Seed priming enhances germination by partially hydrating seeds to activate metabolic processes without allowing radicle emergence, resulting in faster and uniform seedling growth. Seed coating involves applying a protective layer of materials such as polymers, nutrients, or pesticides to improve seed handling, protect against pests, and enhance seedling vigor. Both techniques optimize seed performance in pet seed technology by boosting germination rates and increasing early plant development success.
Table of Comparison
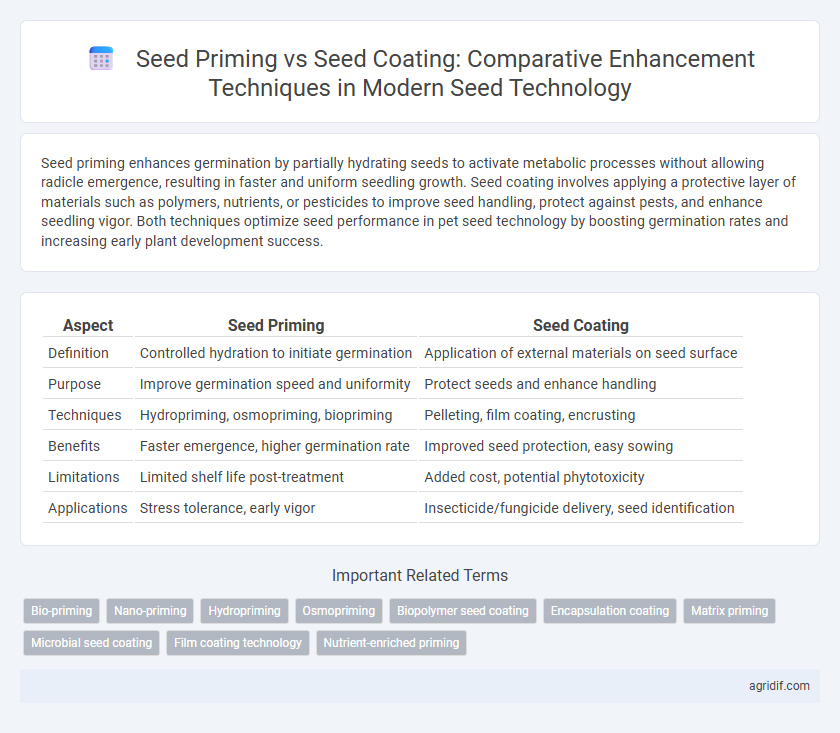
| Aspect | Seed Priming | Seed Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Controlled hydration to initiate germination | Application of external materials on seed surface |
| Purpose | Improve germination speed and uniformity | Protect seeds and enhance handling |
| Techniques | Hydropriming, osmopriming, biopriming | Pelleting, film coating, encrusting |
| Benefits | Faster emergence, higher germination rate | Improved seed protection, easy sowing |
| Limitations | Limited shelf life post-treatment | Added cost, potential phytotoxicity |
| Applications | Stress tolerance, early vigor | Insecticide/fungicide delivery, seed identification |
Introduction to Seed Enhancement Technologies
Seed priming involves controlled hydration of seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, improving germination speed and uniformity. Seed coating applies external materials around seeds to enhance physical protection, nutrient supply, and pest resistance, often incorporating bioactive substances. Both techniques serve as vital seed enhancement technologies, optimizing seed performance and crop establishment under diverse environmental conditions.
Defining Seed Priming and Seed Coating
Seed priming is a pre-sowing hydration technique that initiates seed metabolic processes without allowing radicle emergence, enhancing germination speed and uniformity. Seed coating involves applying physical layers of materials such as polymers, nutrients, or protectants to the seed surface to improve handling, protect against pests, and deliver beneficial substances. Both techniques optimize seed performance but differ in their approach: priming activates physiological processes internally, while coating modifies external seed properties.
Mechanisms of Seed Priming
Seed priming enhances germination by partially hydrating seeds to activate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, improving enzyme activity and repair mechanisms. This controlled hydration triggers DNA repair and synthesis of proteins related to stress tolerance, leading to uniform and faster germination. Unlike seed coating, which mainly provides a physical or chemical barrier, priming directly influences the physiological state of the seed for improved vigor.
Seed Coating Techniques and Materials
Seed coating techniques enhance seed performance by applying a protective layer of materials such as polymers, nutrients, and bioactive agents directly onto the seed surface. These materials improve germination rates, protect against pathogens, and enhance nutrient availability, promoting robust seedling development. Advanced seed coating formulations often include materials like hydrogels, micronutrients, and beneficial microbes tailored to specific crop requirements.
Comparative Benefits: Priming vs Coating
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by initiating metabolic processes before planting, improving seedling vigor under stress conditions. Seed coating, on the other hand, offers targeted delivery of nutrients, pesticides, or growth regulators, providing physical protection and improving seed handling. Both techniques complement each other; priming accelerates early growth while coating enhances protection and resource efficiency.
Influences on Germination and Seedling Vigor
Seed priming enhances germination by initiating metabolic processes within the seed prior to sowing, leading to faster and more uniform emergence. Seed coating improves seedling vigor by providing physical protection and delivering nutrients or growth stimulants directly to the seed microenvironment. Both techniques influence germination rates and seedling development, but priming primarily accelerates physiological readiness while coating offers external support and improved resilience.
Seed Health and Disease Management
Seed priming enhances seed health by initiating metabolic processes prior to sowing, improving germination rates and early seedling vigor, which boosts resistance to soil-borne pathogens. Seed coating serves as a protective barrier incorporating fungicides, insecticides, or beneficial microbes directly on the seed surface, providing targeted disease management during critical growth stages. Combining both techniques can synergistically optimize seed health and reduce the incidence of diseases, leading to healthier crop establishment.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
Seed priming enhances germination speed and uniformity by partially hydrating seeds, consuming less water and minimizing waste, which reduces environmental impact compared to seed coating that often involves synthetic polymers and chemicals. Economically, seed priming is cost-effective due to lower input materials and simpler processes, while seed coating can increase production costs but offers targeted delivery of nutrients and protection, potentially improving crop yields. Both techniques contribute to sustainable agriculture, but seed priming generally presents a greener and more budget-friendly option for small-scale farmers and resource-limited settings.
Applications in Modern Agriculture
Seed priming enhances germination rates and stress tolerance by pre-soaking seeds with water or nutrient solutions, accelerating uniform seedling emergence in crops like wheat and maize. Seed coating involves applying protective layers containing fungicides, nutrients, or growth regulators to improve seed handling, pest resistance, and early vigor in vegetables and cereals. Both techniques are integral to precision agriculture, optimizing crop establishment and yield under varying environmental conditions.
Future Trends in Seed Enhancement Technologies
Future trends in seed enhancement technologies emphasize advanced seed priming methods utilizing precision hydration control to optimize germination rates and stress tolerance. Innovations in seed coating integrate nanomaterials and bioactive agents for targeted nutrient delivery and disease resistance, enhancing seedling vigor. Hybrid approaches combining priming and coating technologies are emerging to maximize seed performance in variable environmental conditions.
Related Important Terms
Bio-priming
Bio-priming, a seed enhancement technique, involves treating seeds with beneficial microorganisms to improve germination and disease resistance, whereas seed coating primarily provides physical protection and controlled release of nutrients or chemicals. Bio-priming integrates microbial inoculants for enhanced seedling vigor and stress tolerance, making it a biologically focused method compared to the primarily mechanical nature of seed coating.
Nano-priming
Seed priming utilizes controlled hydration to activate metabolic processes before sowing, enhancing germination speed and uniformity, whereas seed coating involves applying protective or nutrient-based layers to seeds. Nano-priming integrates nanomaterials into the priming solution, improving seed vigor and stress resistance through targeted delivery of nanoparticles that modulate physiological responses at the cellular level.
Hydropriming
Hydropriming, a seed priming technique, improves germination speed and uniformity by soaking seeds in water to activate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, enhancing seed vigor and stress tolerance. Compared to seed coating, which provides physical protection and nutrient delivery, hydropriming is a cost-effective, simple method primarily targeting physiological activation for improved seedling establishment.
Osmopriming
Osmopriming enhances seed germination by soaking seeds in a controlled osmotic solution, improving water uptake and cellular repair before planting, whereas seed coating primarily involves applying protective or nutrient-rich layers to seeds without directly influencing osmotic balance. This targeted osmopriming technique optimizes seed vigor and stress tolerance by regulating seed hydration levels, resulting in faster and more uniform emergence compared to traditional coating methods.
Biopolymer seed coating
Seed priming enhances germination speed by pre-soaking seeds to initiate metabolic processes, while biopolymer seed coating improves seed protection and nutrient delivery through a biodegradable film that supports seedling vigor and stress resistance. Biopolymer coatings, composed of natural polymers like chitosan or alginate, provide a sustainable method to regulate moisture, incorporate bioactive compounds, and enhance soil adhesion, outperforming traditional priming in field performance and environmental impact.
Encapsulation coating
Seed priming improves germination speed and uniformity by hydrating seeds to initiate metabolic processes without radicle emergence, while encapsulation coating enhances seed protection and nutrient delivery through a biopolymer matrix that surrounds the seed, enabling controlled release of growth promoters and agrochemicals. Encapsulation coating in seed technology offers superior stress tolerance and precision in seed treatment applications compared to traditional seed priming methods.
Matrix priming
Matrix priming enhances seed germination by partially hydrating seeds within a controlled matrix, improving metabolic activity and uniform seedling emergence compared to conventional seed priming methods. Unlike seed coating, which adds physical layers for protection and nutrient delivery, matrix priming optimizes water uptake and respiratory activity without significantly altering seed size or shape.
Microbial seed coating
Microbial seed coating introduces beneficial microorganisms directly onto the seed surface, enhancing nutrient uptake, disease resistance, and stress tolerance more effectively than traditional seed priming. This advanced biotechnological approach ensures targeted microbial colonization, promoting sustainable crop growth and improved yield potential.
Film coating technology
Film coating technology in seed enhancement involves applying a thin, uniform polymer film that protects seeds from environmental stress and improves handling without significantly altering seed size or weight. Unlike seed priming, which initiates metabolic processes to speed germination, film coating focuses on physical protection and controlled-release of nutrients or pesticides, optimizing seed performance and field establishment.
Nutrient-enriched priming
Nutrient-enriched seed priming involves soaking seeds in a nutrient solution to accelerate germination and improve seedling vigor by directly enhancing internal nutrient availability, whereas seed coating applies external layers that may include nutrients but primarily focus on physical protection and controlled release. Priming delivers targeted nutrient uptake at the cellular level, resulting in faster metabolic activation compared to the slower nutrient absorption from coated seed surfaces.
Seed Priming vs Seed Coating for enhancement techniques Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com