Output markets determine the prices at which farmers sell their crops and livestock, directly influencing revenue and profit margins. Input markets involve the acquisition of seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor, affecting production costs and resource allocation. Effective farm decision-making requires balancing input investments with anticipated output returns to optimize overall economic efficiency.
Table of Comparison
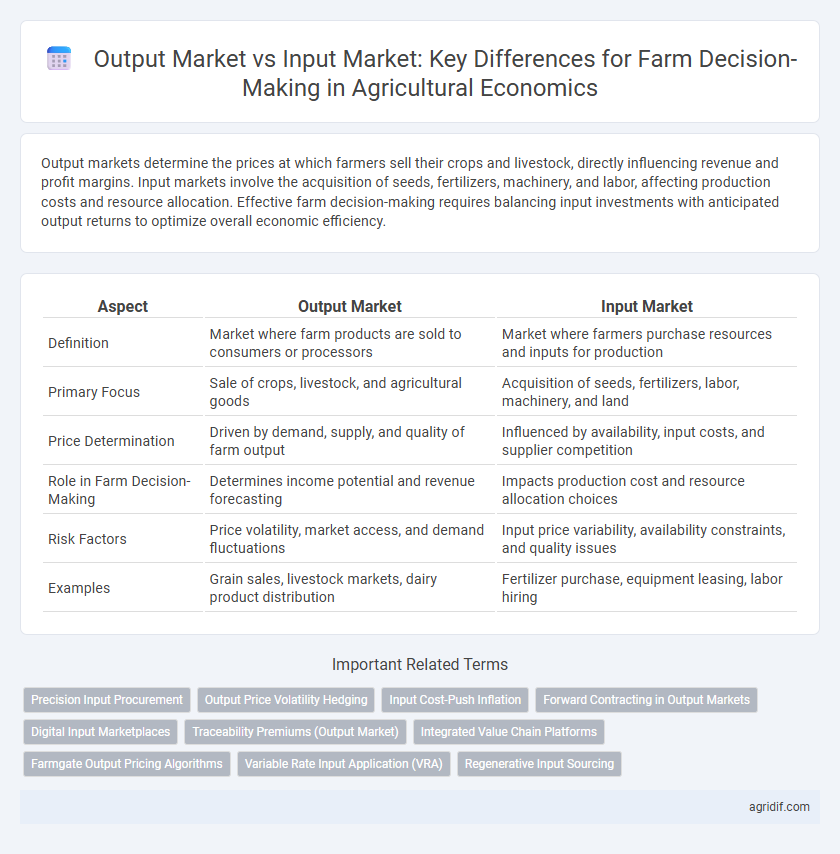
| Aspect | Output Market | Input Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Market where farm products are sold to consumers or processors | Market where farmers purchase resources and inputs for production |
| Primary Focus | Sale of crops, livestock, and agricultural goods | Acquisition of seeds, fertilizers, labor, machinery, and land |
| Price Determination | Driven by demand, supply, and quality of farm output | Influenced by availability, input costs, and supplier competition |
| Role in Farm Decision-Making | Determines income potential and revenue forecasting | Impacts production cost and resource allocation choices |
| Risk Factors | Price volatility, market access, and demand fluctuations | Input price variability, availability constraints, and quality issues |
| Examples | Grain sales, livestock markets, dairy product distribution | Fertilizer purchase, equipment leasing, labor hiring |
Understanding Output and Input Markets in Agriculture
Output markets in agriculture determine the prices farmers receive for their crops and livestock, directly influencing revenue and profitability. Input markets involve the purchase of essential resources such as seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor, impacting production costs and efficiency. Effective farm decision-making requires analyzing both markets to optimize resource allocation, manage risk, and maximize overall farm economic performance.
Key Differences Between Output and Input Markets
Output markets in agricultural economics involve the sale of farm products such as crops and livestock, where prices are influenced by demand, quality, and market access, directly affecting farm revenue. Input markets focus on purchasing essential resources like seeds, fertilizers, machinery, and labor, with costs driven by supply conditions, technological advancements, and policy regulations. Understanding the key differences between these markets helps farmers optimize production decisions by balancing input costs against expected output prices to maximize profitability.
The Role of Output Markets in Farm Profitability
Output markets significantly influence farm profitability by determining the prices and demand for agricultural products, directly impacting farmers' revenue. Efficient output markets enable farmers to sell their produce at optimal prices, enhancing income stability and encouraging investment in productivity improvements. Price volatility and market access challenges in output markets directly affect farm decision-making, guiding choices on production levels and crop diversification.
Input Markets: Impact on Production Costs
Input markets significantly influence farm production costs through the prices of essential resources such as seeds, fertilizers, labor, and machinery. Variations in input prices directly affect profit margins and the scale of production, forcing farmers to optimize resource allocation carefully. Understanding input market dynamics enables better cost management strategies, improving overall farm efficiency and competitiveness.
Price Formation Mechanisms in Output vs Input Markets
Price formation mechanisms in output markets for farm decision-making primarily depend on supply and demand dynamics, where prices are influenced by crop yields, quality, and market access. In contrast, input markets determine prices based on factors such as availability of seeds, fertilizers, labor costs, and technology adoption rates. Understanding the differences in price signals between these markets helps farmers optimize resource allocation and improve profitability.
Market Access Challenges for Farmers
Farmers face significant market access challenges in both output and input markets that impact their decision-making processes. Limited access to output markets can reduce farmers' ability to sell products at competitive prices, while barriers in input markets, such as high costs or scarcity of seeds, fertilizers, and machinery, constrain production capacity. Addressing these challenges through improved infrastructure, transparent pricing, and better market information enhances farmers' profitability and sustainability in agricultural economic systems.
Influence of Market Information on Farm Decisions
Market information on output prices directly affects farm decisions regarding crop selection and sales timing, optimizing revenue. Accurate data on input costs, such as seeds, fertilizers, and labor, guides purchasing decisions to minimize expenses and increase profitability. Timely market intelligence in both output and input markets enables farmers to balance production costs with expected returns, enhancing overall farm efficiency.
Risk Management in Output and Input Markets
Farmers face distinct risk profiles in output and input markets, influencing their decision-making strategies. Output market risks include price volatility and demand fluctuations, affecting revenue stability, while input market risks involve price changes for seeds, fertilizers, and labor, impacting production costs. Effective risk management entails using futures contracts, diversification, and input cost controls to mitigate financial uncertainty in both markets.
Policy Implications for Output and Input Market Efficiency
Efficient output and input markets are critical for optimizing farm decision-making and enhancing agricultural productivity. Policies promoting transparent price signals and reducing transaction costs in input markets like seeds, fertilizers, and machinery encourage timely resource allocation, while output market policies ensuring fair pricing and market access strengthen farmers' income stability. Targeted interventions such as subsidies for advanced inputs and improved market infrastructure boost overall sector efficiency and rural economic development.
Strategic Decision-Making for Farmers: Balancing Input and Output Markets
Farmers strategically balance input and output markets to optimize profitability, considering input costs like seeds, fertilizers, and labor against expected revenues from crop sales. Understanding price volatility and supply-demand trends in both markets enables effective risk management and resource allocation. Integrating market forecasts and cost analyses enhances decision-making for sustainable farm operations and long-term financial stability.
Related Important Terms
Precision Input Procurement
Precision input procurement in agricultural economics enhances farm decision-making by optimizing input market strategies, ensuring accurate selection and timely purchase of seeds, fertilizers, and technology based on yield data analysis. This targeted approach maximizes profitability by aligning input costs with expected output market prices, reducing waste and improving resource allocation efficiency.
Output Price Volatility Hedging
Output market price volatility significantly impacts farm revenue, making effective hedging strategies essential for stabilizing income and managing risk. Utilizing futures contracts and options in commodity markets enables farmers to lock in prices, reducing uncertainty and supporting more informed input decisions and resource allocation.
Input Cost-Push Inflation
Input cost-push inflation significantly impacts farm decision-making by increasing expenses for seeds, fertilizers, and machinery, thereby altering the cost structure in input markets. Farmers must strategically balance these rising input costs against potential output prices to maintain profitability and ensure sustainable production levels.
Forward Contracting in Output Markets
Forward contracting in output markets allows farmers to secure prices for their produce in advance, reducing revenue uncertainty and improving cash flow stability. This strategy enhances farm decision-making by enabling better resource allocation and investment planning based on predetermined market prices rather than volatile spot market conditions.
Digital Input Marketplaces
Digital input marketplaces revolutionize farm decision-making by offering real-time access to agricultural inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, and equipment, enhancing price transparency and supplier competition in input markets. Unlike output markets that focus on selling farm products, these digital platforms optimize input procurement efficiency, reducing costs and improving resource allocation for farmers.
Traceability Premiums (Output Market)
Traceability premiums in the output market enable farmers to capture higher prices by ensuring product origin, quality, and safety, which directly influence farm decision-making and profitability. Investing in traceability systems shifts input choices, encouraging adoption of sustainable practices and certifications to meet market demands and maximize revenue.
Integrated Value Chain Platforms
Integrated Value Chain Platforms enhance farm decision-making by linking output markets with input markets, enabling farmers to optimize production costs while maximizing revenue through real-time price signals and demand forecasts. These platforms facilitate efficient resource allocation and risk management by synchronizing input procurement with market-driven output strategies in agriculture.
Farmgate Output Pricing Algorithms
Farmgate output pricing algorithms play a critical role in agricultural economics by accurately determining farm-level prices for crops and livestock, directly influencing farmers' revenue and production decisions. These algorithms integrate market demand data, quality differentials, and transportation costs to optimize farm output prices, contrasting with input market models that focus primarily on the cost and availability of seeds, fertilizers, and machinery influencing input procurement strategies.
Variable Rate Input Application (VRA)
Variable Rate Input Application (VRA) optimizes input markets by precisely adjusting seed, fertilizer, and pesticide quantities based on spatial variability, enhancing cost efficiency and resource use. Output market decisions rely on VRA data to predict yield potentials and tailor production strategies that maximize profits under fluctuating price conditions.
Regenerative Input Sourcing
Regenerative input sourcing in agricultural economics transforms farm decision-making by prioritizing sustainable and eco-friendly inputs that enhance soil health and biodiversity, thereby optimizing output market potential through increased product quality and consumer demand for green produce. Economic analysis reveals that sourcing regenerative inputs reduces dependency on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, lowering input costs and mitigating market volatility while improving long-term farm profitability in competitive output markets.
Output market vs input market for farm decision-making Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com