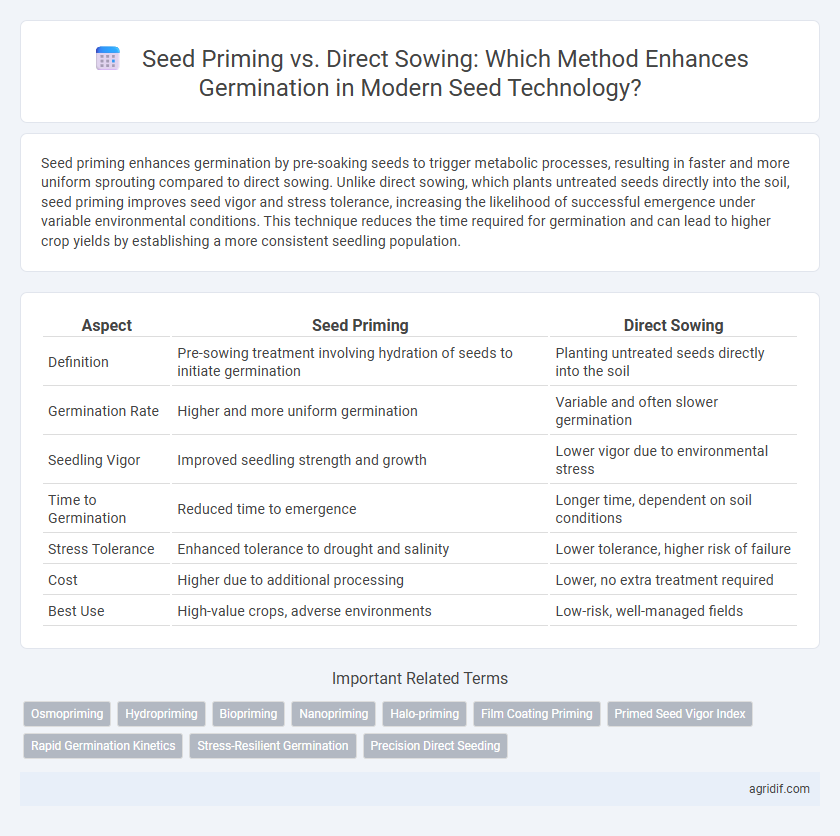
Seed priming enhances germination by pre-soaking seeds to trigger metabolic processes, resulting in faster and more uniform sprouting compared to direct sowing. Unlike direct sowing, which plants untreated seeds directly into the soil, seed priming improves seed vigor and stress tolerance, increasing the likelihood of successful emergence under variable environmental conditions. This technique reduces the time required for germination and can lead to higher crop yields by establishing a more consistent seedling population.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Seed Priming | Direct Sowing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-sowing treatment involving hydration of seeds to initiate germination | Planting untreated seeds directly into the soil |
| Germination Rate | Higher and more uniform germination | Variable and often slower germination |
| Seedling Vigor | Improved seedling strength and growth | Lower vigor due to environmental stress |
| Time to Germination | Reduced time to emergence | Longer time, dependent on soil conditions |
| Stress Tolerance | Enhanced tolerance to drought and salinity | Lower tolerance, higher risk of failure |
| Cost | Higher due to additional processing | Lower, no extra treatment required |
| Best Use | High-value crops, adverse environments | Low-risk, well-managed fields |
Overview of Seed Priming and Direct Sowing
Seed priming enhances germination by pre-treating seeds with controlled hydration, triggering metabolic processes without radicle emergence, leading to faster and uniform seedling growth. Direct sowing involves placing untreated seeds directly into soil, which may result in slower, less uniform germination influenced by environmental conditions. Seed priming significantly improves germination rates and seedling vigor compared to direct sowing by optimizing seed metabolism before planting.
Mechanisms Behind Seed Germination
Seed priming enhances germination by initiating metabolic processes such as enzyme activation and DNA repair prior to sowing, promoting faster and uniform seedling emergence. Direct sowing relies solely on natural imbibition and environmental conditions to trigger these physiological changes, often resulting in slower and uneven germination rates. The controlled hydration during seed priming optimizes cellular respiration and energy mobilization, providing a distinct advantage over conventional direct sowing methods in seed technology.
Advantages of Seed Priming in Agriculture
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by pre-treating seeds with moisture, leading to early seedling vigor and improved crop establishment. This technique increases stress tolerance against drought and salinity, resulting in higher field emergence rates compared to direct sowing. Farmers benefit from optimized resource use, reduced seed wastage, and increased yield potential through seed priming in agriculture.
Benefits of Direct Sowing Techniques
Direct sowing techniques enhance germination by placing seeds directly into the soil, promoting better seed-to-soil contact and optimizing moisture availability. This method reduces transplant shock, accelerates seedling establishment, and supports uniform crop emergence. Compared to seed priming, direct sowing minimizes labor and resource inputs, making it a cost-effective and efficient approach for large-scale agriculture.
Seed Priming Methods and Technologies
Seed priming methods such as hydropriming, osmopriming, and biopriming enhance germination rates by pre-treating seeds to activate metabolic processes before sowing. Technologies like vacuum priming and magnetopriming improve seed water uptake and enzyme activation, leading to uniform and faster seedling emergence compared to direct sowing. These advanced priming techniques increase stress tolerance and seed vigor, optimizing crop establishment in varied environmental conditions.
Factors Affecting Germination Success
Seed priming enhances germination success by pre-treating seeds with moisture, improving enzyme activation and reducing imbibition lag, which leads to uniform and faster germination rates compared to direct sowing. Factors affecting germination success include seed moisture content, temperature, oxygen availability, and seed vigor, all of which seed priming optimizes more effectively than direct sowing. Soil conditions such as salinity, pH, and microbial activity also influence germination, with primed seeds showing greater tolerance and resilience under suboptimal environments.
Comparative Analysis: Primed Seeds vs. Unprimed Seeds
Seed priming significantly enhances germination rates and uniformity compared to direct sowing of unprimed seeds by initiating metabolic processes before planting. Primed seeds exhibit faster emergence, improved stress tolerance, and higher seedling vigor, leading to better stand establishment and yield potential. In contrast, unprimed seeds often result in uneven germination and delayed growth, which can reduce overall crop productivity.
Field Performance and Crop Yield Outcomes
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by initiating metabolic processes before sowing, resulting in improved seedling vigor and higher field establishment rates compared to direct sowing. Field performance shows that primed seeds tolerate environmental stresses better, leading to more consistent crop stands and reduced seedling mortality. Consequently, crop yield outcomes from primed seeds are often significantly higher, with increased biomass and grain production due to optimized early growth and resource utilization.
Cost-Effectiveness of Seed Priming vs. Direct Sowing
Seed priming enhances germination rates and uniformity, reducing seed wastage and lowering overall costs compared to direct sowing. This technique shortens the emergence period, enabling faster crop establishment and potentially higher yields, which improves return on investment. By improving seed vigor, seed priming decreases the need for re-sowing and input resources, making it a more cost-effective method than traditional direct sowing in various agricultural systems.
Recommendations for Farmers and Seed Technologists
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by pre-treating seeds with water or growth regulators, improving field emergence under suboptimal conditions compared to direct sowing. Farmers are recommended to use seed priming techniques for crops sensitive to drought or low soil temperatures, ensuring higher germination rates and early vigor. Seed technologists should optimize priming protocols according to seed species and environmental factors to maximize germination efficiency and crop establishment.
Related Important Terms
Osmopriming
Osmopriming enhances seed germination by regulating water uptake and activating metabolic processes before sowing, resulting in faster and more uniform seedling emergence compared to direct sowing. This technique improves seed vigor, drought tolerance, and stand establishment, particularly under stress conditions where traditional direct sowing may lead to uneven germination and reduced crop yield.
Hydropriming
Hydropriming enhances seed germination by soaking seeds in water to activate metabolic processes before sowing, resulting in faster and more uniform emergence compared to direct sowing. Studies indicate hydroprimed seeds exhibit improved vigor and stress tolerance, leading to higher establishment rates in various crops.
Biopriming
Biopriming enhances seed germination by treating seeds with beneficial microorganisms that improve seed vigor and disease resistance compared to direct sowing, which often faces challenges such as uneven emergence and pathogen susceptibility. This seed priming method optimizes nutrient uptake and stress tolerance, leading to higher and more uniform germination rates essential for successful crop establishment.
Nanopriming
Nanopriming enhances seed germination by improving water uptake and activating enzymatic processes more effectively than traditional seed priming or direct sowing methods. This advanced technique increases seedling vigor and uniformity, resulting in faster and more reliable crop establishment compared to conventional germination approaches.
Halo-priming
Halo-priming enhances seed germination by soaking seeds in a potassium nitrate solution, accelerating enzymatic activities and improving stress tolerance compared to direct sowing. This technique significantly increases germination rates and uniformity, especially under suboptimal soil conditions, making it a superior method in seed technology for early crop establishment.
Film Coating Priming
Film coating priming enhances seed germination by applying a protective layer infused with nutrients and germination stimulants, accelerating water uptake and uniform seedling emergence. Compared to direct sowing, this technology improves stress tolerance, reduces seedling mortality, and optimizes field establishment for higher crop yields.
Primed Seed Vigor Index
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity, significantly improving the Primed Seed Vigor Index compared to direct sowing, which often results in slower and less uniform seedling emergence. Primed seeds exhibit higher enzymatic activity and better stress tolerance, contributing to increased seedling vigor and overall crop establishment.
Rapid Germination Kinetics
Seed priming accelerates germination kinetics by initiating metabolic processes before sowing, resulting in faster and more uniform emergence compared to direct sowing, which relies solely on natural seed hydration and activation. Enhanced enzymatic activity and improved seed vigor in primed seeds significantly reduce lag time, promoting rapid seedling establishment in agricultural practices.
Stress-Resilient Germination
Seed priming enhances stress-resilient germination by pre-conditioning seeds to improve water uptake and metabolic activity, leading to faster and more uniform emergence under adverse conditions such as drought and salinity. Direct sowing, while cost-effective, often results in lower germination rates and increased vulnerability to environmental stresses due to lack of seed treatment.
Precision Direct Seeding
Seed priming enhances germination rates by initiating metabolic processes within the seed before sowing, leading to uniform seedling emergence and improved stress tolerance. Precision direct seeding optimizes seed placement, depth, and spacing, reducing seed wastage and maximizing field efficiency compared to traditional direct sowing methods.
Seed priming vs Direct sowing for germination Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com