Supply management in dairy production stabilizes prices and ensures fair income for farmers by controlling production quotas and import levels. Free market systems promote competition, potentially lowering consumer prices but exposing producers to volatile market fluctuations and income instability. Balancing these approaches requires evaluating economic sustainability, consumer interests, and industry resilience.
Table of Comparison
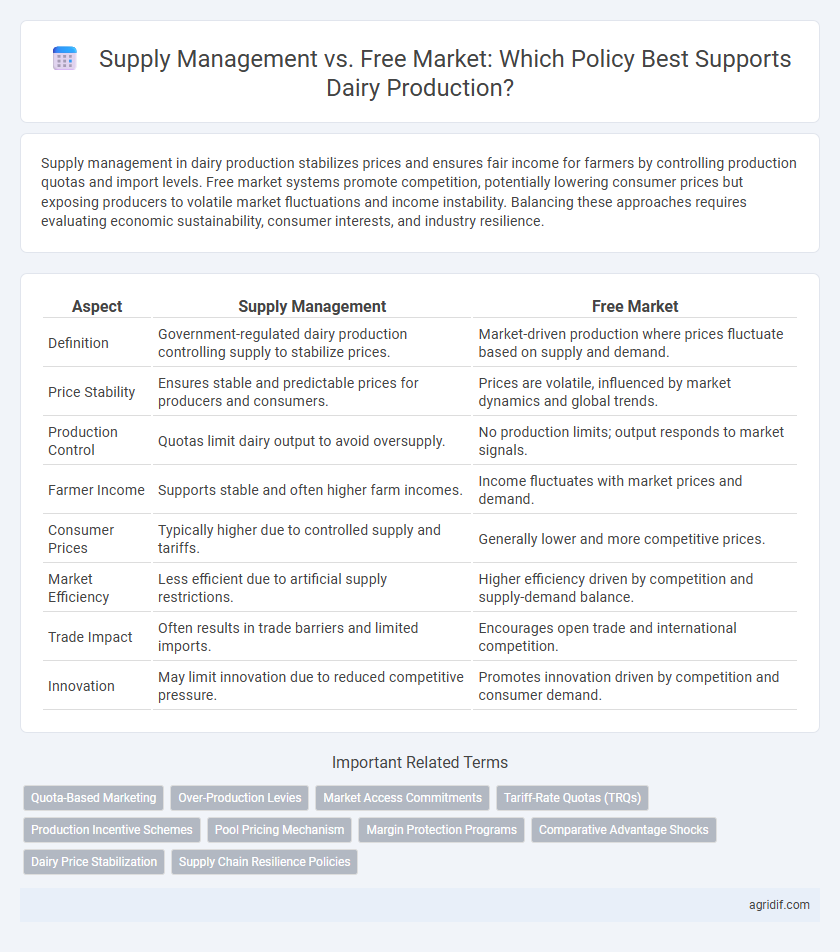
| Aspect | Supply Management | Free Market |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-regulated dairy production controlling supply to stabilize prices. | Market-driven production where prices fluctuate based on supply and demand. |
| Price Stability | Ensures stable and predictable prices for producers and consumers. | Prices are volatile, influenced by market dynamics and global trends. |
| Production Control | Quotas limit dairy output to avoid oversupply. | No production limits; output responds to market signals. |
| Farmer Income | Supports stable and often higher farm incomes. | Income fluctuates with market prices and demand. |
| Consumer Prices | Typically higher due to controlled supply and tariffs. | Generally lower and more competitive prices. |
| Market Efficiency | Less efficient due to artificial supply restrictions. | Higher efficiency driven by competition and supply-demand balance. |
| Trade Impact | Often results in trade barriers and limited imports. | Encourages open trade and international competition. |
| Innovation | May limit innovation due to reduced competitive pressure. | Promotes innovation driven by competition and consumer demand. |
Introduction to Dairy Supply Management and Free Market Systems
Dairy supply management systems regulate production quotas and control imports to stabilize prices and ensure consistent income for farmers. Free market systems allow prices to fluctuate based on supply and demand, often leading to greater market volatility but increased competition and innovation. Understanding these contrasting approaches is crucial for evaluating economic impacts on dairy producers and consumers.
Historical Evolution of Dairy Policy Frameworks
Dairy policy frameworks have evolved significantly, with supply management systems emerging in countries like Canada during the mid-20th century to stabilize prices and protect farmers from market volatility. Contrarily, nations such as the United States shifted toward freer market approaches, emphasizing competition and efficiency, leading to fluctuating dairy prices and producer incomes. Historical shifts in these policies reflect broader economic ideologies and trade agreements influencing dairy production and market stability globally.
Key Principles of Supply Management in Dairy Production
Supply management in dairy production relies on controlled production quotas, price stabilization mechanisms, and coordinated marketing to match supply with consumer demand. This system ensures consistent farmer income by preventing price volatility and overproduction common in free market scenarios. By balancing supply and demand, supply management promotes sustainable dairy farming and protects the industry from unpredictable market fluctuations.
Free Market Approaches in Dairy Industries
Free market approaches in dairy industries promote competitive pricing by allowing supply and demand to dictate production and sales, leading to innovation and efficiency gains. Deregulation can reduce costs for consumers and encourage producers to diversify product offerings and adopt new technologies. However, the volatility in milk prices can pose financial risks for small-scale farmers, requiring adaptive strategies for market fluctuations.
Economic Impacts on Dairy Farmers: Supply Management vs Free Market
Supply management systems stabilize dairy prices and ensure predictable incomes for farmers by controlling production and import quotas, reducing market volatility. In contrast, a free market exposes farmers to price fluctuations driven by global supply and demand, often resulting in lower profit margins and increased financial risk. Economic impacts show that supply management supports long-term sustainability and investment in dairy farms, while free market models encourage efficiency but may lead to farm closures during price downturns.
Effects on Consumer Prices and Dairy Affordability
Supply management in dairy production stabilizes consumer prices by controlling production quotas and import limits, preventing market oversupply and price volatility. Free market systems often lead to fluctuating dairy prices due to supply-demand imbalances, frequently causing periods of both affordability and premium pricing for consumers. Research indicates supply management results in higher average consumer prices but greater price predictability, while free markets offer lower prices during surplus but risk sharp price spikes during shortages.
Trade Implications: Export Opportunities and Market Access
Supply management in dairy production restricts output to stabilize prices, which can limit export volumes and create trade tensions due to quota restrictions. Free market systems encourage higher production levels, enhancing export opportunities but risking domestic price volatility and reduced income stability for farmers. Trade agreements often challenge supply management by promoting market access and reducing barriers, impacting the ability of protected domestic industries to compete internationally.
Impacts on Dairy Quality and Food Security
Supply management systems in dairy production ensure stable prices and consistent quality by regulating production quotas, which helps maintain high standards and reduces market volatility. Free market models encourage competition and innovation but can lead to fluctuating milk quality and risks of oversupply or shortages, potentially undermining food security. Effective agricultural policies balance supply control with market flexibility to optimize dairy quality and ensure long-term food security.
Policy Challenges and Reform Debates
Supply management in dairy production controls production quotas and prices to stabilize farmer income and market supply, yet it often faces criticism for limiting competition and increasing consumer prices. Free market approaches promote competition and efficiency but expose farmers to volatile prices and income uncertainty, raising concerns about sustainability and rural livelihoods. Policy challenges revolve around balancing market stability with innovation and fairness, fueling ongoing reform debates on protecting farmers while ensuring affordable dairy products for consumers.
Future Outlook: Balancing Stability and Competitiveness in Dairy Policy
Supply management in dairy production ensures price stability and income predictability for farmers, supporting rural economies and reducing market volatility. Free market approaches promote competitiveness and innovation but expose producers to global price fluctuations and increased financial risks. Future dairy policy must balance these elements by integrating market responsiveness with mechanisms that safeguard farmer livelihoods and maintain supply reliability.
Related Important Terms
Quota-Based Marketing
Quota-based marketing in dairy production stabilizes supply by limiting the amount farmers can produce, ensuring price consistency and protecting farm incomes. This system contrasts with free market models, where production fluctuates according to demand, often leading to price volatility and income uncertainty for producers.
Over-Production Levies
Over-production levies in supply management systems cap dairy production by imposing financial penalties on farmers exceeding quota limits, ensuring price stability and reducing surplus waste. Free market frameworks lack such levies, often resulting in volatile prices and fluctuating supply levels driven by market demand and production costs.
Market Access Commitments
Supply management in dairy production restricts output to stabilize prices and protect domestic farmers, often limiting market access commitments by imposing quotas and tariffs on imports. Free market approaches encourage competition and lower prices through fewer trade barriers, increasing market access but exposing producers to global price volatility.
Tariff-Rate Quotas (TRQs)
Tariff-Rate Quotas (TRQs) regulate dairy imports by allowing a set quantity at low tariff rates while imposing higher tariffs beyond that threshold, balancing domestic supply management with market access. This mechanism helps stabilize dairy prices and protect local producers while enabling controlled competition and consumer choice in free market frameworks.
Production Incentive Schemes
Supply management in dairy production uses production incentive schemes that stabilize prices and control output through quotas, ensuring farmers receive consistent income and reducing market volatility. In contrast, free market policies rely on price signals and competitive forces, encouraging efficiency and innovation but exposing producers to greater income fluctuations and price instability.
Pool Pricing Mechanism
Pool pricing mechanisms in supply-managed dairy systems stabilize farmer income by aggregating milk production and distributing revenue based on a standardized price, contrasting with free market models where prices fluctuate according to supply and demand dynamics. This approach reduces market volatility, ensures consistent quality standards, and supports rural economies, although it may limit producer flexibility and consumer choice.
Margin Protection Programs
Margin Protection Programs in dairy production offer farmers financial stability by compensating for losses when the margin between milk prices and feed costs falls below a predetermined level, balancing income security and market risk. Unlike pure free market systems that expose producers to volatile price fluctuations, supply management with margin programs ensures predictable revenue streams, supporting sustainable dairy operations in fluctuating economic conditions.
Comparative Advantage Shocks
Supply management in dairy production stabilizes prices and protects farmers from comparative advantage shocks like sudden shifts in global demand or feed costs, ensuring consistent income and domestic supply. In contrast, a free market exposes producers to volatility, where shocks can lead to overproduction or shortages, significantly impacting producer profitability and consumer prices.
Dairy Price Stabilization
Supply management in dairy production stabilizes prices through production quotas and import controls, ensuring consistent farmer income and preventing market gluts. Free market approaches expose dairy prices to volatility driven by global demand and supply fluctuations, often resulting in unpredictable income for producers and potential price crashes.
Supply Chain Resilience Policies
Supply management in dairy production stabilizes prices and supports farmers through production quotas and import controls, enhancing supply chain resilience by reducing volatility and ensuring steady supply. Free market policies encourage competition and innovation but often result in price fluctuations and supply instability, posing risks to consistent dairy availability in the supply chain.
Supply Management vs Free Market for Dairy Production Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com