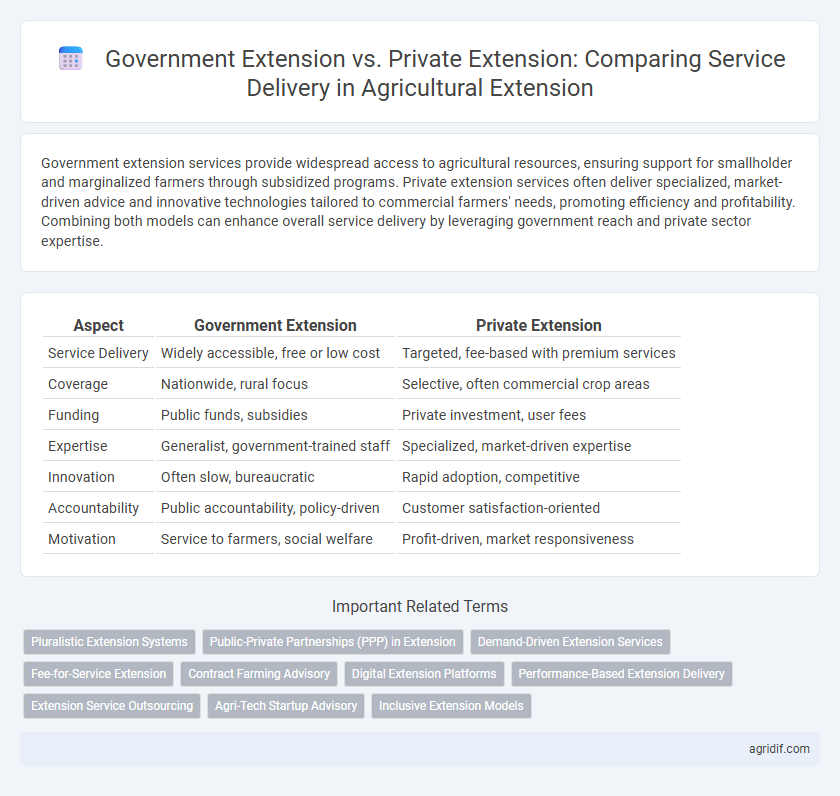
Government extension services provide widespread access to agricultural resources, ensuring support for smallholder and marginalized farmers through subsidized programs. Private extension services often deliver specialized, market-driven advice and innovative technologies tailored to commercial farmers' needs, promoting efficiency and profitability. Combining both models can enhance overall service delivery by leveraging government reach and private sector expertise.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Government Extension | Private Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Service Delivery | Widely accessible, free or low cost | Targeted, fee-based with premium services |
| Coverage | Nationwide, rural focus | Selective, often commercial crop areas |
| Funding | Public funds, subsidies | Private investment, user fees |
| Expertise | Generalist, government-trained staff | Specialized, market-driven expertise |
| Innovation | Often slow, bureaucratic | Rapid adoption, competitive |
| Accountability | Public accountability, policy-driven | Customer satisfaction-oriented |
| Motivation | Service to farmers, social welfare | Profit-driven, market responsiveness |
Overview of Government and Private Agricultural Extension Services
Government agricultural extension services provide widespread access to farmers by leveraging public funding, ensuring equitable dissemination of knowledge and support across diverse regions. Private extension services offer specialized, market-driven solutions that focus on efficiency, innovation, and responsiveness to specific client needs, often complementing public efforts. Both models play critical roles in enhancing agricultural productivity, with government extension emphasizing inclusivity and private extension driving commercial viability.
Structural Differences Between Government and Private Extension
Government extension services typically operate under hierarchical bureaucratic structures with centralized decision-making and publicly funded resources, emphasizing widespread accessibility and standardized protocols. In contrast, private extension systems are often characterized by decentralized, market-driven frameworks with flexible management, relying on client fees and profit motives that prioritize efficiency and customization. These structural differences influence service delivery models, with government programs focusing on equity and coverage while private entities emphasize innovation and responsiveness to specific farmer needs.
Funding Models: Public vs Private Sector Extension
Government extension services primarily rely on public funding sourced from national and local budgets, ensuring widespread access to agricultural support with a focus on smallholder farmers and public goods. Private extension operates through fee-for-service models, agribusiness partnerships, and donor-funded projects, emphasizing market-driven innovation and commercial agriculture. The contrast in funding models influences service coverage, sustainability, and the prioritization of farmer needs, with public extension prioritizing equity and private extension emphasizing efficiency and specialization.
Service Coverage and Accessibility in Extension Delivery
Government extension services traditionally offer broader service coverage, reaching remote and underserved rural areas with well-established networks and public funding. Private extension providers often focus on accessible, market-oriented advisory services tailored to commercial farmers, leveraging digital platforms and fee-based models to enhance responsiveness. Combining government's widespread reach with private sector's innovation can optimize overall accessibility and effectiveness in agricultural extension delivery.
Quality and Expertise of Extension Personnel
Government extension services often provide widespread coverage and standardized training, ensuring a consistent baseline of expertise across regions. Private extension services, however, typically emphasize specialized knowledge and tailored solutions, leveraging industry-specific expertise to enhance service quality. Both sectors contribute uniquely to agricultural innovation, with private extension frequently leading in advanced technical skills while government extension ensures accessibility and regulatory support.
Innovation and Technology Adoption in Extension Services
Government extension services play a critical role in disseminating innovations and facilitating technology adoption by providing widespread access to research-based knowledge and subsidized resources. Private extension services often leverage market-driven approaches and advanced digital tools to tailor solutions, enhancing responsiveness and efficiency in technology transfer. Combining the strengths of both sectors can accelerate innovation diffusion and improve overall agricultural productivity.
Accountability and Monitoring Mechanisms
Government agricultural extension services typically feature structured accountability frameworks and centralized monitoring systems to ensure compliance with national agricultural policies, enhancing transparency and standardized reporting. Private extension providers often employ performance-based accountability models and utilize advanced digital monitoring technologies for real-time data collection and impact assessment, fostering flexibility and responsiveness to client needs. Effective service delivery is optimized when government oversight mechanisms integrate with private sector innovation, promoting both regulatory compliance and adaptive extension methodologies.
Farmer Engagement and Feedback Systems
Government extension services often provide broad coverage with systematic farmer engagement through structured feedback mechanisms such as surveys and farmer field schools, ensuring inclusivity and public accountability. Private extension agencies typically offer more tailored, market-driven advisory services with real-time feedback loops facilitated by digital platforms and direct farmer interactions, enhancing responsiveness and innovation. Combining both approaches can optimize service delivery by balancing wide accessibility with personalized support and efficient feedback integration.
Sustainability of Service Delivery Approaches
Government extension services provide widespread coverage and leverage public funding to ensure accessibility, yet often face challenges in resource constraints and bureaucratic delays impacting long-term sustainability. Private extension services introduce specialized knowledge and market-driven incentives, which promote innovation and responsiveness but may exclude smallholder farmers due to higher costs. Integrating both models through public-private partnerships enhances sustainability by combining the extensive reach of government programs with the efficiency and adaptability of private sector approaches.
Policy Implications and Future Prospects for Extension Systems
Government extension systems often prioritize equitable access and public goods provision, supported by policy frameworks that emphasize rural development and farmer welfare. Private extension services tend to focus on market-driven innovations and efficiency, influenced by policies that encourage private sector participation and technology adoption. Future prospects for extension systems suggest a hybrid approach combining public oversight with private sector agility, necessitating policies that foster collaboration, capacity building, and sustainable financing mechanisms.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Systems
Government extension services provide widespread coverage and focus on public goods such as research dissemination and smallholder support, whereas private extension services offer specialized, market-driven advice tailored to commercial farmers. Pluralistic extension systems integrate both sectors to enhance resource efficiency, innovation diffusion, and farmer access to diverse knowledge and technologies.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in Extension
Government extension services provide widespread reach and regulatory oversight, ensuring equitable access to agricultural innovations, while private extension offers specialized, market-driven expertise and technology adoption. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in agricultural extension integrate government infrastructure with private sector innovation, enhancing service delivery efficiency, resource mobilization, and farmer empowerment through collaborative knowledge transfer and input provision.
Demand-Driven Extension Services
Government extension services often face challenges in responsiveness and resource allocation, limiting their effectiveness in meeting specific farmer demands, while private extension providers tend to offer more tailored, market-oriented solutions that align closely with farmer needs. Demand-driven extension services prioritize farmer input and local context, enhancing adoption rates and productivity by leveraging private sector flexibility and innovative approaches.
Fee-for-Service Extension
Government extension services primarily offer free or subsidized agricultural support funded by public resources, ensuring wide accessibility but often limited in customization and responsiveness. In contrast, private extension services operate on a fee-for-service model, delivering tailored, market-driven expertise that enhances innovation and efficiency but may restrict access for smallholder farmers due to cost barriers.
Contract Farming Advisory
Government extension services in contract farming advisory emphasize regulatory compliance, cost-free guidance, and support for smallholder inclusion, leveraging public resources to ensure equitable access. Private extension providers prioritize specialized, market-driven advice, rapid innovation adoption, and customized solutions tailored to commercial farming operations, enhancing productivity and profitability.
Digital Extension Platforms
Government extension services leverage extensive networks and public funding to ensure widespread access to digital extension platforms, emphasizing inclusivity and standardized information dissemination. Private extension providers prioritize innovation and customization, using digital tools to deliver tailored advisory services that enhance farmer engagement and drive rapid adoption of advanced agricultural technologies.
Performance-Based Extension Delivery
Performance-based agricultural extension delivery in government systems often faces challenges such as limited funding, bureaucratic delays, and less flexibility in responding to farmer needs, resulting in lower efficiency compared to private extension services. Private extension services leverage market-driven incentives, quicker adaptation to innovation, and stronger performance metrics to deliver tailored, timely support that enhances farm productivity and technology adoption rates.
Extension Service Outsourcing
Government extension services often face limitations in resources and reach, making private extension service outsourcing a strategic approach to enhance efficiency and farmer access to specialized knowledge. Outsourcing enables integration of private sector innovations and market-driven solutions, improving overall extension service delivery and responsiveness in agricultural innovation dissemination.
Agri-Tech Startup Advisory
Government agricultural extension services provide widespread access to essential resources and regulatory guidance, fostering inclusive support for agri-tech startups focused on sustainable innovation. Private extension services offer specialized, market-driven advisory with flexible solutions, enabling agri-tech startups to adopt cutting-edge technologies and scale efficiently in competitive agricultural sectors.
Inclusive Extension Models
Government extension services often ensure broad access to agricultural knowledge and resources, targeting marginalized and smallholder farmers through subsidized programs and public funding. Private extension models tend to offer specialized, market-driven solutions with a focus on efficiency and innovation but may exclude resource-poor farmers, making inclusive extension models that combine public support with private sector expertise essential for equitable service delivery.
Government Extension vs Private Extension for service delivery Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com