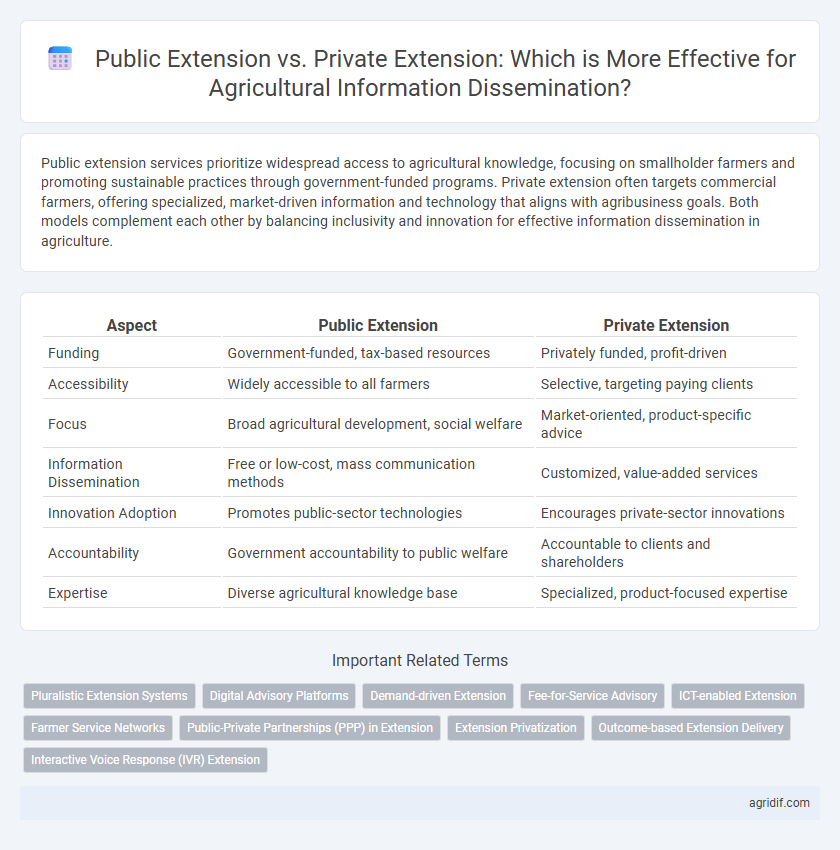
Public extension services prioritize widespread access to agricultural knowledge, focusing on smallholder farmers and promoting sustainable practices through government-funded programs. Private extension often targets commercial farmers, offering specialized, market-driven information and technology that aligns with agribusiness goals. Both models complement each other by balancing inclusivity and innovation for effective information dissemination in agriculture.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Public Extension | Private Extension |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government-funded, tax-based resources | Privately funded, profit-driven |
| Accessibility | Widely accessible to all farmers | Selective, targeting paying clients |
| Focus | Broad agricultural development, social welfare | Market-oriented, product-specific advice |
| Information Dissemination | Free or low-cost, mass communication methods | Customized, value-added services |
| Innovation Adoption | Promotes public-sector technologies | Encourages private-sector innovations |
| Accountability | Government accountability to public welfare | Accountable to clients and shareholders |
| Expertise | Diverse agricultural knowledge base | Specialized, product-focused expertise |
Overview of Public and Private Extension Systems
Public extension systems are government-funded programs designed to provide farmers with unbiased, research-based information and services, ensuring widespread access regardless of economic status. Private extension systems operate through agribusinesses or NGOs, offering specialized, market-driven advice and technologies, often tailored to clients who can afford paid services. Both systems play complementary roles in agricultural innovation diffusion, with public extension emphasizing inclusivity and private extension focusing on efficiency and customization.
Key Differences in Extension Service Delivery
Public extension services typically operate through government agencies, providing free or subsidized agricultural information aimed at smallholder farmers, ensuring wide coverage and focus on social welfare. Private extension services, delivered by agribusinesses or private consultants, prioritize profit-driven models, targeting commercial farmers with tailored advice and advanced technology adoption. Key differences include funding sources, target clientele, service scope, and emphasis on innovation versus inclusivity in extension service delivery.
Funding Models: Public vs Private Extension
Public extension services primarily rely on government funding and international donor agencies, ensuring widespread access to agricultural information for smallholder farmers. In contrast, private extension models depend on subscription fees, agribusiness partnerships, and commercial services, often targeting profit-driven innovations for larger-scale producers. The funding structure significantly influences the reach, affordability, and customization of information dissemination within agricultural extension systems.
Accessibility and Reach of Extension Services
Public extension services offer widespread accessibility by leveraging government funding to reach remote and marginalized farming communities, ensuring equitable information dissemination. Private extension providers often target commercially viable regions and crops, potentially limiting reach but delivering specialized, market-driven advice. Combining both approaches can enhance overall coverage and cater to diverse agricultural needs across different demographics.
Quality and Reliability of Information Dissemination
Public extension services typically offer higher reliability in information dissemination due to government oversight and standardized training of extension agents. Private extension providers often prioritize market-driven approaches, which can lead to faster innovation but may vary in the quality and consistency of the information shared. Combining public and private extension methods can enhance the overall quality and accessibility of agricultural knowledge for farmers.
Role in Technology Adoption and Innovation Transfer
Public extension services play a crucial role in technology adoption by providing widespread access to research-based information and ensuring equitable dissemination to smallholder farmers. Private extension often drives innovation transfer through market-oriented approaches, leveraging commercial incentives to introduce advanced technologies and customized solutions to farmers. Combining public and private extension efforts enhances the scalability and sustainability of agricultural innovations, accelerating overall technology adoption rates.
Efficiency and Responsiveness to Farmer Needs
Public agricultural extension systems often face challenges in efficiency due to limited resources and bureaucratic constraints, which can delay the dissemination of critical information to farmers. Private extension services typically demonstrate higher responsiveness by offering tailored advice and innovative solutions that directly address specific farmer needs, leveraging market incentives to improve service quality. Efficient information flow in private extension enhances timely decision-making, while public extension ensures broader access and inclusivity, highlighting a complementary role in agricultural knowledge transfer.
Accountability and Monitoring Mechanisms
Public agricultural extension services emphasize strong accountability through government oversight, ensuring transparent information dissemination and adherence to national agricultural policies. Private extension providers often implement performance-based monitoring systems, utilizing client feedback and market-driven metrics to enhance service quality and responsiveness. Effective integration of both public and private monitoring mechanisms can lead to improved accountability and more targeted agricultural information delivery.
Collaboration and Partnerships in Extension Services
Collaboration between public and private extension services enhances agricultural information dissemination by leveraging government resources and private sector innovation. Public extension programs often provide widespread access and regulatory support, while private entities contribute specialized knowledge, technology, and market-driven solutions. Partnerships between these sectors foster integrated approaches, improve outreach efficiency, and promote sustainable agricultural development.
Future Trends: Integrating Public and Private Approaches
Future trends in agricultural extension emphasize integrating public and private approaches to enhance information dissemination efficiency and reach. Leveraging digital platforms and mobile technologies enables real-time knowledge sharing, combining public sector credibility with private sector innovation and resource capacity. Collaborative models foster farmer empowerment, sustainable practices, and data-driven decision-making, driving inclusive agricultural development globally.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Systems
Public extension services provide widespread access to essential agricultural knowledge through government-funded programs, ensuring equitable support for smallholder farmers. Private extension offers specialized, market-driven information and innovations, complementing public efforts within pluralistic extension systems to enhance overall productivity and farmer empowerment.
Digital Advisory Platforms
Public extension systems leverage government resources to provide broad access to digital advisory platforms, enhancing smallholder farmers' ability to obtain unbiased, region-specific agricultural information. In contrast, private extension services often deliver tailored, subscription-based digital tools funded by agribusinesses, focusing on precision agriculture and market-driven insights for commercial farmers.
Demand-driven Extension
Public extension services traditionally provide broad access to agricultural information but often lack responsiveness to specific farmer demands, while private extension providers tailor solutions to individual needs, driving demand-driven extension models through targeted, market-oriented approaches that enhance farmer engagement and technology adoption. Demand-driven extension emphasizes customized advisory services, leveraging real-time market data and farmer feedback to optimize resource allocation and improve productivity outcomes in both public and private sectors.
Fee-for-Service Advisory
Public extension services primarily offer free or subsidized agricultural advisory to smallholder farmers, enabling widespread access to knowledge and innovations, whereas private extension operates on a fee-for-service model that targets commercial farmers willing to pay for specialized, timely information and tailored recommendations. Fee-for-service advisory systems enhance accountability and efficiency in information dissemination by incentivizing quality consultations but may limit reach among resource-constrained farmers who cannot afford the service fees.
ICT-enabled Extension
Public extension services leverage ICT platforms such as mobile apps, SMS, and radio broadcasts to provide unbiased, widespread access to agricultural knowledge, ensuring inclusivity for smallholder and marginalized farmers. Private extension firms utilize advanced digital tools, including AI-driven advisory apps and online marketplaces, offering specialized, timely information tailored to commercial farmers' specific needs for enhanced productivity and market access.
Farmer Service Networks
Public extension services leverage government resources to provide wide-reaching, subsidized agricultural information, ensuring accessibility for smallholder farmers through Farmer Service Networks. Private extension, driven by agribusinesses and NGOs, offers specialized, market-oriented advice and technologies, often facilitated by Farmer Service Networks that enhance targeted, demand-driven dissemination.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in Extension
Public extension services, traditionally funded by governments, focus on broad-reaching agricultural knowledge dissemination, while private extension providers emphasize specialized, market-driven solutions. Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in extension leverage the strengths of both sectors, combining public accessibility with private innovation to enhance farmer outreach, technology adoption, and sustainable agricultural development.
Extension Privatization
Extension privatization in agricultural information dissemination shifts service delivery from public agencies to private entities, enhancing efficiency and innovation but potentially limiting smallholder access due to cost barriers. This model leverages market-driven approaches to tailor advisory services, emphasizing profitability and client responsiveness over universal coverage.
Outcome-based Extension Delivery
Public extension services often prioritize broad accessibility and equity in agricultural knowledge dissemination, using outcome-based delivery to improve smallholder productivity and sustainability. Private extension focuses on market-driven approaches, enhancing specific crop or technology adoption outcomes by tailoring information to farmer profitability and input provider objectives.
Interactive Voice Response (IVR) Extension
Public extension systems often have broader reach and subsidized access to Interactive Voice Response (IVR) services, facilitating large-scale dissemination of agricultural information to smallholder farmers. Private extension providers typically offer more tailored IVR solutions with advanced analytics and personalized advisory services, enhancing decision-making but at higher costs.
Public extension vs Private extension for information dissemination Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com