Certified seed undergoes rigorous quality control and meets strict standards for genetic purity and germination, ensuring reliable crop performance. Foundation seed serves as the initial source in seed multiplication, produced under controlled conditions to maintain genetic identity and provide high-quality stock for subsequent seed classes. Using certified seed in seed multiplication guarantees consistent yields and disease resistance, while foundation seed ensures the preservation of superior traits from the breeder's original variety.
Table of Comparison
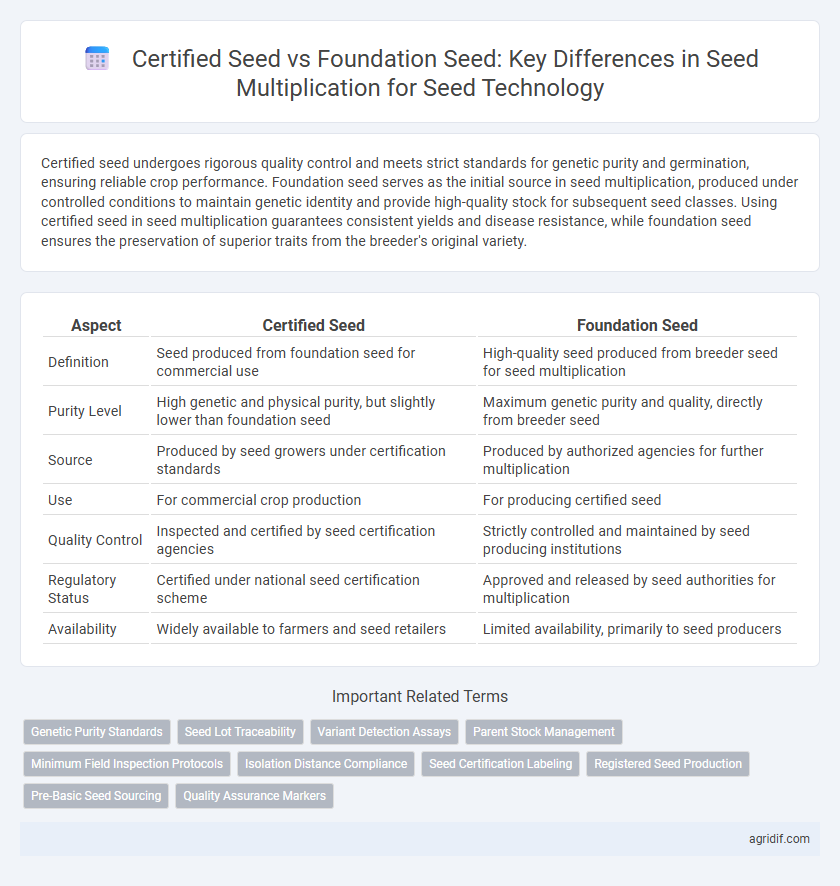
| Aspect | Certified Seed | Foundation Seed |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Seed produced from foundation seed for commercial use | High-quality seed produced from breeder seed for seed multiplication |
| Purity Level | High genetic and physical purity, but slightly lower than foundation seed | Maximum genetic purity and quality, directly from breeder seed |
| Source | Produced by seed growers under certification standards | Produced by authorized agencies for further multiplication |
| Use | For commercial crop production | For producing certified seed |
| Quality Control | Inspected and certified by seed certification agencies | Strictly controlled and maintained by seed producing institutions |
| Regulatory Status | Certified under national seed certification scheme | Approved and released by seed authorities for multiplication |
| Availability | Widely available to farmers and seed retailers | Limited availability, primarily to seed producers |
Defining Certified Seed and Foundation Seed
Foundation seed represents genetically pure, high-quality seed produced under strict conditions and serves as the initial source for certified seed production. Certified seed is derived from foundation seed through controlled multiplication processes, ensuring high genetic purity, germination rate, and seed health for commercial planting. The distinction lies in foundation seed's role as the primary registered seed, while certified seed is the subsequent generation used widely by farmers for crop production.
Importance of Seed Classes in Agriculture
Certified seed maintains genetic purity and high germination rates essential for consistent crop performance, while foundation seed serves as the primary source for producing certified seed, ensuring reliability in seed multiplication. The importance of seed classes lies in preserving genetic integrity and enhancing yield potential, which directly impacts food security and farmer income. Utilizing a structured seed production system from foundation to certified seed supports sustainable agricultural practices and quality seed distribution.
Genetic Purity: Certified vs Foundation Seed
Foundation seed maintains the highest genetic purity as it is directly derived from breeder seed under strict isolation and rigorous inspections, serving as the primary source for certified seed production. Certified seed, produced from foundation seed, ensures good genetic purity but may exhibit slight genetic variability due to the larger-scale multiplication process and environmental influences. Maintaining genetic purity is critical for preserving seed quality, crop uniformity, and yield potential throughout seed multiplication stages.
Seed Multiplication Process Overview
Certified seed undergoes strict quality control measures to ensure genetic purity and high germination rates, making it ideal for large-scale seed multiplication. Foundation seed serves as the primary source in the seed multiplication process, characterized by the highest genetic purity and is maintained under controlled conditions to produce certified seeds. This hierarchical multiplication system guarantees improved seed quality and uniformity throughout the production cycle.
Certification Standards for Foundation and Certified Seeds
Certified seeds undergo rigorous testing to meet strict Quality Assurance Standards, ensuring genetic purity, germination rate, and freedom from disease, as mandated by national seed certification agencies. Foundation seeds, produced from breeder seeds, serve as the primary source for Certified seed multiplication and must comply with higher genetic purity and seed health standards to maintain the integrity of subsequent seed generations. Certification standards for both seed classes involve field inspections, laboratory testing, and traceability protocols to guarantee seed quality, uniformity, and compliance with regulatory frameworks essential for successful seed multiplication.
Role of Foundation Seed in Seed Production Chain
Foundation seed serves as the initial high-quality genetic source in the seed production chain, ensuring genetic purity and uniformity for subsequent multiplication stages. It acts as a bridge between breeder seed and certified seed, maintaining genetic integrity while increasing seed quantity. By providing a reliable base, foundation seed supports the production of certified seed that farmers ultimately use for crop cultivation.
Advantages of Using Certified Seed
Certified seed offers enhanced genetic purity and higher germination rates compared to foundation seed, ensuring consistent crop performance. It undergoes rigorous quality control and disease testing, reducing risks of contamination and crop failure. Farmers benefit from improved yield potential and marketability by using certified seed in seed multiplication processes.
Quality Assurance Measures in Seed Multiplication
Certified seed undergoes rigorous field inspections and laboratory testing to ensure genetic purity, germination rate, and absence of seed-borne diseases, making it suitable for commercial crop production. Foundation seed serves as the primary source for producing certified seed, with stringent quality assurance protocols including controlled sourcing, isolation distances, and pedigree verification to maintain genetic integrity. High standards in both certified and foundation seed production guarantee seed vigor, uniformity, and compliance with regulatory seed certification schemes, essential for successful seed multiplication.
Seed Replacement Rate: Foundation vs Certified Seed
Certified seed ensures high genetic purity and germination rates, playing a crucial role in maintaining crop quality during seed multiplication. Foundation seed serves as the original, genetically stable source from which certified seed is produced, impacting seed replacement rates by sustaining a reliable supply of high-quality planting material. Seed Replacement Rate is typically higher with certified seed compared to foundation seed, as farmers prefer certified seed for improved yield and disease resistance in successive planting cycles.
Economic Impact on Farmers: Certified vs Foundation Seed
Certified seed offers farmers higher genetic purity and germination rates than foundation seed, directly increasing crop yield and quality, which enhances farm income. Foundation seed, being the initial seed class, is typically reserved for producing certified seed and incurs limited direct economic benefit to farmers due to its restricted availability and higher cost. Transitioning from foundation to certified seed empowers farmers with reliable, disease-free planting materials, substantially improving return on investment and promoting sustainable agricultural productivity.
Related Important Terms
Genetic Purity Standards
Certified seed undergoes rigorous inspections and meets stringent genetic purity standards to ensure true-to-type characteristics essential for consistent crop performance. Foundation seed, produced under controlled conditions with stricter genetic purity criteria, serves as the primary source for producing certified seed in the seed multiplication chain.
Seed Lot Traceability
Certified seed undergoes rigorous quality control and is tracked through a documented seed lot traceability system ensuring genetic purity and authenticity for commercial seed multiplication. Foundation seed serves as the initial breeder-approved seed source with strict traceability protocols to maintain genetic identity before scaling up to certified seed production.
Variant Detection Assays
Certified seed undergoes rigorous quality checks including variant detection assays to ensure genetic purity and performance consistency, whereas foundation seed serves as the initial high-quality genetic source from which certified seed is multiplied using precise molecular markers. Variant detection assays in seed multiplication help identify unintended mutations or off-types, safeguarding the genetic integrity from foundation seed to certified seed in the seed production chain.
Parent Stock Management
Certified seed is produced from foundation seed, ensuring genetic purity and high quality for commercial planting, while foundation seed acts as the primary parent stock managed under strict protocols to maintain genetic identity and vigor. Effective parent stock management in foundation seed involves rigorous isolation, controlled pollination, and regular field inspections to prevent contamination and safeguard seed lineage throughout seed multiplication stages.
Minimum Field Inspection Protocols
Certified seed undergoes rigorous minimum field inspection protocols including isolation distances, disease monitoring, and genetic purity assessments to ensure high-quality seed multiplication. Foundation seed is subject to even stricter field inspections with enhanced criteria for varietal purity, pest resistance, and uniformity to maintain the genetic integrity critical for producing certified seed.
Isolation Distance Compliance
Certified seed requires strict isolation distance compliance to prevent genetic contamination and maintain varietal purity during seed multiplication, typically exceeding 20 meters depending on crop species. Foundation seed demands even greater isolation distances, often double that of certified seed, to ensure maximal genetic fidelity for subsequent seed production stages and uphold certification standards.
Seed Certification Labeling
Certified seed undergoes rigorous testing and meets strict quality standards, ensuring genetic purity, germination rate, and freedom from pests and diseases, which is verified through official Seed Certification Labeling. Foundation seed serves as the genetically pure source for producing certified seed and carries distinct labeling that guarantees its origin and compliance with seed production protocols.
Registered Seed Production
Certified seed ensures high genetic purity and quality, meeting strict standards for germination, purity, and disease resistance, making it ideal for commercial planting. Foundation seed serves as the initial source with verified genetic identity and purity, from which registered seed is produced during the intermediate stage of registered seed production for large-scale multiplication.
Pre-Basic Seed Sourcing
Certified seed offers high genetic purity and quality assurance for large-scale crop production, while foundation seed serves as the critical pre-basic seed source ensuring genetic integrity and uniformity before certified seed multiplication. Effective pre-basic seed sourcing from foundation seed enables consistent seed multiplication by maintaining varietal identity and minimizing genetic variation.
Quality Assurance Markers
Certified seed undergoes rigorous quality assurance markers including genetic purity tests, physical purity assessments, and germination rate evaluations to ensure high seed quality for farmers. Foundation seed serves as the genetically stable source, meeting strict quality parameters such as varietal conformity and health status, providing the essential base for reliable seed multiplication programs.
Certified seed vs Foundation seed for seed multiplication Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com