Public extension services provide widespread access to agricultural knowledge and resources, emphasizing support for smallholder farmers and marginalized communities through government-funded programs. Private extension services often offer specialized, market-driven solutions with a focus on innovation and profitability, catering primarily to commercial farms and agribusinesses. Combining both approaches enhances outreach effectiveness by balancing inclusivity and tailored expertise for diverse agricultural needs.
Table of Comparison
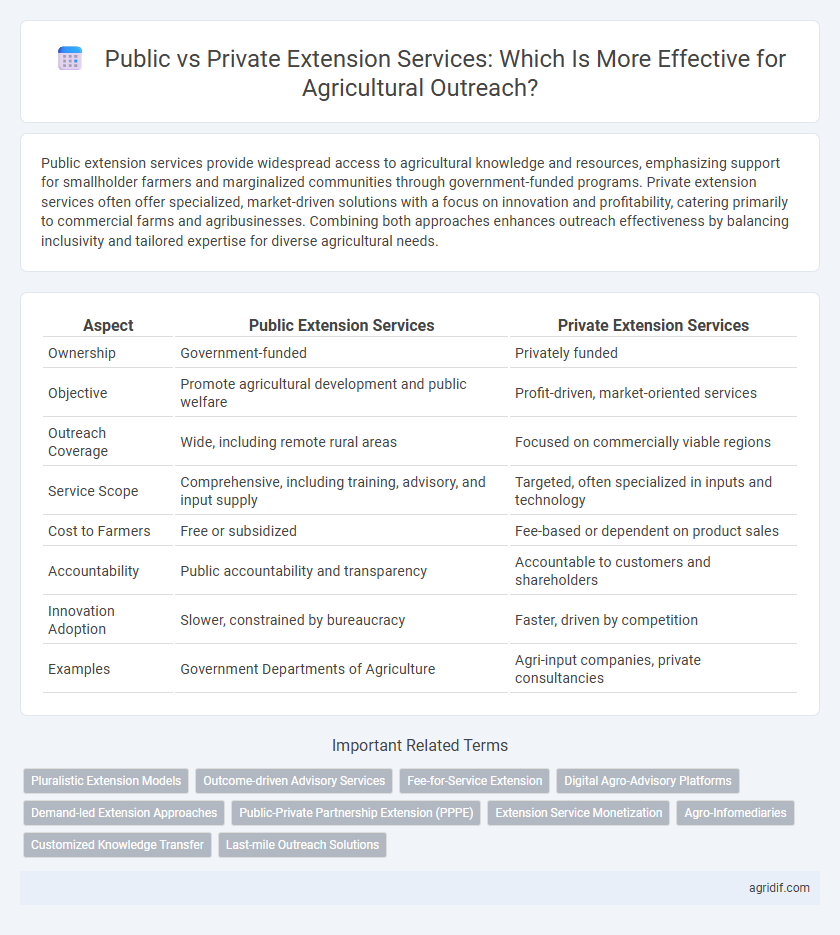
| Aspect | Public Extension Services | Private Extension Services |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Government-funded | Privately funded |
| Objective | Promote agricultural development and public welfare | Profit-driven, market-oriented services |
| Outreach Coverage | Wide, including remote rural areas | Focused on commercially viable regions |
| Service Scope | Comprehensive, including training, advisory, and input supply | Targeted, often specialized in inputs and technology |
| Cost to Farmers | Free or subsidized | Fee-based or dependent on product sales |
| Accountability | Public accountability and transparency | Accountable to customers and shareholders |
| Innovation Adoption | Slower, constrained by bureaucracy | Faster, driven by competition |
| Examples | Government Departments of Agriculture | Agri-input companies, private consultancies |
Overview of Agricultural Extension Services
Public extension services in agriculture primarily focus on providing broad access to knowledge, training, and resources to smallholder farmers, emphasizing sustainability and public good. Private extension services often offer specialized, market-driven advice and innovations tailored to commercial farmers, leveraging advanced technologies and input supply networks. Both systems play complementary roles in enhancing agricultural productivity, with public services targeting inclusivity and private services driving efficiency and innovation.
Evolution of Public and Private Extension Models
Public agricultural extension services have historically prioritized broad-based outreach, focusing on smallholder farmers through government-backed programs emphasizing capacity building and sustainability. In contrast, private extension models have evolved to deliver specialized, market-driven services tailored to commercial farmers, leveraging technology and agribusiness partnerships for efficiency and innovation. The convergence of these models is fostering hybrid approaches that combine public sector inclusivity with private sector expertise to enhance agricultural productivity and rural livelihoods.
Funding Sources and Sustainability in Extension Services
Public extension services primarily rely on government funding and grants, ensuring broader accessibility but often facing budget constraints that affect long-term sustainability. Private extension services attract investment through fees, corporate sponsorships, and agribusiness partnerships, enabling more specialized and market-driven outreach. Sustainable extension models often integrate public-private partnerships to balance funding stability with innovation and responsiveness to farmers' needs.
Accessibility: Reaching Diverse Farmer Populations
Public extension services provide widespread accessibility by targeting smallholder and marginalized farmers through government-funded programs, ensuring rural and remote areas receive crucial agricultural support. Private extension services often focus on commercially viable farmers and regions with higher profitability, leveraging market-driven approaches but sometimes limiting reach to less accessible populations. Combining both models can enhance overall outreach, maximizing accessibility across diverse farmer populations with tailored services and resources.
Quality and Specialization of Advisory Services
Public extension services often provide broad, generalized advisory support aimed at smallholder farmers, emphasizing accessibility and coverage but sometimes lacking in-depth specialization. Private extension services typically offer higher-quality, specialized advice tailored to commercial farmers' specific needs, leveraging expert knowledge and advanced technologies. This specialization enhances targeted solutions, improving productivity and resource management outcomes in agricultural outreach.
Cost Implications for Farmers
Public extension services typically offer low-cost or free advisory support funded by government budgets, making them accessible to smallholder farmers with limited financial resources. Private extension services often involve higher fees as they operate on a profit basis, targeting commercial farmers who can invest in specialized expertise and innovative technologies. Cost implications influence farmers' decisions, where public services enhance inclusion and reach, while private services provide tailored, market-driven solutions at a premium.
Technology Adoption and Innovation Transfer
Public extension services prioritize widespread access to agricultural technology adoption, leveraging government resources to support smallholder farmers with outreach programs focused on sustainability and food security. Private extension services drive innovation transfer through targeted, market-oriented approaches, emphasizing profitability and tailored solutions for commercial farmers using advanced digital tools. Both models play complementary roles, where public services ensure inclusivity and equity, while private services accelerate technology diffusion and innovation with specialized expertise.
Collaboration and Partnership Opportunities
Public extension services often leverage government resources and local expertise to foster broad-based agricultural outreach, emphasizing collaboration with universities, non-profits, and farmer cooperatives. Private extension services bring innovation through market-driven approaches and specialized knowledge, creating opportunities for partnerships with agribusinesses and technology providers to enhance service delivery. Strategic alliances between public and private entities can maximize resource efficiency, expand reach, and improve technology adoption among farmers.
Monitoring, Evaluation, and Accountability Measures
Public extension services implement comprehensive monitoring and evaluation frameworks to ensure accountability and widespread outreach, often funded by government resources. Private extension services prioritize targeted, results-driven approaches with data analytics and client feedback mechanisms to enhance service efficiency and impact. Both sectors emphasize transparency and continuous improvement but differ in scale and resource allocation for accountability measures.
Policy Impacts and Future Directions in Extension Services
Public extension services, often funded by government policies, prioritize widespread accessibility and aim to support smallholder farmers through subsidized training and resources, promoting inclusive agricultural development. Private extension services focus on market-driven approaches, leveraging technology and innovation to offer specialized advisory tailored to commercial farming enterprises, influencing policy shifts towards public-private partnerships. Future directions emphasize integrating digital tools and policy reforms to enhance collaboration, efficiency, and scalability between public and private extension models for sustainable agricultural outreach.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Models
Pluralistic extension models combine public extension services, which offer broad outreach and focus on smallholder farmers, with private extension services that provide specialized, market-driven advisory tailored to commercial agriculture. This integrated approach enhances the accessibility, relevance, and sustainability of agricultural knowledge transfer, leveraging the strengths of both sectors to improve farmer productivity and rural livelihoods.
Outcome-driven Advisory Services
Public extension services prioritize widespread accessibility and government-funded outreach, ensuring smallholder farmers receive essential knowledge and resources, while private extension services emphasize outcome-driven advisory tailored to market demands and profitability. Integrating data analytics and client feedback, private advisors optimize customized solutions that enhance productivity and sustainability, complementing the broad, inclusive coverage of public programs.
Fee-for-Service Extension
Public extension services often prioritize broad accessibility and government-funded programs to support smallholder farmers, while private extension services emphasize fee-for-service models targeting commercial clients with specialized expertise. Fee-for-service extension fosters innovation and accountability by linking service quality directly to client payment, but may limit access for resource-poor farmers due to cost barriers.
Digital Agro-Advisory Platforms
Public extension services provide widespread access to digital agro-advisory platforms, leveraging government support to offer free or low-cost agricultural information and training to smallholder farmers. Private extension services focus on specialized, subscription-based digital tools that deliver tailored advice, leveraging advanced analytics and real-time data to optimize farm productivity and profitability.
Demand-led Extension Approaches
Public extension services traditionally offer broad, subsidized outreach focusing on smallholder farmers, emphasizing capacity building and sustainability, while private extension services prioritize demand-led extension approaches tailored to market-driven clients with customized solutions and innovation adoption. Demand-led extension improves efficiency by aligning technical support with farmers' specific needs and commercial opportunities, fostering competitive agriculture and better resource allocation.
Public-Private Partnership Extension (PPPE)
Public extension services primarily focus on broad-reaching agricultural education and resource dissemination to smallholder farmers, ensuring equitable access to technology and knowledge. Public-Private Partnership Extension (PPPE) leverages combined resources and expertise from both sectors to enhance outreach efficiency, customize solutions for diverse farming needs, and foster innovation adoption in rural communities.
Extension Service Monetization
Public extension services prioritize broad accessibility and knowledge dissemination funded by government budgets, ensuring equitable outreach to smallholder farmers but often facing resource constraints. Private extension services focus on specialized, market-driven solutions with monetization strategies that enhance service quality and innovation but may limit access for low-income farmers.
Agro-Infomediaries
Public extension services offer widespread access to agricultural knowledge, emphasizing smallholder farmers and rural development through government-funded programs. Private extension services, driven by commercial interests, focus on agro-infomediaries that facilitate technology transfer and market access, enhancing efficiency and customization for agribusiness stakeholders.
Customized Knowledge Transfer
Public extension services emphasize broad dissemination of standardized agricultural practices to support smallholder farmers, while private extension services focus on delivering customized, market-driven knowledge transfer tailored to specific client needs. Customized knowledge transfer in private services enhances precision agriculture adoption by addressing individual farm challenges and leveraging advanced technologies for optimized productivity.
Last-mile Outreach Solutions
Public extension services offer widespread access to agricultural knowledge, leveraging government resources to reach smallholder farmers often underserved by markets, while private extension services focus on tailored, market-driven solutions with advanced technologies for efficient last-mile outreach. Combining the scalability of public networks with the innovation and customization of private providers enables comprehensive last-mile outreach that enhances farmer adoption of sustainable practices and improves productivity.
Public extension services vs Private extension services for outreach Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com