds play a crucial role in preserving landrace genetic diversity by maintaining traditional, locally adapted varieties that harbor unique traits lost in genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Unlike GMOs, which often prioritize uniformity and specific engineered traits, heirloom seeds support resilient agroecosystems through diverse gene pools essential for long-term food security and climate adaptability.
Open-pollinated resilience
Heirloom seeds, being open-pollinated, promote genetic diversity and resilience by allowing natural selection to enhance adaptation to local environments, unlike GMOs which often rely on uniform genetic modifications. This open-pollinated nature of heirloom seeds supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining diverse gene pools essential for resistance to pests, diseases, and climate variability.
Transgenic drift
Heirloom seeds maintain genetic diversity through open pollination and stable traits passed down generations, minimizing the risk of transgenic drift. In contrast, GMOs carry transgenic traits that can unintentionally spread via cross-pollination, potentially contaminating heirloom and wild plant populations and reducing overall biodiversity.
Genome editing (CRISPR-cas9 in seeds)
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity through traditional breeding and open-pollination, maintaining unique traits across generations without genetic modification. Genome editing technologies like CRISPR-Cas9 enable precise, targeted alterations in seed genomes, offering potential to enhance crop resilience and yield while raising debates about biodiversity impacts compared to non-GMO heirloom varieties.
Seed sovereignty
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining unique, non-hybridized traits passed down through generations, supporting seed sovereignty and local agricultural resilience. In contrast, GMOs often involve patented genetics controlled by corporations, limiting farmers' ability to save and exchange seeds, thereby reducing genetic variety and sovereignty.
Heritage crop revival
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining open-pollinated, non-hybridized varieties that sustain unique traits lost in commercial farming, crucial for heritage crop revival and ecosystem resilience. Unlike GMOs, which introduce specific engineered traits, heirlooms support a broad gene pool that enhances adaptability to changing climates and protects agricultural biodiversity.
GMO cross-contamination
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity through natural pollination and open-pollination practices, maintaining unique traits passed down for generations. GMO cross-contamination threatens this diversity by introducing modified genes into heirloom varieties, potentially compromising their purity and resilience.
Epigenetic seed memory
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity through natural selection and epigenetic seed memory, enabling plants to adapt to local environmental stresses over generations without genetic modification. In contrast, GMOs often rely on inserted genes that may reduce epigenetic variation, potentially limiting the adaptive resilience inherent in heirloom varieties.
Dynamic gene pool management
Heirloom seeds preserve dynamic gene pool management by maintaining diverse, open-pollinated genetics, ensuring resilience against environmental changes and pests. GMOs often rely on uniform traits, which can limit genetic variability and reduce adaptability within agricultural ecosystems.
Heirloom Seeds vs GMOs for Genetic Diversity Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com