Mechanical planters for rice transplantation enhance precision and efficiency by ensuring uniform seed placement and optimal spacing, reducing labor intensity compared to manual sowing methods. Manual sowing, while cost-effective for small-scale farming, often results in irregular seed distribution and higher labor demands, impacting crop uniformity and yield. Adopting mechanical planters improves overall plant health and productivity by facilitating timely and consistent rice transplantation.
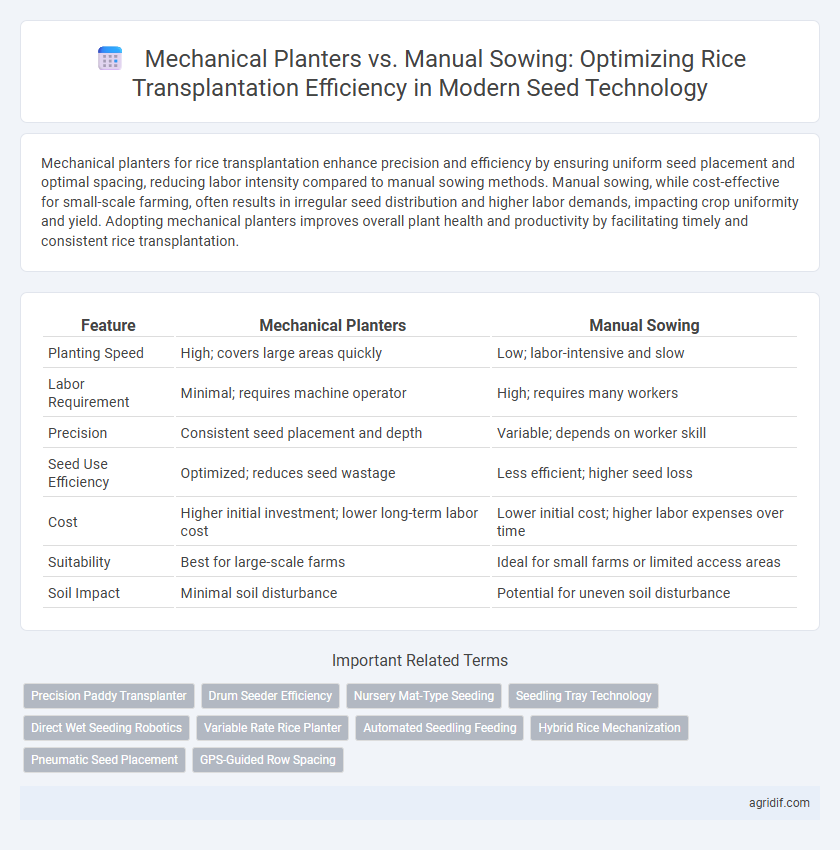
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mechanical Planters | Manual Sowing |
|---|---|---|
| Planting Speed | High; covers large areas quickly | Low; labor-intensive and slow |
| Labor Requirement | Minimal; requires machine operator | High; requires many workers |
| Precision | Consistent seed placement and depth | Variable; depends on worker skill |
| Seed Use Efficiency | Optimized; reduces seed wastage | Less efficient; higher seed loss |
| Cost | Higher initial investment; lower long-term labor cost | Lower initial cost; higher labor expenses over time |
| Suitability | Best for large-scale farms | Ideal for small farms or limited access areas |
| Soil Impact | Minimal soil disturbance | Potential for uneven soil disturbance |
Introduction to Rice Transplantation Methods
Rice transplantation methods include mechanical planters and manual sowing, each with distinct advantages affecting crop efficiency. Mechanical planters offer uniform seedling placement, enhanced planting speed, and reduced labor costs, contributing to higher productivity. Manual sowing relies on skilled labor for precise seedling handling, allowing adaptation to varied field conditions but requires more time and effort.
Overview of Mechanical Planters in Rice Cultivation
Mechanical planters in rice cultivation offer precise seed placement and uniform spacing, significantly enhancing crop establishment compared to manual sowing. These machines increase planting efficiency by reducing labor costs and time, while ensuring consistent seed depth and improving germination rates. Adoption of mechanical planters contributes to higher productivity and better crop management in large-scale rice farming operations.
Manual Sowing Techniques for Rice Fields
Manual sowing techniques for rice fields involve precise hand broadcasting or line sowing methods that enhance seed placement and germination rates. Farmers often use tools like seed drills or dibblers to maintain optimal spacing and depth, improving seedling establishment and uniform crop growth. This approach supports better weed control and reduces seed wastage compared to traditional random scattering methods.
Comparative Efficiency: Mechanical vs. Manual Rice Planting
Mechanical planters significantly enhance rice transplantation efficiency by enabling faster seedling placement with consistent depth and spacing, reducing labor intensity and time requirements. Manual sowing depends heavily on skilled labor, which can lead to variability in seedling placement and increased transplanting duration. Consequently, mechanical planters increase operational productivity and uniform crop establishment, optimizing resource utilization in rice cultivation.
Labor and Time Requirements for Each Sowing Method
Mechanical planters significantly reduce labor intensity and time required for rice transplantation by automating seed placement with precision, enabling faster field coverage compared to manual sowing. Manual sowing demands extensive labor input and prolonged periods to complete, often leading to increased human fatigue and inconsistent seed spacing. Utilizing mechanical planters enhances efficiency, decreases labor costs, and accelerates the transplantation process in rice cultivation.
Seed Rate and Uniformity in Plant Distribution
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation significantly reduce seed rate by precisely placing seedlings at optimal spacing, resulting in uniform plant distribution and enhanced crop efficiency. Manual sowing often leads to irregular spacing and higher seed rates due to inconsistent seed placement, which can cause competition among plants and lower yields. Improved uniformity via mechanical planting optimizes resource use, reduces seed wastage, and supports better growth conditions compared to traditional manual methods.
Impact on Crop Yield and Plant Health
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation increase crop yield by ensuring uniform seed spacing and optimal planting depth, promoting healthier root development and enhanced nutrient uptake. Manual sowing often results in uneven seed distribution, causing competition among seedlings and reducing overall plant vigor. Consistent mechanized planting reduces transplant shock and supports robust crop establishment, leading to higher productivity and better disease resistance.
Cost Analysis: Machinery Investment vs. Manual Labor
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation require significant upfront machinery investment, often costing thousands of dollars for equipment purchase and maintenance, but reduce labor dependency and increase efficiency. Manual sowing incurs lower initial costs but demands higher ongoing labor expenses, which can escalate in regions with rising wages or labor shortages. Cost analysis favors mechanical planters in long-term usage due to labor savings and increased planting speed, while manual sowing may be preferable for small-scale or budget-constrained farmers.
Environmental and Soil Considerations
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation reduce soil disturbance and minimize water usage compared to manual sowing, promoting better soil structure and reducing erosion risks. Automated machinery ensures uniform seed placement, enhancing germination rates and optimizing nutrient uptake while decreasing labor intensity. Manual sowing, although flexible in small plots, often leads to uneven seed distribution and increased soil compaction, which can negatively impact soil health and environmental sustainability.
Future Trends in Rice Transplantation Technology
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation are advancing with precision seed placement and automated depth control, enhancing planting uniformity and reducing labor dependency compared to manual sowing. Emerging technologies integrate AI and IoT sensors to optimize seed spacing and environmental monitoring, leading to higher yields and resource efficiency. Future trends emphasize robotic systems and sustainable machinery designed to minimize soil compaction and energy consumption in rice cultivation.
Related Important Terms
Precision Paddy Transplanter
Precision paddy transplanters significantly enhance planting accuracy and uniformity compared to manual sowing, ensuring optimal seed spacing and depth for improved crop establishment. Mechanical planters reduce labor costs and time, increase planting efficiency, and support higher yields by minimizing human error during rice transplantation.
Drum Seeder Efficiency
Drum seeders increase rice transplantation efficiency by delivering uniform seed distribution and precise depth control, reducing labor intensity compared to manual sowing. Their mechanical operation enhances seed placement accuracy and crop establishment, leading to higher yield potential and reduced seed wastage.
Nursery Mat-Type Seeding
Mechanical planters for rice transplantation using nursery mat-type seeding enhance precision and uniformity, leading to higher plant density and reduced labor costs compared to manual sowing. This technology optimizes seedling establishment, improves field efficiency, and supports better crop management practices.
Seedling Tray Technology
Mechanical planters using seedling tray technology enhance rice transplantation efficiency by ensuring uniform seedling spacing and depth, improving crop establishment and yield. Compared to manual sowing, mechanical planters reduce labor costs and transplanting time while minimizing seedling damage and promoting better root development.
Direct Wet Seeding Robotics
Direct wet seeding robotics for rice transplantation significantly enhances precision and efficiency compared to mechanical planters and manual sowing by automating seed placement in flooded fields with uniform depth control. This advanced technology reduces labor costs, minimizes seed wastage, and improves crop establishment rates, resulting in higher yields and sustainable resource management.
Variable Rate Rice Planter
Variable rate rice planters optimize seed distribution by adjusting seed placement and density according to soil variability, enhancing crop uniformity and yield compared to traditional manual sowing. Mechanical planters reduce labor costs and improve planting efficiency while ensuring precise seed depth and spacing, critical for maximizing rice transplant success.
Automated Seedling Feeding
Mechanical planters equipped with automated seedling feeding systems enhance precision and uniformity in rice transplantation, significantly reducing labor costs and increasing planting speed compared to manual sowing. These automated systems optimize seedling handling and placement, leading to improved crop establishment and higher yields.
Hybrid Rice Mechanization
Hybrid rice mechanization significantly enhances planting efficiency and crop uniformity compared to manual sowing, reducing labor costs and transplanting time by up to 50%. Mechanical planters ensure precise seed placement and optimal plant density, promoting higher yields and better resource utilization in hybrid rice cultivation.
Pneumatic Seed Placement
Mechanical planters equipped with pneumatic seed placement technology ensure precise and uniform rice seed distribution, significantly enhancing germination rates and crop yields compared to manual sowing methods. This technology reduces labor intensity, minimizes seed wastage, and promotes optimal seed-to-soil contact, leading to better stand establishment and overall field productivity in rice transplantation.
GPS-Guided Row Spacing
Mechanical planters equipped with GPS-guided row spacing significantly enhance planting precision and uniformity in rice transplantation, leading to optimized crop density and improved yield potential. In contrast, manual sowing often results in uneven spacing and inconsistent plant establishment, reducing overall field efficiency and increasing labor costs.
Mechanical Planters vs Manual Sowing for Rice Transplantation Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com