Export markets demand strict adherence to quality standards and certifications, offering higher profit margins for agricultural produce. Domestic markets provide easier access and lower transportation costs but often face limited price premiums and seasonal demand fluctuations. Strategic distribution balances these factors to maximize revenue and market reach for farmers and agribusinesses.
Table of Comparison
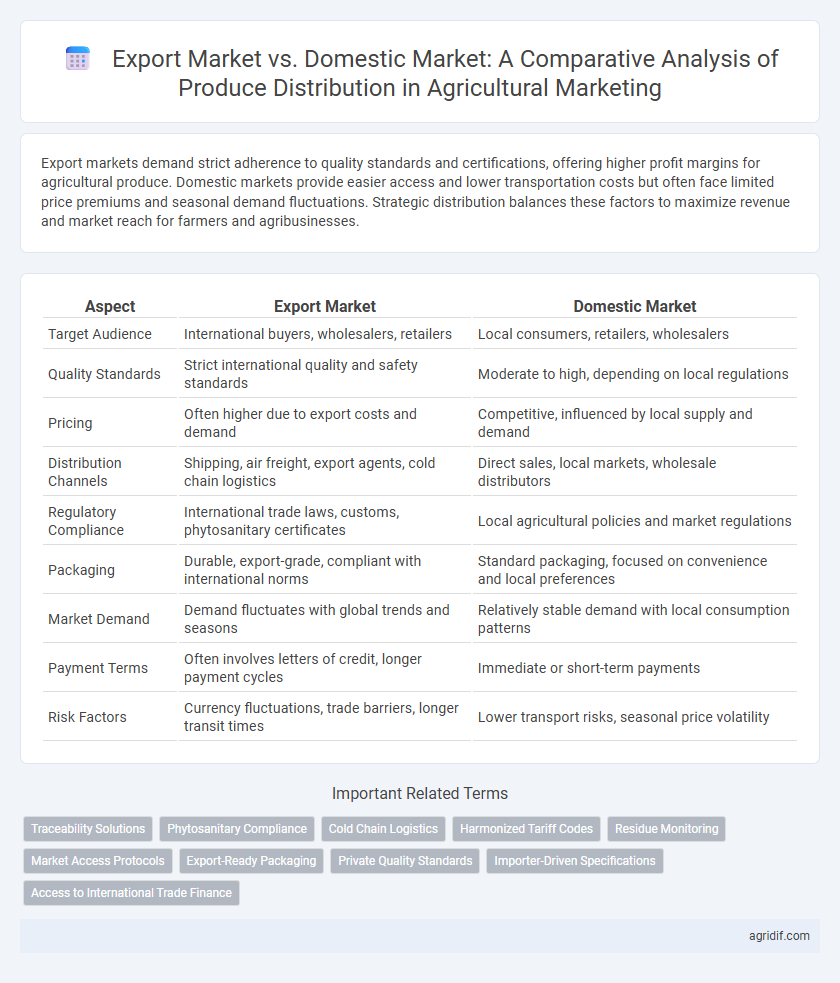
| Aspect | Export Market | Domestic Market |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | International buyers, wholesalers, retailers | Local consumers, retailers, wholesalers |
| Quality Standards | Strict international quality and safety standards | Moderate to high, depending on local regulations |
| Pricing | Often higher due to export costs and demand | Competitive, influenced by local supply and demand |
| Distribution Channels | Shipping, air freight, export agents, cold chain logistics | Direct sales, local markets, wholesale distributors |
| Regulatory Compliance | International trade laws, customs, phytosanitary certificates | Local agricultural policies and market regulations |
| Packaging | Durable, export-grade, compliant with international norms | Standard packaging, focused on convenience and local preferences |
| Market Demand | Demand fluctuates with global trends and seasons | Relatively stable demand with local consumption patterns |
| Payment Terms | Often involves letters of credit, longer payment cycles | Immediate or short-term payments |
| Risk Factors | Currency fluctuations, trade barriers, longer transit times | Lower transport risks, seasonal price volatility |
Overview of Export and Domestic Produce Markets
Export produce markets generate significant revenue by accessing international demand, often requiring compliance with global quality standards and stringent packaging regulations. Domestic markets prioritize freshness and quick distribution, leveraging established local supply chains to meet consumer preferences and seasonal variability. Both markets influence pricing strategies and distribution logistics, impacting overall agricultural profitability and sustainability.
Key Differences Between Export and Domestic Distribution
Export market distribution involves navigating complex international regulations, tariffs, and longer supply chains, contrasting with domestic market distribution's simpler logistics and regulatory frameworks. Quality standards and packaging requirements are typically more stringent for exports to meet diverse consumer preferences and legal mandates abroad. Pricing strategies also differ significantly, as export markets must account for currency fluctuations, transportation costs, and competitive global pricing.
Market Access Requirements and Regulations
Export markets impose stringent access requirements including phytosanitary certifications, quality standards, and traceability systems to ensure produce meets international regulations and consumer safety. Domestic markets often have less complex regulatory demands but emphasize compliance with national food safety laws and packaging standards tailored to local preferences. Efficient navigation of these regulations determines competitive advantage and market penetration for agricultural producers.
Pricing Strategies in Export vs Domestic Markets
Pricing strategies for agricultural produce differ significantly between export and domestic markets due to factors such as currency fluctuations, tariff barriers, and varying consumer purchasing power. Export market pricing often incorporates additional costs like international shipping, compliance with foreign regulations, and competitive positioning against global suppliers, resulting in higher price points compared to domestic markets. Domestic market pricing strategies prioritize volume sales, local demand elasticity, and shorter supply chains, enabling more flexible and competitive price adjustments.
Quality Standards and Certifications Demanded
Export markets for agricultural produce require stringent quality standards and internationally recognized certifications such as GlobalGAP, Organic, and HACCP to ensure safety, traceability, and consumer confidence. Domestic markets often have more varied quality requirements depending on regional regulations but typically demand certifications like ISO 22000 and local food safety approvals to assure product integrity. Meeting these standards directly influences market access, pricing, and brand reputation in both export and domestic distribution channels.
Logistics and Supply Chain Challenges
Export market distribution for agricultural produce faces complex logistics challenges such as stringent customs regulations, longer transit times, and the need for cold chain infrastructure to maintain product freshness across international borders. Domestic market supply chains prioritize speed and flexibility, with shorter transportation routes and less regulatory burden but often lack advanced storage facilities that are critical for perishables. Efficient coordination between growers, transporters, and retailers is essential in both markets to reduce spoilage, minimize costs, and ensure timely delivery.
Consumer Preferences and Demand Trends
Consumer preferences in the export market often prioritize consistent quality standards, exotic varieties, and sustainable packaging, driving producers to adopt advanced grading and certification processes. Domestic market demand trends tend to favor freshness, local varieties, and cost-effectiveness, influencing distribution strategies to emphasize speed and regional sourcing. Understanding these distinct preferences enables agricultural marketers to tailor supply chains, optimize pricing, and enhance competitive positioning across both markets.
Role of Government Policies and Support
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the distribution strategies between export and domestic markets by providing subsidies, trade incentives, and infrastructure development specifically targeting agricultural producers. Export market expansion benefits from policies that reduce tariffs, streamline certification processes, and promote international trade agreements, enhancing competitiveness and global reach. Domestic market support focuses on stabilizing prices, improving supply chain logistics, and ensuring food security through regulatory frameworks and direct assistance to farmers.
Profit Margins and Revenue Potential Comparison
Export markets typically offer higher profit margins for agricultural produce due to premium pricing linked to quality standards and international demand. Domestic markets, while providing lower revenue potential per unit, benefit from reduced logistics and tariff costs, leading to faster turnover and steady cash flow. Producers must balance export complexities with domestic market stability to optimize overall profitability in agricultural marketing.
Risk Factors in Export and Domestic Produce Marketing
Export market for agricultural produce faces significant risk factors including currency fluctuations, stringent international quality standards, and complex logistics that can lead to delays and spoilage. Domestic markets encounter risks such as seasonal price volatility, local pest outbreaks, and inadequate storage infrastructure, impacting timely distribution. Understanding these distinct risk profiles is essential for producers to develop tailored marketing and risk mitigation strategies for each market type.
Related Important Terms
Traceability Solutions
Export market demands stringent traceability solutions to comply with international food safety standards and enhance consumer trust, using advanced technologies like blockchain and IoT for real-time tracking. Domestic market traceability focuses on regulatory compliance and quality assurance, often leveraging simpler systems to ensure produce origin and handling transparency.
Phytosanitary Compliance
Export market distribution requires stringent phytosanitary compliance to meet international quarantine regulations and prevent the spread of pests and diseases, ensuring produce quality and market access. Domestic markets often have less rigorous phytosanitary standards, allowing faster distribution but with increased risk of pest proliferation affecting local crops.
Cold Chain Logistics
Efficient cold chain logistics enhance produce quality preservation, reducing post-harvest losses in both export and domestic markets, but export markets demand stricter temperature controls and compliance with international standards. Investment in advanced refrigeration technology and real-time monitoring systems ensures freshness and extends shelf life, crucial for competitive positioning in global supply chains versus cost-sensitive domestic distribution channels.
Harmonized Tariff Codes
Harmonized Tariff Codes play a critical role in agricultural marketing by streamlining customs processes and reducing barriers in the export market compared to the domestic market, where such codes are less emphasized. Accurate classification under Harmonized Tariff Codes ensures competitive pricing, compliance with international trade regulations, and efficient distribution channels for fresh produce in global markets.
Residue Monitoring
Export markets for agricultural produce demand stringent residue monitoring to comply with international food safety standards such as the Codex Alimentarius, ensuring pesticide and chemical levels are within allowable limits. Domestic markets often have varying residue regulations, but increasingly adopt rigorous monitoring to safeguard consumer health and enhance market competitiveness.
Market Access Protocols
Export market access for agricultural produce requires compliance with stringent international market access protocols, including phytosanitary certifications, quality standards, and traceability systems, which often surpass domestic market regulations. Domestic market distribution benefits from more flexible protocols and lower barriers, enabling faster produce turnover, but offers limited revenue growth compared to export markets driven by global demand and premium pricing.
Export-Ready Packaging
Export-ready packaging in agricultural marketing ensures produce meets international standards for durability, shelf-life, and safety, enhancing marketability in export markets. In contrast, domestic market packaging prioritizes cost-effectiveness and convenience, often with less stringent requirements due to shorter transportation distances and quicker turnover.
Private Quality Standards
Private quality standards in agricultural marketing often play a crucial role in distinguishing export markets from domestic markets, with export markets typically demanding stricter certification and compliance to meet international buyer requirements. These enhanced private quality standards ensure consistent produce quality, reduce post-harvest losses, and improve market access, whereas domestic markets may have more lenient quality benchmarks reflecting local consumer preferences and regulatory frameworks.
Importer-Driven Specifications
Export markets impose stringent importer-driven specifications, including quality standards, packaging requirements, and traceability protocols that often exceed those in domestic markets. Compliance with these detailed criteria ensures access to international buyers while domestic markets typically allow more flexibility in produce grading and distribution methods.
Access to International Trade Finance
Access to international trade finance enhances exporters' ability to manage cash flow, mitigate risks, and invest in scaling production for global markets, contrasting with domestic market sales that typically rely on local financial institutions with limited cross-border financing options. Exporters benefit from specialized instruments such as export credit guarantees and foreign exchange hedging, which are less prevalent in domestic trade, enabling smoother distribution and competitive pricing in international agricultural markets.
Export Market vs Domestic Market for produce distribution Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com