Quotas in dairy production regulate supply to stabilize prices and protect farmers' income, preventing market oversupply and price crashes. Free market approaches encourage competition, innovation, and efficiency by allowing producers to respond directly to consumer demand without production limits. Balancing quotas with free market principles can optimize dairy sector sustainability and profitability while ensuring stable food supply.
Table of Comparison
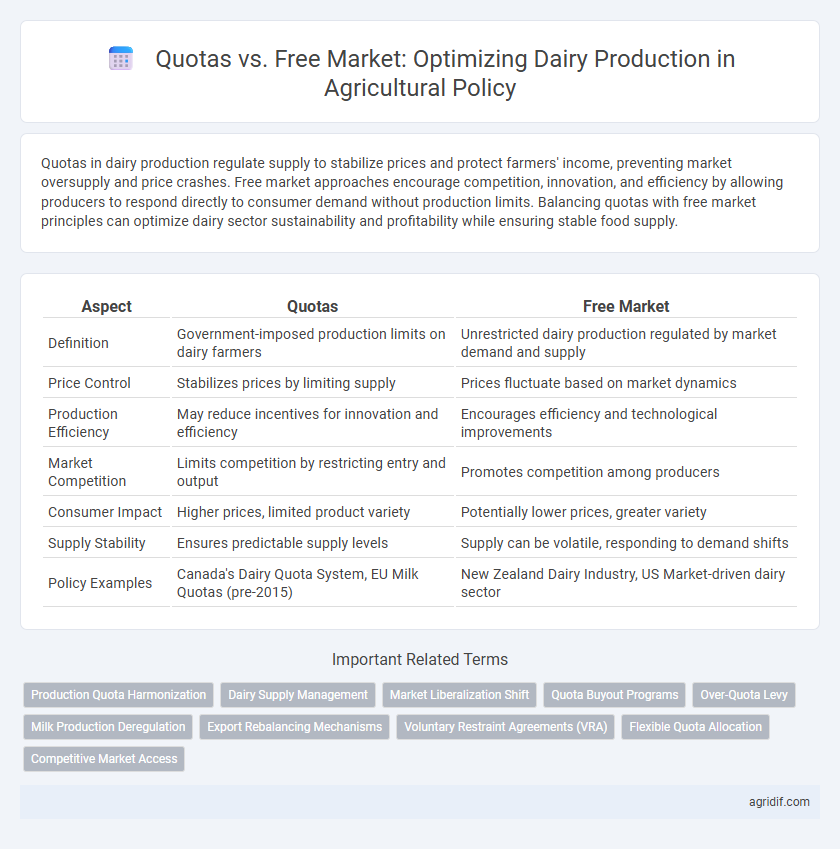
| Aspect | Quotas | Free Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-imposed production limits on dairy farmers | Unrestricted dairy production regulated by market demand and supply |
| Price Control | Stabilizes prices by limiting supply | Prices fluctuate based on market dynamics |
| Production Efficiency | May reduce incentives for innovation and efficiency | Encourages efficiency and technological improvements |
| Market Competition | Limits competition by restricting entry and output | Promotes competition among producers |
| Consumer Impact | Higher prices, limited product variety | Potentially lower prices, greater variety |
| Supply Stability | Ensures predictable supply levels | Supply can be volatile, responding to demand shifts |
| Policy Examples | Canada's Dairy Quota System, EU Milk Quotas (pre-2015) | New Zealand Dairy Industry, US Market-driven dairy sector |
Understanding Dairy Production Policies
Dairy production policies often revolve around the debate between quota systems and free market approaches, with quotas limiting supply to stabilize prices and support farmer incomes. Quota systems, as seen in countries like Canada, directly control milk production volumes to prevent market oversupply and ensure predictable revenue for dairy farmers. In contrast, free market policies promote competition and price fluctuations, allowing producers to respond to consumer demand but potentially resulting in greater income volatility and market instability.
Quotas in Dairy Production: An Overview
Quotas in dairy production regulate the volume of milk farmers are allowed to produce, aiming to stabilize prices and prevent market oversupply. These production limits help maintain consistent income for dairy farmers by controlling supply and supporting fair market conditions. However, quotas can also restrict growth potential and reduce competitiveness in a global free market environment.
The Free Market Approach in Dairy Sector
The free market approach in dairy production allows supply and demand to determine output levels, promoting efficiency and innovation among producers. Without restrictive quotas, dairy farmers can scale production based on market signals, leading to competitive pricing and greater consumer choice. However, this approach may result in price volatility and requires robust risk management strategies to stabilize incomes and supply chains.
Economic Impacts of Dairy Quotas
Dairy quotas limit production, stabilizing prices and providing predictable income for farmers, but they restrict market supply, potentially leading to higher consumer prices and inefficiencies. Free market dairy production encourages competition and innovation, driving down costs and increasing consumer choice but may cause price volatility and financial instability for producers. Economic impacts of dairy quotas include reduced market flexibility and limited growth opportunities, affecting both domestic markets and export competitiveness.
Market Efficiency in Quota vs Free Market Systems
Quota systems in dairy production often lead to reduced market efficiency by limiting supply and causing price distortions, which can result in higher consumer prices and reduced incentives for innovation. Free market systems promote efficient allocation of resources through supply and demand dynamics, encouraging productivity improvements and competitive pricing. Empirical studies indicate that removing quotas enhances overall market responsiveness, increases output, and drives cost reductions in the dairy sector.
Price Stability and Volatility in Dairy Markets
Dairy production quotas help maintain price stability by limiting milk supply, preventing market oversaturation and sharp price declines. Free market systems expose producers to greater price volatility as supply fluctuates with demand, often leading to unpredictable income and market instability. Price stability under quota systems supports consistent profitability but may reduce market efficiency compared to the responsiveness of free market dynamics.
Effects on Dairy Farmers’ Income
Dairy quotas stabilize market prices by limiting production, directly supporting farmers' income stability and preventing oversupply-induced price drops. In contrast, free market systems expose farmers to volatile prices, often resulting in income fluctuations that can threaten the financial viability of smaller dairy operations. Studies show quota systems reduce income risk, whereas free markets incentivize efficiency but can increase economic uncertainty for dairy producers.
Consumer Prices: Quotas vs Free Market
Dairy production quotas stabilize consumer prices by controlling supply and preventing market glut, ensuring steady income for farmers and predictable retail costs. Free market dairy pricing often leads to greater price volatility as supply fluctuates with demand and production levels, which can result in sudden increases or decreases in consumer prices. Data from countries with quota systems, such as Canada, show lower price fluctuations compared to free market systems like the United States, where dairy prices are more sensitive to global commodity shifts.
International Trade Implications
Dairy production quotas restrict output to stabilize prices but limit export potential, affecting global supply chains and trade balances. Free market policies encourage competitive production, fostering greater international trade and market responsiveness but may lead to price volatility and trade disputes. Trade negotiations often hinge on quota regulations, influencing tariff agreements and access to key dairy markets worldwide.
Future Trends in Dairy Production Policies
Emerging trends in dairy production policies emphasize a gradual shift from rigid quotas toward flexible, market-driven mechanisms that incentivize sustainable practices and innovation. Policymakers are increasingly adopting dynamic quota adjustments and tradeable permits to balance production stability with environmental goals. Technological advancements and consumer demand for organic and plant-based alternatives also influence regulatory frameworks shaping the future of dairy markets.
Related Important Terms
Production Quota Harmonization
Production quota harmonization in dairy markets standardizes output limits across regions, preventing overproduction and stabilizing prices while ensuring fair competition among producers. Aligning quotas supports sustainable supply management and mitigates market volatility compared to unregulated free market dynamics.
Dairy Supply Management
Dairy supply management systems utilize production quotas to stabilize milk prices and ensure consistent farmer income, limiting overproduction and market volatility. In contrast, free-market approaches allow unrestricted dairy production, leading to price fluctuations, increased competition, and potential supply gluts that can harm small-scale producers.
Market Liberalization Shift
Market liberalization in dairy production has spurred the gradual dismantling of quotas, fostering increased competition and efficiency in the industry. This shift encourages producers to respond to consumer demand and price signals, promoting innovation and potentially lowering prices.
Quota Buyout Programs
Quota buyout programs in dairy production aim to transition from restrictive quota systems to a free market by compensating farmers for relinquishing production limits, thereby encouraging efficiency and competitive pricing. These programs influence supply dynamics, market stability, and farmer income, playing a critical role in shaping agricultural policy towards deregulation and market responsiveness.
Over-Quota Levy
Over-quota levies impose financial penalties on dairy producers exceeding set production limits, serving as a regulatory tool to control supply and stabilize milk prices within quota systems. In contrast, free market approaches eliminate such levies, allowing producers to respond dynamically to market demand without production caps, potentially increasing efficiency but risking market oversupply and price volatility.
Milk Production Deregulation
Milk production deregulation in dairy markets eliminates quotas, allowing farmers to produce based on market demand and price signals, which often leads to increased supply and competitive pricing. This shift fosters innovation and efficiency but may also cause price volatility and pressure on small-scale producers struggling to compete without quota protections.
Export Rebalancing Mechanisms
Export rebalancing mechanisms in dairy production under quota systems limit supply to stabilize prices but constrain international competitiveness, whereas free market policies promote dynamic export adjustments driven by global demand and price signals. Efficient export rebalancing enhances trade balance, supports farmer income stability, and aligns domestic production with evolving international market trends in the dairy sector.
Voluntary Restraint Agreements (VRA)
Voluntary Restraint Agreements (VRA) in dairy production serve as a strategic tool to balance supply and demand by allowing producers to self-impose quotas, thereby stabilizing prices without strict government intervention. By comparing VRAs to traditional quota systems and free markets, VRAs offer flexibility and reduce market distortions while maintaining industry sustainability and farmer income security.
Flexible Quota Allocation
Flexible quota allocation in dairy production enhances market responsiveness by allowing quotas to be traded or adjusted based on regional demand and supply fluctuations, promoting efficient resource distribution. This system contrasts with rigid quotas by minimizing production bottlenecks and supporting farmers' adaptability to price signals within the free market framework.
Competitive Market Access
Dairy production quotas limit supply, stabilizing prices but restricting market access and competition, which can hinder innovation and efficiency in the sector. Free market policies increase competitive market access by allowing producers to respond to demand signals, fostering innovation, efficiency, and potentially lower consumer prices.
Quotas vs Free Market for Dairy Production Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com