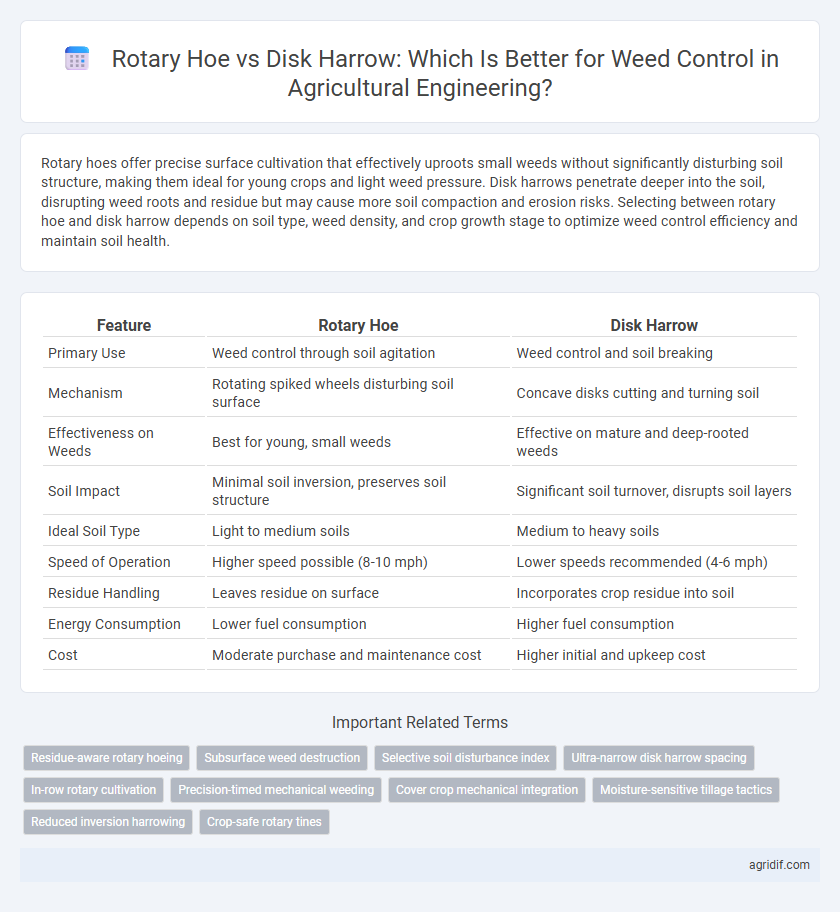
Rotary hoes offer precise surface cultivation that effectively uproots small weeds without significantly disturbing soil structure, making them ideal for young crops and light weed pressure. Disk harrows penetrate deeper into the soil, disrupting weed roots and residue but may cause more soil compaction and erosion risks. Selecting between rotary hoe and disk harrow depends on soil type, weed density, and crop growth stage to optimize weed control efficiency and maintain soil health.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rotary Hoe | Disk Harrow |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Weed control through soil agitation | Weed control and soil breaking |
| Mechanism | Rotating spiked wheels disturbing soil surface | Concave disks cutting and turning soil |
| Effectiveness on Weeds | Best for young, small weeds | Effective on mature and deep-rooted weeds |
| Soil Impact | Minimal soil inversion, preserves soil structure | Significant soil turnover, disrupts soil layers |
| Ideal Soil Type | Light to medium soils | Medium to heavy soils |
| Speed of Operation | Higher speed possible (8-10 mph) | Lower speeds recommended (4-6 mph) |
| Residue Handling | Leaves residue on surface | Incorporates crop residue into soil |
| Energy Consumption | Lower fuel consumption | Higher fuel consumption |
| Cost | Moderate purchase and maintenance cost | Higher initial and upkeep cost |
Overview of Rotary Hoe and Disk Harrow in Modern Agriculture
Rotary hoes and disk harrows are essential tillage tools in modern agriculture for effective weed control and soil preparation. Rotary hoes use multiple rotating wheels with spikes to aerate soil and disrupt weed seedlings without deeply disturbing the soil profile, making them ideal for early-stage weed management. Disk harrows consist of concave metal discs that slice and turn soil, breaking up clods and uprooting weeds while also incorporating crop residue, thus preparing the seedbed for planting and controlling more established weeds.
Mechanisms of Weed Control: Rotary Hoe vs Disk Harrow
Rotary hoes control weeds by uprooting small seedlings through aggressive, spiked wheels that create soil disturbances on the surface, effectively disturbing weed emergence without deep soil turnover. Disk harrows use concave, sharp-edged blades to cut and slice weeds below the soil surface, promoting soil aeration and burial of weed residues, which suppresses weed regrowth. The rotary hoe excels in shallow, early-stage weed control while the disk harrow is more effective for post-emergence weed management and soil incorporation of crop residues.
Effectiveness on Different Weed Types and Growth Stages
Rotary hoes demonstrate high effectiveness against small, emerging weed seedlings by uprooting and desiccating them, particularly in light, sandy soils, while disk harrows excel in managing larger, established weeds with robust root systems across various soil types. The rotary hoe's shallow tillage is optimal for early weed growth stages, minimizing soil disturbance and preserving moisture, whereas disk harrows perform deeper cultivation, disrupting older weeds but potentially impacting soil structure. Crops like corn and soybeans benefit from rotary hoe weed control during the seedling phase, while disk harrows are preferable for heavier weed infestations in later growth stages or tougher weed species such as perennial grasses.
Soil Impact: Comparing Disturbance and Compaction
Rotary hoes create shallow, targeted soil disturbance that effectively uproots weed seedlings while minimizing soil compaction compared to disk harrows. Disk harrows tend to penetrate deeper and cause greater soil disruption, which can lead to increased compaction and negatively impact soil structure. Selecting rotary hoes for weed control preserves soil porosity and enhances microbial activity, promoting better crop root development and overall soil health.
Operational Speed and Field Efficiency
Rotary hoes operate at higher speeds ranging from 5 to 8 mph, enabling quicker coverage of large fields compared to disk harrows, which typically function at slower speeds of 3 to 5 mph. The faster operational speed of rotary hoes enhances field efficiency by increasing the area treated per hour and reducing fuel consumption. Disk harrows, while slower, provide more aggressive soil disturbance, but their reduced speed limits overall field efficiency during weed control operations.
Suitability for Various Crops and Soil Conditions
Rotary hoes excel in weed control for row crops like corn and soybeans, especially in light to medium soils with low residue, providing shallow cultivation that minimizes crop damage. Disk harrows offer effective weed management in tougher soil conditions and heavier residue, making them suitable for grains and field crops with deeper weed roots. Selecting between rotary hoes and disk harrows depends on crop sensitivity, soil texture, and residue levels to optimize weed control and soil health.
Cost Analysis: Purchase, Maintenance, and Operation
Rotary hoes generally have a higher initial purchase cost compared to disk harrows, but they offer lower maintenance expenses due to fewer moving parts and less wear. Disk harrows require more frequent blade replacements and lubrication, increasing operational costs over time. In terms of fuel consumption, rotary hoes tend to use more power, leading to higher fuel expenses, while disk harrows are typically more fuel-efficient for large-scale weed control.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Rotary hoes offer reduced soil disturbance compared to disk harrows, promoting soil health and minimizing erosion, which is crucial for sustainable weed control in agricultural engineering. Disk harrows, while effective in breaking up soil and managing crop residues, can lead to increased soil compaction and organic matter loss, negatively impacting long-term soil fertility. Choosing rotary hoes supports environmental sustainability by enhancing soil structure and encouraging beneficial microbial activity, thereby reducing the need for chemical herbicides.
User Experience: Ease of Use and Adjustability
Rotary hoes offer superior ease of use with simple depth adjustments and minimal maintenance, making them ideal for quick weed cultivation in various soil types. Disk harrows provide effective weed control through adjustable gang angles but require more effort for setup and frequent calibration to optimize performance. Users benefit from the rotary hoe's versatility and straightforward operation, while disk harrows excel in heavier residue management but demand greater mechanical skill for precise adjustments.
Recommendations for Optimal Weed Management Strategies
Rotary hoe is most effective for early-stage weed control in lighter soils due to its ability to disrupt weed seedlings without excessive soil disturbance, while disk harrow excels in heavier soils by burying weed residues and improving seedbed conditions. For optimal weed management, integrate rotary hoe passes early in the season followed by disk harrowing to manage established weeds and crop residue. Combining both tools in a timely sequence enhances weed suppression, improves soil aeration, and supports sustainable crop growth.
Related Important Terms
Residue-aware rotary hoeing
Residue-aware rotary hoeing enhances weed control by selectively disturbing weed seedlings while preserving crop residue, improving soil moisture retention and reducing erosion compared to disk harrows. Unlike disk harrows that aggressively mix soil and residue, residue-aware rotary hoes maintain surface cover, supporting sustainable tillage practices in conservation agriculture.
Subsurface weed destruction
Rotary hoes excel in subsurface weed destruction by disturbing the soil just below the surface, uprooting young weed seedlings without significant soil inversion, which preserves soil structure and moisture. Disk harrows, while effective for surface weed control, primarily cut and mix soil layers, potentially burying weed seeds deeper rather than eliminating them at subsurface levels.
Selective soil disturbance index
The Rotary hoe demonstrates a higher Selective Soil Disturbance Index (SSDI) compared to the Disk harrow, enabling precise weed control by targeting specific weed zones while preserving crop seedbeds. SSDI metrics reveal that the Rotary hoe's maneuverability and tine action minimize soil disruption, thus promoting optimal soil health and reducing erosion risks relative to the broad, aggressive action of the Disk harrow.
Ultra-narrow disk harrow spacing
Ultra-narrow disk harrow spacing enhances weed control by increasing soil disturbance and reducing weed seed germination compared to traditional rotary hoes, which primarily uproot weeds without significantly disrupting soil structure. This precise spacing in disk harrows improves residue incorporation and soil aeration, promoting better crop emergence and minimizing herbicide reliance in sustainable agricultural engineering practices.
In-row rotary cultivation
In-row rotary cultivation with a rotary hoe offers precise weed control by targeting weeds directly in the crop row, minimizing crop disturbance and promoting soil aeration. Compared to a disk harrow, which primarily works the soil surface and can disrupt both weeds and crops broadly, rotary hoes provide finer, targeted weed disruption ideal for early-stage crop growth management.
Precision-timed mechanical weeding
Rotary hoes offer precision-timed mechanical weeding by aerating soil and uprooting young weeds with minimal crop disturbance, ideal for early crop stages. Disk harrows provide aggressive soil slicing to cut and bury weed residue but may risk crop damage if used improperly during critical growth periods.
Cover crop mechanical integration
Rotary hoes effectively control weeds in cover crop systems by disturbing soil surfaces and uprooting small weed seedlings without significantly damaging the cover crop residue, promoting soil aeration and moisture retention. Disk harrows, while efficient in breaking up soil clods and incorporating cover crop biomass, can sometimes disrupt root structures and reduce cover crop efficacy in suppressing weeds, making rotary hoes preferable for minimal soil disturbance and sustainable weed management.
Moisture-sensitive tillage tactics
Rotary hoes provide gentle soil aeration and precise weed uprooting without excessive moisture loss, making them ideal for moisture-sensitive tillage in early crop growth stages. Disk harrows, while effective for residue management and deeper weed control, can disrupt soil structure and increase evaporation rates, posing risks in dry soil conditions.
Reduced inversion harrowing
Rotary hoes effectively control weeds by agitating soil surface without significant inversion, preserving soil structure and organic layers. Disk harrows, while effective for deeper soil penetration, tend to cause more soil inversion, disrupting soil microbial activity and increasing erosion risk.
Crop-safe rotary tines
Crop-safe rotary tines on rotary hoes effectively control weeds by uprooting them without damaging crops, making them suitable for row crops with delicate stems. In contrast, disk harrows can be more aggressive, often disturbing soil structure and risking crop injury while managing larger weed infestations.
Rotary hoe vs Disk harrow for weed control Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com