State-led extension services play a crucial role in disseminating agricultural knowledge, ensuring equitable access to resources and innovations for smallholder farmers. In contrast, private advisory services often offer specialized, market-driven expertise that can accelerate technology adoption and enhance productivity among commercial farmers. Balancing both approaches can optimize the reach and effectiveness of agricultural knowledge transfer, fostering sustainable development in the sector.
Table of Comparison
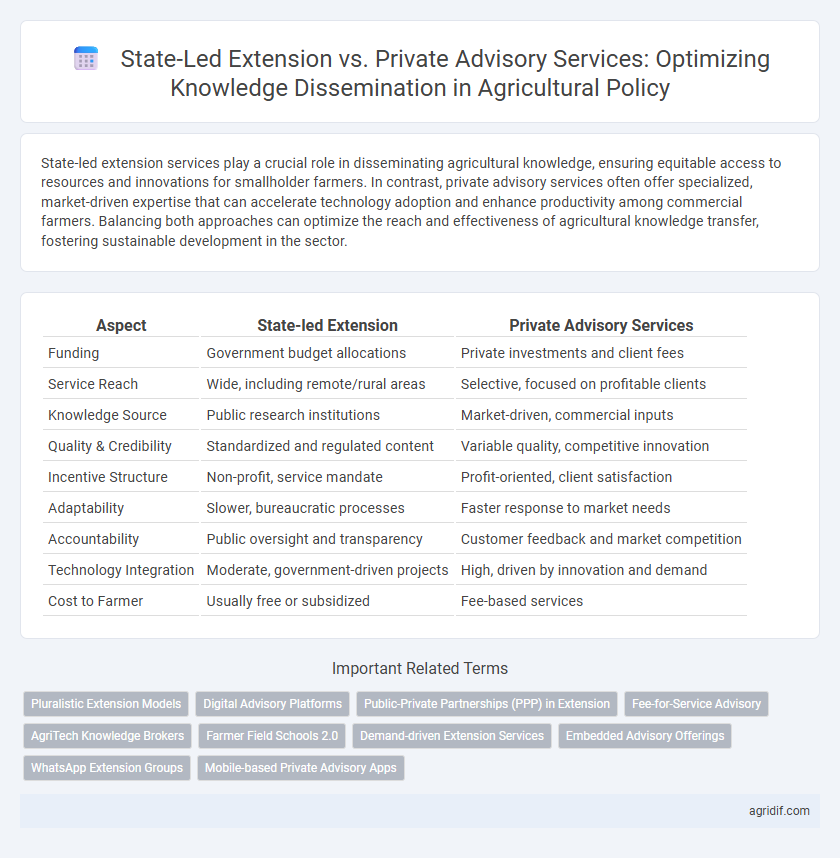
| Aspect | State-led Extension | Private Advisory Services |
|---|---|---|
| Funding | Government budget allocations | Private investments and client fees |
| Service Reach | Wide, including remote/rural areas | Selective, focused on profitable clients |
| Knowledge Source | Public research institutions | Market-driven, commercial inputs |
| Quality & Credibility | Standardized and regulated content | Variable quality, competitive innovation |
| Incentive Structure | Non-profit, service mandate | Profit-oriented, client satisfaction |
| Adaptability | Slower, bureaucratic processes | Faster response to market needs |
| Accountability | Public oversight and transparency | Customer feedback and market competition |
| Technology Integration | Moderate, government-driven projects | High, driven by innovation and demand |
| Cost to Farmer | Usually free or subsidized | Fee-based services |
Overview of Agricultural Knowledge Dissemination Systems
State-led extension services historically dominate agricultural knowledge dissemination by providing publicly funded training, research outputs, and resources aimed at smallholder farmers and rural communities. Private advisory services complement these efforts by offering specialized, market-driven expertise tailored to commercial farmers and agro-enterprises, often emphasizing technology adoption and input optimization. Effective agricultural knowledge dissemination systems integrate both approaches to enhance outreach, innovation diffusion, and farmer empowerment.
State-Led Extension Services: Structures and Roles
State-led extension services operate through government agencies structured at national, regional, and local levels to disseminate agricultural knowledge, focusing on smallholder farmers and priority crops. These services provide training, resources, and technological support, aiming to improve productivity, sustainability, and food security while addressing regional disparities. Public funding ensures widespread access and equitable outreach, enabling participation of marginalized communities often overlooked by private advisory services.
Private Advisory Services: Models and Approaches
Private advisory services in agricultural policy employ diverse models such as fee-for-service, contract-based consultation, and technology-driven platforms to deliver tailored knowledge dissemination to farmers. These approaches leverage market incentives to enhance innovation adoption, improve farm productivity, and ensure cost-effective, demand-driven extension support. Integrating digital tools like mobile apps and remote sensing further optimizes real-time advisory precision and scalability across varied agricultural landscapes.
Comparative Effectiveness in Reaching Smallholder Farmers
State-led extension services often provide broad coverage and standardized agricultural knowledge to smallholder farmers, leveraging government resources for widespread dissemination. Private advisory services tend to offer tailored, market-driven advice that can be more responsive to individual farmer needs but may be limited by cost and accessibility. Comparative studies indicate that integrating state-led outreach with private sector innovation enhances knowledge transfer efficiency and adoption rates among smallholder farmers.
Funding Mechanisms and Sustainability Issues
State-led extension services primarily rely on government funding and face sustainability challenges due to budget constraints and political shifts, often limiting their long-term impact. Private advisory services utilize market-driven funding models, encouraging innovation and responsiveness but may exclude smallholder farmers due to cost barriers. Blending public subsidies and private investments can enhance sustainability by balancing accessibility with quality knowledge dissemination in agricultural policy frameworks.
Impact on Technology Adoption and Innovation
State-led extension services often provide broad access to agricultural knowledge, facilitating widespread technology adoption by offering subsidized training and resources. Private advisory services tend to deliver tailored, market-driven innovations that address specific farmer needs, fostering targeted adoption of advanced practices. Combining both approaches can enhance overall innovation diffusion and improve agricultural productivity.
Accessibility and Equity in Service Provision
State-led extension services ensure broader accessibility and equitable knowledge dissemination by prioritizing marginalized and smallholder farmers, often operating in remote areas where private advisory services lack presence. Private advisory services, while often more specialized and demand-driven, tend to concentrate in profitable regions, limiting equitable access for disadvantaged groups. Balancing public and private roles in agricultural policy can enhance overall service reach and inclusivity, promoting sustainable rural development.
Quality Assurance and Professional Standards
State-led extension services play a crucial role in ensuring quality assurance and maintaining professional standards by adhering to government-regulated training programs and standardized protocols. Private advisory services often provide specialized, innovative solutions but vary widely in quality due to the lack of uniform certification and oversight frameworks. Establishing a collaborative model that integrates state-led quality control with private sector flexibility can enhance the effectiveness and reliability of agricultural knowledge dissemination.
Policy Implications for Agricultural Extension Reform
State-led extension services provide widespread access to essential agricultural knowledge, ensuring equitable support for smallholder farmers and promoting food security. Private advisory services offer tailored expertise and innovation-driven solutions, enhancing productivity and market integration for commercial farms. Agricultural extension reform policies must balance public investment with private sector incentives to foster inclusive, efficient, and sustainable knowledge dissemination systems.
Future Trends: Integrating State and Private Advisory Services
Future trends in agricultural policy emphasize integrating state-led extension with private advisory services to enhance knowledge dissemination efficiency and reach. Combining public resources with market-driven innovation leverages strengths in scale, expertise, and responsiveness to evolving farmer needs. Data-driven platforms and digital tools will underpin this hybrid model, promoting sustainable agricultural productivity and climate-resilient practices.
Related Important Terms
Pluralistic Extension Models
Pluralistic extension models integrate state-led extension and private advisory services to enhance agricultural knowledge dissemination, leveraging diverse expertise and resources for broader reach and impact. These models improve farmer access to tailored information, fostering innovation adoption and sustainable practices through coordinated institutional collaboration.
Digital Advisory Platforms
State-led extension programs focus on widespread agricultural knowledge dissemination through government-funded digital advisory platforms, ensuring equitable access for smallholder farmers. Private advisory services leverage advanced data analytics and personalized digital tools to deliver targeted, market-driven recommendations, enhancing productivity and farm profitability.
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in Extension
Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) in agricultural extension integrate state-led expertise with private advisory services to enhance knowledge dissemination efficiency and reach. By leveraging government resources and private sector innovation, PPP models improve farmers' access to tailored information, promoting sustainable agricultural practices and boosting productivity.
Fee-for-Service Advisory
Fee-for-service advisory models under state-led extension face challenges in scalability compared to private advisory services, which leverage market-driven incentives to enhance farmer access to tailored agricultural knowledge. Empirical studies indicate private advisory services boost adoption rates of innovative farming practices by providing specialized, demand-responsive expertise, but require regulatory frameworks to ensure quality and affordability.
AgriTech Knowledge Brokers
State-led extension services provide broad agricultural outreach with established local networks, while private advisory services leverage specialized AgriTech knowledge brokers to deliver tailored, innovative solutions directly to farmers; integrating these approaches enhances technology adoption and sustainable farm management. Efficient AgriTech knowledge brokers act as critical intermediaries, translating complex digital tools and data-driven insights into practical guidance, accelerating precision agriculture and improving crop yields.
Farmer Field Schools 2.0
State-led extension services, traditionally responsible for disseminating agricultural knowledge, face limitations in scalability and customization, prompting a shift towards Farmer Field Schools 2.0 that integrate participatory learning with digital tools for enhanced farmer engagement. Private advisory services complement this evolution by offering specialized, market-driven advice tailored to diverse farmer needs, creating a synergistic landscape for effective knowledge transfer and sustainable agricultural development.
Demand-driven Extension Services
Demand-driven extension services prioritize farmer needs through tailored advice, enhancing productivity and sustainability by aligning knowledge dissemination with market and environmental demands. State-led extension often provides broad, standardized information, whereas private advisory services customize support, promoting innovation and efficient resource use in agriculture.
Embedded Advisory Offerings
State-led extension services provide embedded advisory offerings within public agricultural programs, ensuring wide accessibility and alignment with national policy goals, while private advisory services embed specialized knowledge tailored to individual farmer needs, often enhancing innovation adoption through customized support. Embedding advisory functions in both public and private sectors fosters knowledge dissemination efficiency, combines global best practices with localized expertise, and drives sustainable agricultural productivity improvements.
WhatsApp Extension Groups
State-led extension programs leveraging WhatsApp groups facilitate widespread, cost-effective agricultural knowledge dissemination, ensuring equitable access for smallholder farmers in rural areas. Private advisory services on WhatsApp offer specialized, timely guidance tailored to commercial farms, enhancing crop productivity through personalized expert interactions.
Mobile-based Private Advisory Apps
Mobile-based private advisory apps are transforming agricultural extension by providing farmers with real-time, tailored advice on crop management, pest control, and market trends, enhancing productivity and income. These digital platforms complement state-led extension services by offering scalable, cost-effective knowledge dissemination that leverages smartphone penetration and data analytics for precision agriculture.
State-led Extension vs Private Advisory Services for knowledge dissemination Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com