Conservation compliance mandates farmers to implement specific land use practices to qualify for federal benefits, ensuring soil and water protection through regulatory measures. Voluntary stewardship encourages landowners to adopt sustainable practices by choice, promoting environmental responsibility without legal obligations. Balancing these approaches enhances agricultural productivity while safeguarding natural resources and biodiversity.
Table of Comparison
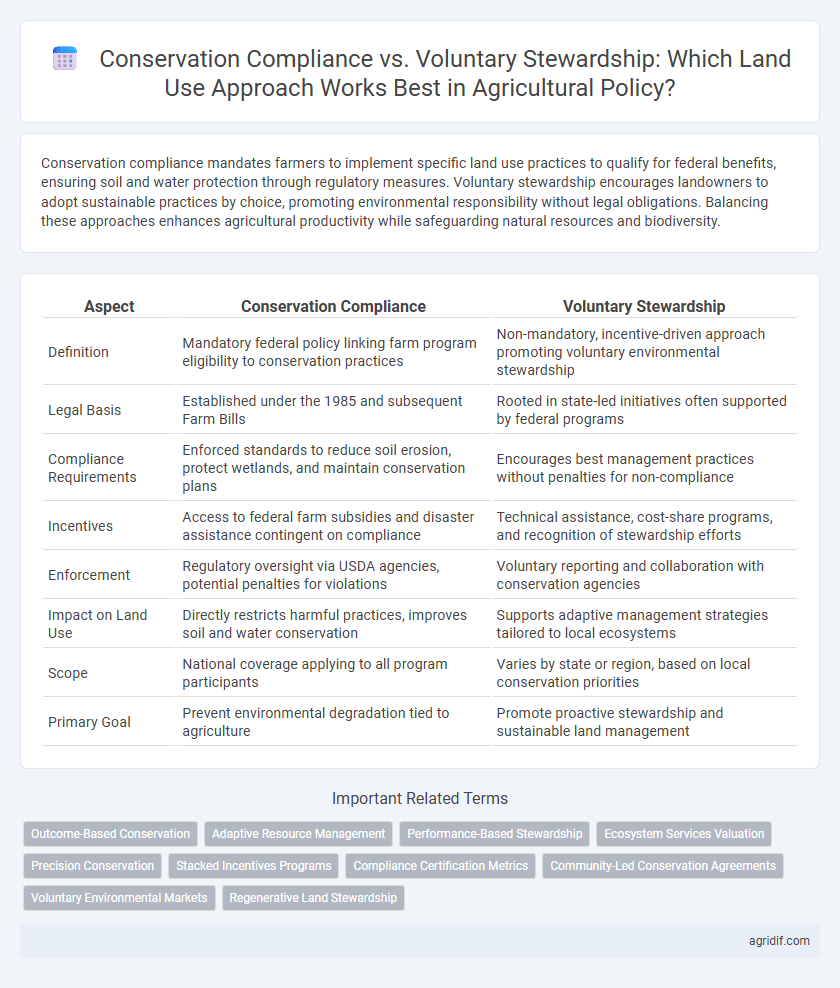
| Aspect | Conservation Compliance | Voluntary Stewardship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mandatory federal policy linking farm program eligibility to conservation practices | Non-mandatory, incentive-driven approach promoting voluntary environmental stewardship |
| Legal Basis | Established under the 1985 and subsequent Farm Bills | Rooted in state-led initiatives often supported by federal programs |
| Compliance Requirements | Enforced standards to reduce soil erosion, protect wetlands, and maintain conservation plans | Encourages best management practices without penalties for non-compliance |
| Incentives | Access to federal farm subsidies and disaster assistance contingent on compliance | Technical assistance, cost-share programs, and recognition of stewardship efforts |
| Enforcement | Regulatory oversight via USDA agencies, potential penalties for violations | Voluntary reporting and collaboration with conservation agencies |
| Impact on Land Use | Directly restricts harmful practices, improves soil and water conservation | Supports adaptive management strategies tailored to local ecosystems |
| Scope | National coverage applying to all program participants | Varies by state or region, based on local conservation priorities |
| Primary Goal | Prevent environmental degradation tied to agriculture | Promote proactive stewardship and sustainable land management |
Understanding Conservation Compliance in Agricultural Policy
Conservation compliance in agricultural policy mandates farmers to adopt soil and water conservation practices to qualify for federal subsidies, thereby reducing environmental degradation and promoting sustainable land use. This regulatory approach ensures compliance with established conservation standards, linking financial incentives directly to environmental stewardship. Understanding these requirements is crucial for balancing agricultural productivity with long-term land preservation and resource conservation.
Voluntary Stewardship: Principles and Practices
Voluntary Stewardship programs emphasize landowner collaboration to promote sustainable agricultural practices that protect soil, water, and wildlife habitats without mandatory regulations. By incentivizing conservation through education and technical support, these programs foster proactive environmental responsibility while maintaining productivity. Implementation relies on adaptive management principles, continuous monitoring, and community engagement to optimize land use outcomes.
Key Differences Between Compliance and Voluntary Approaches
Conservation compliance mandates adherence to specific environmental standards as a prerequisite for receiving federal farm program benefits, ensuring soil and water protection through enforced regulations. Voluntary stewardship relies on landowners' willingness to implement sustainable practices without legal obligation, promoting flexibility but potentially varying in effectiveness. The key difference lies in compliance's regulatory enforcement versus stewardship's incentive-driven participation, impacting overall conservation outcomes and land use management.
Environmental Impacts: Comparative Outcomes
Conservation Compliance programs enforce mandatory land management practices that significantly reduce soil erosion and improve water quality by requiring farmers to adhere to specific environmental standards. Voluntary Stewardship relies on landowners' willingness to adopt sustainable practices, often resulting in varied environmental outcomes due to inconsistent participation and commitment levels. Comparative studies indicate that Conservation Compliance delivers more measurable reductions in nutrient runoff and habitat degradation compared to the generally lower but more flexible conservation benefits from Voluntary Stewardship initiatives.
Economic Incentives and Farmer Participation
Conservation Compliance links eligibility for federal farm programs and crop insurance premium discounts to adherence to environmental standards, incentivizing farmers through direct economic benefits. Voluntary Stewardship encourages proactive land management without mandatory requirements, relying on educational outreach and potential cost-sharing programs to boost farmer participation. Economic incentives in Conservation Compliance tend to drive higher enrollment rates, while Voluntary Stewardship offers flexibility that appeals to farmers seeking autonomy in conservation efforts.
Policy Effectiveness: Measuring Success Rates
Conservation Compliance policies demonstrate measurable success rates by directly linking eligibility for farm subsidies to adherence to specific land management practices, resulting in significant reductions in soil erosion and improvement in water quality. Voluntary Stewardship programs rely on landowner participation and incentives, often yielding variable outcomes that depend heavily on local engagement and resources, making standardized measurement more challenging. Comparative studies indicate that mandatory compliance policies achieve higher consistency in environmental benefits, while voluntary approaches foster biodiversity through tailored, site-specific stewardship efforts.
Barriers to Adoption: Compliance vs. Voluntary Models
Conservation compliance programs often face barriers such as regulatory complexity, fear of penalties, and lack of flexibility, deterring farmers from full participation. Voluntary stewardship models encounter challenges including limited financial incentives, varying levels of awareness, and inconsistent technical support, which hinder widespread adoption. Both approaches wrestle with trust issues between landowners and regulatory bodies, impacting the effectiveness of land use conservation efforts.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementation
Case studies reveal that Conservation Compliance programs, such as the USDA's enforcement tied to Farm Bill subsidies, effectively reduce soil erosion and improve water quality on agricultural lands. Conversely, Voluntary Stewardship programs, exemplified by Washington State's voluntary approach to protecting critical habitats, foster collaborative relationships with landowners, encouraging sustainable practices through incentives rather than mandates. Comparative data indicate that while Conservation Compliance ensures baseline environmental protections, Voluntary Stewardship can achieve higher participation rates and localized ecological benefits when supported by strong community engagement.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Land Use Policies
Conservation Compliance mandates adherence to environmental standards for eligibility in federal farm programs, effectively reducing soil erosion and protecting water quality through enforceable regulations. Voluntary Stewardship encourages proactive land management practices by providing incentives and technical support, fostering farmer engagement in sustainable agriculture without the constraints of mandatory rules. Future sustainable land use policies are likely to integrate both approaches, leveraging regulatory frameworks to ensure baseline conservation while promoting voluntary enhancements to address emerging environmental challenges and climate resilience.
Integrating Compliance and Voluntary Stewardship: A Holistic Approach
Integrating conservation compliance with voluntary stewardship programs fosters a holistic approach to sustainable land use by combining regulatory mandates and proactive land management practices. This synergy enhances soil health, water quality, and biodiversity conservation while encouraging landowner engagement and adaptive management strategies. Leveraging both compliance requirements and voluntary initiatives increases effectiveness in achieving long-term agricultural sustainability and resilience.
Related Important Terms
Outcome-Based Conservation
Outcome-based conservation under conservation compliance mandates farmers implement specific soil and water protection measures to maintain eligibility for federal benefits, ensuring measurable environmental results. Voluntary stewardship emphasizes flexibility and innovation, encouraging landowners to adopt sustainable practices tailored to their land with incentives but without regulatory penalties.
Adaptive Resource Management
Conservation compliance mandates farmers to adhere to specific land-use practices to maintain eligibility for federal benefits, ensuring baseline environmental protections, while voluntary stewardship encourages proactive, adaptive resource management tailored to local ecosystems and evolving conditions. Adaptive resource management in voluntary stewardship fosters continuous monitoring and adjustment of conservation strategies, promoting sustainable land use that responds dynamically to environmental feedback and agricultural needs.
Performance-Based Stewardship
Performance-based stewardship in agricultural policy emphasizes measurable environmental outcomes over prescriptive practices, encouraging landowners to adopt conservation compliance through tangible improvements in soil health, water quality, and habitat preservation. Voluntary stewardship programs offer flexibility but often lack the enforceable standards necessary to ensure consistent, long-term ecological benefits compared to compliance frameworks tied to incentive eligibility.
Ecosystem Services Valuation
Conservation compliance mandates adherence to specific land management practices to maintain eligibility for federal agricultural programs, directly linking ecosystem services valuation to regulatory incentives and measurable environmental benefits. Voluntary stewardship relies on voluntary participation, emphasizing flexible, locally adapted land use strategies that leverage ecosystem services valuation for personalized conservation outcomes and enhanced farmer engagement.
Precision Conservation
Precision conservation integrates advanced data analytics and GPS technology to optimize land use, ensuring compliance with agricultural policies by targeting specific areas for conservation practices. Voluntary stewardship encourages farmers to adopt precision conservation methods, enhancing soil health and water quality while meeting regulatory requirements without mandatory enforcement.
Stacked Incentives Programs
Conservation compliance mandates adherence to specific environmental standards for eligibility in federal farm programs, ensuring soil and water protection, while voluntary stewardship encourages farmers to adopt sustainable practices through flexible participation and additional incentives. Stacked incentives programs combine regulatory requirements with market-based rewards, enhancing land use outcomes by promoting comprehensive conservation efforts alongside voluntary environmental improvements.
Compliance Certification Metrics
Conservation compliance certification metrics emphasize measurable benchmarks such as soil erosion rates, wetland protection status, and nutrient management effectiveness to enforce regulatory standards in agricultural land use. Voluntary stewardship relies on self-reported indicators like conservation plan adoption, habitat restoration activities, and sustainable farming practices, often lacking the rigorous, standardized data required for formal compliance verification.
Community-Led Conservation Agreements
Community-led conservation agreements empower local stakeholders to implement voluntary stewardship practices that enhance soil health, water quality, and biodiversity, fostering sustainable agricultural land use while promoting compliance with federal conservation standards. These agreements leverage collaborative decision-making and tailored conservation measures, increasing landowners' commitment to environmental goals compared to traditional compliance mandates.
Voluntary Environmental Markets
Voluntary environmental markets incentivize farmers to adopt sustainable land use practices by providing financial rewards for ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water quality improvement, and biodiversity conservation. These markets complement conservation compliance by promoting proactive stewardship beyond regulatory requirements, enhancing both environmental outcomes and economic resilience in agriculture.
Regenerative Land Stewardship
Conservation compliance mandates adherence to specific land-use practices tied to federal farm program eligibility, ensuring soil and water quality protection through enforced standards. Voluntary stewardship encourages regenerative land management by incentivizing farmers with flexible, market-driven approaches that enhance biodiversity, carbon sequestration, and long-term soil health.
Conservation Compliance vs Voluntary Stewardship for Land Use Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com