Dry spell analysis provides critical data on prolonged periods without rainfall, guiding farmers on the risks of soil moisture deficits that can hinder seed germination. Wet spell analysis helps identify periods of excessive rainfall that might cause waterlogging or soil erosion, impacting seed placement and crop establishment. Understanding both dry and wet spells enables optimized sowing schedules, improving crop resilience and yield outcomes.
Table of Comparison
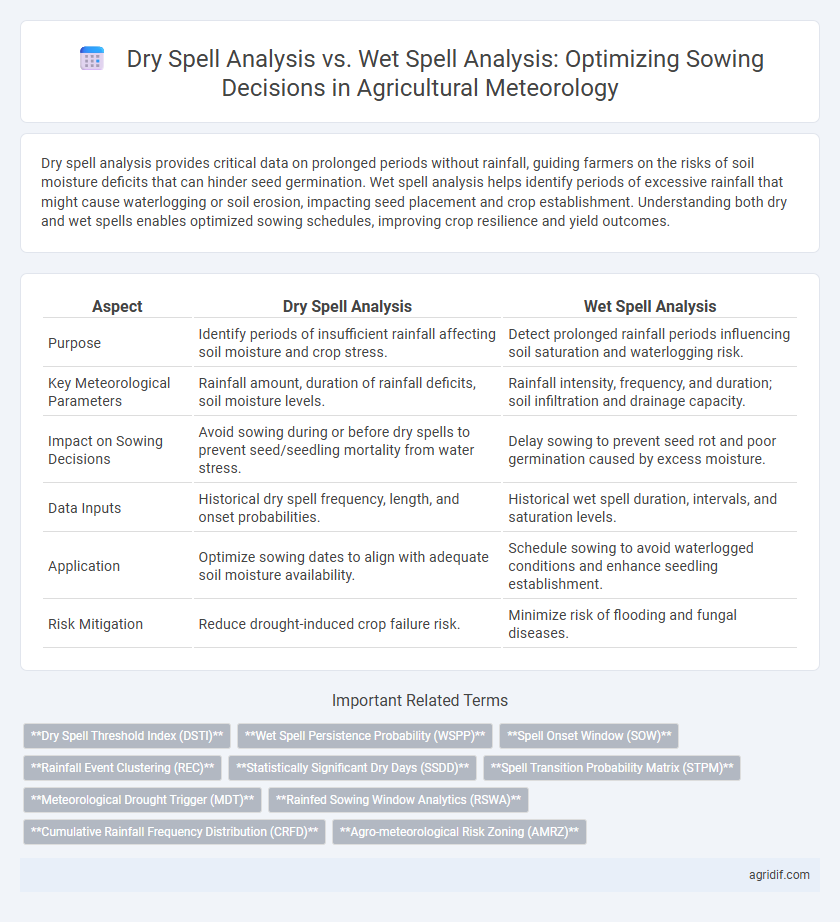
| Aspect | Dry Spell Analysis | Wet Spell Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify periods of insufficient rainfall affecting soil moisture and crop stress. | Detect prolonged rainfall periods influencing soil saturation and waterlogging risk. |
| Key Meteorological Parameters | Rainfall amount, duration of rainfall deficits, soil moisture levels. | Rainfall intensity, frequency, and duration; soil infiltration and drainage capacity. |
| Impact on Sowing Decisions | Avoid sowing during or before dry spells to prevent seed/seedling mortality from water stress. | Delay sowing to prevent seed rot and poor germination caused by excess moisture. |
| Data Inputs | Historical dry spell frequency, length, and onset probabilities. | Historical wet spell duration, intervals, and saturation levels. |
| Application | Optimize sowing dates to align with adequate soil moisture availability. | Schedule sowing to avoid waterlogged conditions and enhance seedling establishment. |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduce drought-induced crop failure risk. | Minimize risk of flooding and fungal diseases. |
Introduction to Agricultural Meteorology and Crop Sowing
Dry spell analysis assesses periods of insufficient rainfall critical for identifying drought risks during crop growth stages, guiding sowing decisions to avoid water stress. Wet spell analysis examines prolonged rainfall patterns influencing soil moisture and disease prevalence, helping farmers optimize sowing timing for maximum crop establishment and yield. Integrating these meteorological insights enhances precision in agricultural planning by aligning sowing schedules with climatic conditions.
Understanding Dry Spells in Agriculture
Dry spell analysis in agricultural meteorology involves identifying periods of below-average precipitation critical for assessing soil moisture deficits that directly impact seed germination and crop establishment. Understanding dry spells helps farmers optimize sowing schedules by avoiding planting during extended dry periods, thereby reducing the risk of crop failure and improving yield stability. Precise monitoring of dry spells complements wet spell data to create balanced sowing decisions that align with regional climate patterns and soil water availability.
Wet Spells: Definition and Impact on Cropping
Wet spells, defined as consecutive days with rainfall exceeding a specific threshold, critically influence sowing decisions by affecting soil moisture availability and seed germination rates. Extended wet spells enhance soil infiltration and nutrient mobility but may also increase the risk of waterlogging, which can delay planting and reduce crop emergence. Accurate wet spell analysis supports optimized scheduling of sowing to maximize crop yield potential by aligning planting with favorable moisture conditions.
Methodologies for Dry Spell Analysis
Dry spell analysis in agricultural meteorology primarily utilizes threshold-based methods and statistical techniques such as Markov chains and Weibull distribution to identify and predict periods of consecutive dry days crucial for sowing decisions. These methodologies assess dry spell duration, frequency, and intensity by analyzing historical rainfall data and employing temporal rainfall occurrence sequences to determine drought risk during critical crop growth stages. Accurate dry spell predictions help optimize sowing times, minimize crop stress, and improve water resource management in rainfed agriculture.
Techniques for Wet Spell Analysis
Wet spell analysis in agricultural meteorology employs statistical methods like the Weibull distribution and Markov chain models to predict the frequency and duration of wet periods critical for sowing decisions. Remote sensing technologies and rainfall time series data enhance the accuracy of identifying optimal wet spells, ensuring precise timing for seed germination and crop establishment. Incorporating these techniques improves risk assessment and supports adaptive farming strategies in variable climatic conditions.
Comparative Importance: Dry vs Wet Spell Analysis
Dry spell analysis is crucial for assessing the risk of water stress during critical crop growth stages, directly influencing sowing decisions to avoid periods prone to drought. Wet spell analysis helps identify excessive moisture conditions that may lead to waterlogging and hinder seed germination or root development. Comparing both, dry spell analysis often takes priority in semi-arid regions due to its impact on irrigation planning and drought resilience, while wet spell analysis is vital in humid areas to prevent crop failure from flooding.
Role of Meteorological Data in Sowing Decisions
Meteorological data plays a crucial role in dry spell and wet spell analysis for sowing decisions by providing accurate temporal patterns of precipitation and soil moisture levels essential for crop germination. Dry spell analysis helps identify periods of insufficient rainfall that can risk seedling establishment, while wet spell analysis determines optimal planting windows to ensure adequate water availability. Integrating these analyses with temperature and humidity data enhances the precision of sowing schedules, improving crop yield and resource efficiency.
Case Studies: Sowing Outcomes under Different Spell Conditions
Dry spell analysis in agricultural meteorology critically informs sowing decisions by predicting periods of moisture deficit, enabling farmers to avoid planting during high drought risk windows. Wet spell analysis complements this by identifying optimal moisture conditions that support germination and early crop growth, reducing the likelihood of water stress. Case studies in regions such as the Indo-Gangetic Plain demonstrate that sowing during identified wet spells significantly increases seedling survival rates, while avoiding dry spells minimizes crop failure and enhances yield stability.
Integrating Spell Analysis into Decision Support Tools
Integrating dry and wet spell analysis into agricultural decision support tools enhances precision in sowing time predictions by leveraging historical climate data and real-time weather forecasts. These tools analyze patterns of consecutive dry or wet days, enabling farmers to optimize planting windows and mitigate risks of seedling stress or crop failure. Incorporation of spell metrics into predictive models supports adaptive management strategies tailored to local agroclimatic conditions, improving overall crop yield reliability.
Future Perspectives in Meteorological Sowing Advisories
Dry spell analysis provides critical insights into periods of water deficit, aiding in optimizing sowing schedules to minimize crop stress and maximize yield potential. Wet spell analysis evaluates consecutive rainfall events, helping forecast soil moisture availability and reduce the risk of waterlogging during germination. Future perspectives in meteorological sowing advisories emphasize integrating high-resolution climate models and remote sensing data to enhance the precision and timeliness of dry and wet spell forecasts for adaptive agricultural decision-making.
Related Important Terms
Dry Spell Threshold Index (DSTI)
Dry Spell Threshold Index (DSTI) quantitatively measures consecutive dry days to assess the risk of moisture deficiency critical for timely sowing decisions in agricultural meteorology. DSTI helps farmers optimize crop germination by identifying the minimum dry period thresholds, ensuring seeds are sown during favorable moisture conditions to maximize yield potential.
Wet Spell Persistence Probability (WSPP)
Wet Spell Persistence Probability (WSPP) is a critical metric in agricultural meteorology used to assess the likelihood of continuous wet periods, which directly influence sowing decisions by indicating suitable conditions for seed germination and early crop establishment. Accurate estimation of WSPP enables farmers to optimize sowing schedules, minimize the risk of seed rot due to prolonged moisture, and enhance overall crop yield by aligning planting times with favorable wet spell durations.
Spell Onset Window (SOW)
Spell Onset Window (SOW) defines the critical period for identifying the start of dry and wet spells, directly influencing optimal sowing dates by signaling moisture availability for seed germination. Precise analysis of SOW allows farmers to improve crop establishment and minimize drought or waterlogging risks through timely agricultural interventions.
Rainfall Event Clustering (REC)
Rainfall Event Clustering (REC) plays a critical role in both Dry Spell and Wet Spell Analysis by identifying patterns of consecutive rainfall days, which directly influence soil moisture availability for sowing decisions. Analyzing REC helps optimize sowing windows by predicting dry or wet spell durations, ensuring crops are planted under favorable moisture conditions to enhance germination and early growth.
Statistically Significant Dry Days (SSDD)
Statistically Significant Dry Days (SSDD) play a critical role in dry spell analysis for sowing decisions by identifying periods with prolonged moisture deficits that can adversely affect seed germination and crop establishment. In contrast, wet spell analysis focuses on rainfall patterns that inform irrigation scheduling and flood risk, but SSDD specifically helps optimize sowing windows by minimizing drought stress during early crop stages.
Spell Transition Probability Matrix (STPM)
Spell Transition Probability Matrix (STPM) quantifies the likelihood of transitioning between dry and wet spells, providing critical insights for optimizing sowing schedules in agricultural meteorology. By analyzing STPM, farmers can predict the duration and frequency of dry or wet periods, enabling better risk management and enhancing crop yield decisions based on historical weather pattern transitions.
Meteorological Drought Trigger (MDT)
Meteorological Drought Trigger (MDT) is a critical parameter in dry spell analysis, providing precise thresholds for rainfall deficits that influence sowing decisions by predicting periods of moisture stress. Wet spell analysis complements MDT by identifying intervals of adequate precipitation, optimizing irrigation planning and seed germination timing for improved crop establishment.
Rainfed Sowing Window Analytics (RSWA)
Rainfed Sowing Window Analytics (RSWA) leverages dry spell and wet spell analysis to optimize sowing decisions by identifying critical periods of moisture stress and adequate rainfall for crop germination and growth. Understanding the duration and frequency of dry spells alongside wet spells enables precise prediction of the optimal sowing window, minimizing crop failure risk in rainfed agriculture.
Cumulative Rainfall Frequency Distribution (CRFD)
Cumulative Rainfall Frequency Distribution (CRFD) plays a critical role in both Dry Spell Analysis and Wet Spell Analysis by quantifying the probability and persistence of rainfall events essential for optimal sowing timing. Accurate interpretation of CRFD enables farmers to predict dry or wet spells, minimizing crop stress from water deficit or excess, thus enhancing sowing decisions and improving agricultural productivity.
Agro-meteorological Risk Zoning (AMRZ)
Agro-meteorological Risk Zoning (AMRZ) leverages Dry Spell Analysis and Wet Spell Analysis to identify optimal sowing windows by assessing rainfall patterns and drought frequency, thereby minimizing crop failure risks. Integrating these analyses into AMRZ enables precise tailoring of agricultural practices to regional climatic variability, enhancing resilience against weather extremes.
Dry Spell Analysis vs Wet Spell Analysis for Sowing Decisions Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com