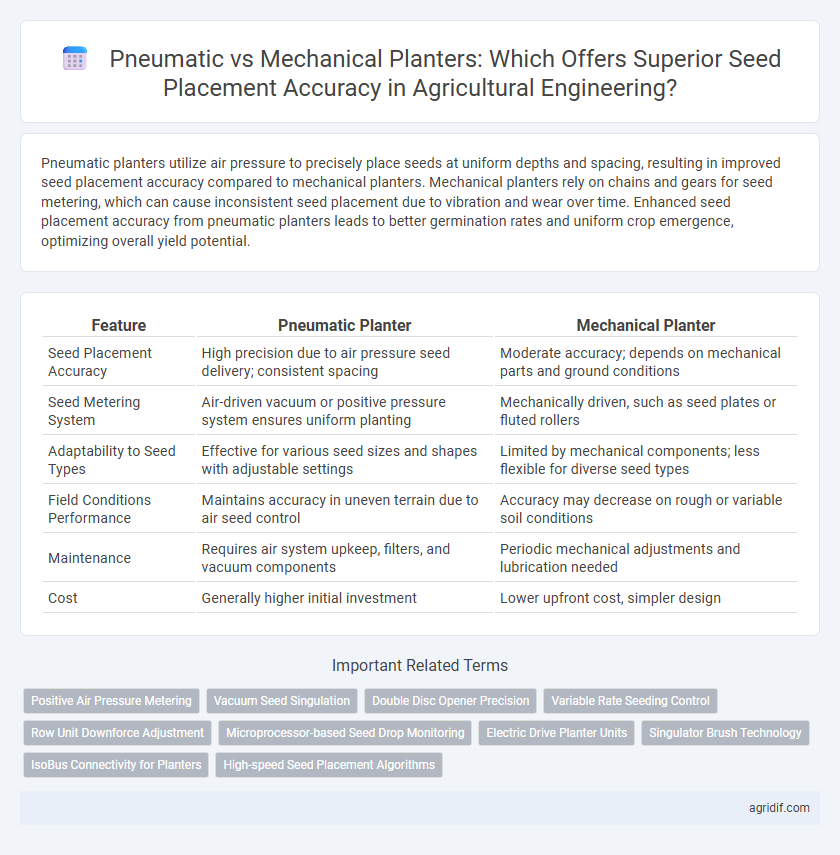
Pneumatic planters utilize air pressure to precisely place seeds at uniform depths and spacing, resulting in improved seed placement accuracy compared to mechanical planters. Mechanical planters rely on chains and gears for seed metering, which can cause inconsistent seed placement due to vibration and wear over time. Enhanced seed placement accuracy from pneumatic planters leads to better germination rates and uniform crop emergence, optimizing overall yield potential.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pneumatic Planter | Mechanical Planter |
|---|---|---|
| Seed Placement Accuracy | High precision due to air pressure seed delivery; consistent spacing | Moderate accuracy; depends on mechanical parts and ground conditions |
| Seed Metering System | Air-driven vacuum or positive pressure system ensures uniform planting | Mechanically driven, such as seed plates or fluted rollers |
| Adaptability to Seed Types | Effective for various seed sizes and shapes with adjustable settings | Limited by mechanical components; less flexible for diverse seed types |
| Field Conditions Performance | Maintains accuracy in uneven terrain due to air seed control | Accuracy may decrease on rough or variable soil conditions |
| Maintenance | Requires air system upkeep, filters, and vacuum components | Periodic mechanical adjustments and lubrication needed |
| Cost | Generally higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost, simpler design |
Introduction to Seed Placement Accuracy in Agriculture
Seed placement accuracy in agricultural engineering directly impacts crop yield and uniformity. Pneumatic planters utilize air pressure systems to deliver seeds precisely into the soil, significantly reducing seed bounce and improving depth consistency compared to mechanical planters, which rely on mechanical components like seed plates and discs. Research shows pneumatic planters achieve seed spacing accuracy up to 95%, whereas mechanical planters typically range between 80-90%, influencing overall planting efficiency and resource use.
Overview of Pneumatic Planters
Pneumatic planters leverage air pressure to deliver seeds precisely into the soil, ensuring consistent seed placement depth and spacing, which enhances germination rates and crop uniformity. These planters reduce mechanical wear and seed damage compared to mechanical planters by utilizing airflow to transport seeds gently through tubes. Ideal for diverse seed types and variable field conditions, pneumatic planters offer superior accuracy and efficiency in modern agricultural planting operations.
Overview of Mechanical Planters
Mechanical planters use physical components such as discs, coulters, and seed plates to create furrows and place seeds at consistent depths, enabling precise seed spacing and reducing seed damage. These planters rely on ground-driven mechanisms that synchronize seed release with planter movement, optimizing seed placement accuracy for various soil conditions. Their robust design allows for effective operation in uneven terrain, making them a reliable choice for maintaining uniform crop emergence.
Key Differences in Seed Placement Mechanisms
Pneumatic planters use air pressure to deliver seeds uniformly and precisely into the soil, reducing seed bounce and misplacement, resulting in higher seed placement accuracy compared to mechanical planters. Mechanical planters rely on physical components like seed plates and cups, which may cause inconsistent seed spacing due to variations in seed size and shape. The key difference lies in pneumatic systems providing more controlled seed metering and placement through air flow, improving germination rates and yield potential.
Factors Affecting Seed Placement Precision
Seed placement precision in pneumatic planters is influenced by factors such as air pressure consistency, seed population density, and seed size uniformity, which optimize accurate depth and spacing. Mechanical planters rely heavily on the condition of moving parts, ground speed, and seed singulation mechanisms to maintain precision, where wear and inconsistent rotation can cause seed misplacement. Both systems must also account for soil type, moisture levels, and terrain variability, as these external factors critically affect seed depth and alignment accuracy during planting operations.
Comparative Analysis: Pneumatic vs Mechanical Planters
Pneumatic planters utilize air pressure to precisely place seeds at consistent depths and spacing, resulting in higher seed placement accuracy compared to mechanical planters. Mechanical planters rely on seed plates and ground-driven mechanisms, which are more prone to variability due to field conditions and seed size differences. Studies indicate pneumatic planters enhance uniformity and emergence rates by minimizing seed bounce and misplacement, leading to optimized crop stands and increased yield potential.
Field Performance and Case Studies
Pneumatic planters demonstrate superior seed placement accuracy compared to mechanical planters, ensuring uniform seed depth and spacing across variable field conditions, which enhances crop emergence consistency. Field performance evaluations reveal that pneumatic systems reduce seed bounce and misplacement, leading to increased germination rates and yield potential in diverse soil types. Case studies in large-scale corn and soybean production highlight pneumatic planters' effectiveness in optimizing seed distribution, minimizing seed waste, and improving overall planting efficiency.
Impact on Crop Emergence and Yield
Pneumatic planters enhance seed placement accuracy by using air pressure to distribute seeds uniformly at precise depths and spacing, which significantly improves crop emergence rates and overall yield. Mechanical planters rely on physical components that may cause uneven seed placement, leading to variable emergence and potential yield loss. Studies indicate pneumatic systems reduce seed bounce and misalignment, ensuring consistent germination and maximizing productivity in diverse soil conditions.
Maintenance and Operational Considerations
Pneumatic planters offer superior seed placement accuracy through precise air pressure control, requiring regular maintenance of air compressors and vacuum systems to prevent clogging and ensure consistent seed singulation. Mechanical planters rely on gears and chains, demanding frequent lubrication and inspection to avoid wear that can lead to uneven seed spacing and depth variations. Operational efficiency favors pneumatic planters in large-scale farming due to their faster adjustment capabilities, while mechanical planters often present a lower initial cost but higher susceptibility to mechanical failure and downtime.
Future Trends in Seeder Technology
Pneumatic planters offer superior seed placement accuracy by using air pressure to deliver seeds precisely into the soil, reducing spacing errors common in mechanical planters. Future trends in seeder technology emphasize integrating advanced sensors and GPS-guided automation to enhance precision and adaptability in various field conditions. Innovations such as variable-rate seeding and real-time monitoring systems are set to improve efficiency and crop yields significantly.
Related Important Terms
Positive Air Pressure Metering
Pneumatic planters utilize positive air pressure metering to achieve higher seed placement accuracy by precisely controlling seed singulation and spacing, reducing seed damage and increasing uniformity. Mechanical planters, relying on seed plates and vacuum systems, often face inconsistencies in seed drop timing and spacing, resulting in less precise seed placement compared to pneumatic counterparts.
Vacuum Seed Singulation
Vacuum seed singulation in pneumatic planters provides superior seed placement accuracy by using controlled airflow to separate and position individual seeds precisely, reducing seed damage and ensuring uniform crop emergence. Mechanical planters rely on physical seed metering mechanisms that often result in inconsistent spacing and higher chances of seed multiples or skips, affecting overall planting efficiency.
Double Disc Opener Precision
Pneumatic planters with double disc openers provide superior seed placement accuracy by maintaining consistent seed depth and minimizing soil disturbance compared to mechanical planters. The precise air pressure control in pneumatic systems ensures uniform seed singulation and spacing, enhancing overall planting efficiency and crop yield potential.
Variable Rate Seeding Control
Pneumatic planters offer superior seed placement accuracy in variable rate seeding control by utilizing precise air pressure systems to deliver seeds consistently at targeted depths and spacing, minimizing seed damage and ensuring uniform emergence. Mechanical planters rely on physical seed metering mechanisms that may result in inconsistent seed delivery under variable seeding rates, reducing overall planting efficiency and potentially impacting crop yield.
Row Unit Downforce Adjustment
Pneumatic planters use air pressure to provide consistent row unit downforce, improving seed placement accuracy by maintaining uniform soil contact across varying field conditions. Mechanical planters rely on physical springs or weights for downforce adjustment, which can result in less precise seed depth control and variable seed-to-soil contact due to inconsistent pressure distribution.
Microprocessor-based Seed Drop Monitoring
Microprocessor-based seed drop monitoring in pneumatic planters enhances seed placement accuracy by precisely controlling seed release and spacing through real-time data feedback, outperforming traditional mechanical planters that rely on fixed mechanical components. This advanced technology minimizes seed singulation errors and optimizes planting uniformity, resulting in improved crop emergence and yield potential.
Electric Drive Planter Units
Electric drive pneumatic planters provide superior seed placement accuracy by using precise air pressure control to deliver seeds consistently into the furrow, reducing seed bounce and ensuring uniform spacing. Mechanical planters, driven by ground wheels, often suffer from variable seed drop rates due to terrain irregularities and mechanical wear, making electric drive pneumatic units more reliable for precision agriculture applications.
Singulator Brush Technology
Pneumatic planters with Singulator Brush Technology provide superior seed placement accuracy by using air pressure combined with precisely controlled brushes to singulate seeds individually, minimizing double drops and skips. Mechanical planters rely on physical seed belts or plates, which often result in inconsistent spacing and reduced seed singulation compared to the air-driven, brush-assisted mechanism.
IsoBus Connectivity for Planters
Pneumatic planters equipped with IsoBus connectivity offer superior seed placement accuracy by enabling precise control of seed spacing and depth through real-time data exchange between sensors and the tractor's control system. Mechanical planters lack advanced IsoBus integration, resulting in less consistent seed placement and limited monitoring capabilities during planting operations.
High-speed Seed Placement Algorithms
Pneumatic planters utilize advanced high-speed seed placement algorithms to enhance accuracy by precisely controlling seed spacing and depth through air pressure systems, outperforming traditional mechanical planters in variable field conditions. Mechanical planters rely on physical mechanisms that often result in less consistent seed placement, especially at higher speeds, making pneumatic technology preferable for optimizing crop yield and uniform emergence.
Pneumatic planter vs Mechanical planter for seed placement accuracy Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com