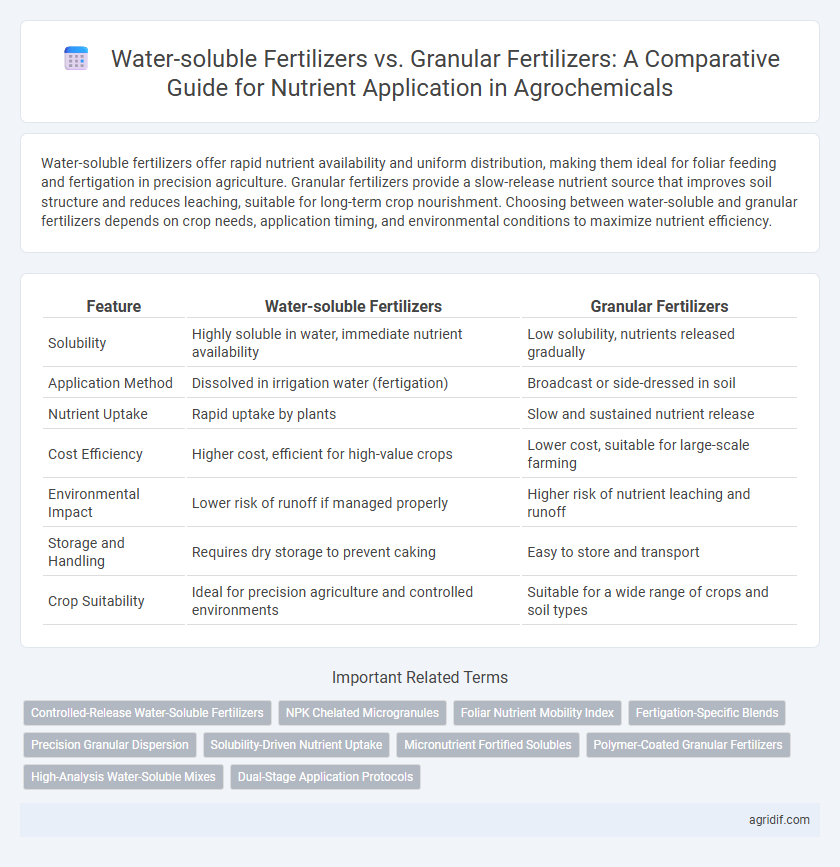
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability and uniform distribution, making them ideal for foliar feeding and fertigation in precision agriculture. Granular fertilizers provide a slow-release nutrient source that improves soil structure and reduces leaching, suitable for long-term crop nourishment. Choosing between water-soluble and granular fertilizers depends on crop needs, application timing, and environmental conditions to maximize nutrient efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Water-soluble Fertilizers | Granular Fertilizers |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Highly soluble in water, immediate nutrient availability | Low solubility, nutrients released gradually |
| Application Method | Dissolved in irrigation water (fertigation) | Broadcast or side-dressed in soil |
| Nutrient Uptake | Rapid uptake by plants | Slow and sustained nutrient release |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher cost, efficient for high-value crops | Lower cost, suitable for large-scale farming |
| Environmental Impact | Lower risk of runoff if managed properly | Higher risk of nutrient leaching and runoff |
| Storage and Handling | Requires dry storage to prevent caking | Easy to store and transport |
| Crop Suitability | Ideal for precision agriculture and controlled environments | Suitable for a wide range of crops and soil types |
Introduction to Fertilizer Forms in Modern Agriculture
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability, enhancing precision in fertigation systems and promoting uniform crop uptake. Granular fertilizers provide sustained nutrient release, improving soil nutrient retention and reducing application frequency in large-scale field operations. Selecting between water-soluble and granular forms depends on crop requirements, soil conditions, and irrigation practices for optimized nutrient management in modern agriculture.
Understanding Water-soluble Fertilizers: Composition and Application
Water-soluble fertilizers consist of highly soluble nutrient compounds such as nitrates, phosphates, and potassium salts, enabling rapid nutrient availability for plants. These fertilizers are typically dissolved in irrigation water, facilitating precise and uniform nutrient delivery directly to the root zone. Their composition allows for efficient foliar feeding and fertigation, optimizing nutrient uptake and promoting faster plant growth compared to granular fertilizers.
Granular Fertilizers: Key Features and Use Cases
Granular fertilizers offer precise nutrient delivery through slow-release formulations that improve soil nutrient retention and reduce leaching. Their solid form enables easy application in large-scale agriculture, particularly in crops like cereals, corn, and soybeans, where sustained nutrient availability is critical. These fertilizers are compatible with mechanized spreaders, enhancing efficiency in nutrient management for extensive farming operations.
Nutrient Efficiency: Water-soluble vs Granular Fertilizers
Water-soluble fertilizers provide immediate nutrient availability, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency in crops due to rapid dissolution and uniform distribution in the soil. Granular fertilizers release nutrients slowly, supporting sustained nutrient supply but potentially resulting in lower immediate nutrient use efficiency. Optimizing nutrient efficiency requires selecting fertilizer types based on crop demand timing and soil conditions to maximize nutrient absorption and minimize losses.
Application Methods and Equipment Compatibility
Water-soluble fertilizers are ideal for fertigation and foliar feeding, allowing precise nutrient delivery through drip irrigation systems and spray equipment, which enhances nutrient uptake efficiency. Granular fertilizers require soil incorporation or broadcast application using spreaders or seed drills, demanding more labor-intensive equipment and timing for optimal nutrient release. Compatibility with existing equipment and the crop's growth stage determines the best choice, as water-soluble types offer rapid nutrient availability, while granular fertilizers provide slower, controlled nutrient release.
Crop Response and Nutrient Availability
Water-soluble fertilizers provide rapid nutrient availability, leading to quicker crop response and enhanced uptake efficiency, especially in fertigation and foliar feeding systems. Granular fertilizers release nutrients more slowly, supporting sustained nutrient supply and improved root zone absorption, beneficial for long-term crop growth. Crop response to water-soluble formulations tends to be immediate, while granular fertilizers contribute to steady growth and reduced leaching losses over time.
Cost Analysis: Economic Considerations for Farmers
Water-soluble fertilizers typically involve higher upfront costs due to their refined formulation and application equipment requirements, whereas granular fertilizers are generally more cost-effective for large-scale use and easier storage. Farmers must evaluate the balance between immediate nutrient availability and long-term expense, as water-soluble options can improve crop yield efficiency but increase operational costs. Cost analysis should factor in application method, crop type, and local market prices to optimize economic returns in nutrient management.
Environmental Impact of Different Fertilizer Forms
Water-soluble fertilizers minimize nutrient runoff by providing precise nutrient availability, reducing leaching and environmental contamination compared to granular fertilizers, which often release nutrients unevenly and increase the risk of groundwater pollution. The rapid dissolution of water-soluble forms enhances plant uptake efficiency, leading to lower application rates and decreased soil nutrient accumulation, thereby mitigating eutrophication in adjacent water bodies. Granular fertilizers, while easier to apply and store, tend to contribute to higher ammonia volatilization and nitrous oxide emissions, intensifying greenhouse gas effects and soil degradation.
Suitability for Specific Crops and Soil Types
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient uptake and are ideal for high-value crops and hydroponic systems requiring precise nutrient management, especially in sandy or saline soils with low nutrient retention. Granular fertilizers provide slow-release nutrients suited for field crops and soils with better moisture retention, such as loamy and clay soils, ensuring sustained nutrient availability over time. Crop-specific suitability depends on nutrient demands, with water-soluble options favored for short-cycle crops and granular formulations preferred for long-duration crops in varied soil textures.
Best Practices for Optimal Nutrient Management
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability and precise application rates, enhancing nutrient uptake efficiency in crops. Granular fertilizers provide prolonged nutrient release, supporting sustained plant growth and reducing the risk of leaching in soil with low water retention. Combining both forms with soil and crop monitoring ensures balanced nutrient management, optimizing yield and minimizing environmental impact.
Related Important Terms
Controlled-Release Water-Soluble Fertilizers
Controlled-release water-soluble fertilizers enhance nutrient efficiency by delivering precise doses over time, reducing leaching and volatilization compared to traditional granular fertilizers. Their solubility allows rapid nutrient uptake, promoting uniform crop growth and reducing environmental impact in precision agriculture.
NPK Chelated Microgranules
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability and uniform distribution, enhancing the efficiency of NPK chelated microgranules in foliar and fertigation applications. Granular fertilizers provide controlled release and long-lasting nutrient supply, making them ideal for soil incorporation and sustained nutrient delivery in crop production.
Foliar Nutrient Mobility Index
Water-soluble fertilizers exhibit a higher Foliar Nutrient Mobility Index compared to granular fertilizers, enhancing rapid nutrient uptake and translocation within plant tissues. This improved mobility supports efficient foliar nutrient application, particularly for micronutrients and mobile macronutrients such as nitrogen and potassium.
Fertigation-Specific Blends
Water-soluble fertilizers enable precise nutrient delivery through fertigation systems, ensuring rapid plant uptake and uniform distribution in irrigation water, while granular fertilizers release nutrients slowly, requiring soil moisture for nutrient availability. Fertigation-specific blends optimize crop nutrition by combining water solubility with tailored nutrient formulations, enhancing efficiency and reducing nutrient loss in drip or sprinkler irrigation setups.
Precision Granular Dispersion
Water-soluble fertilizers offer rapid nutrient availability but often lack precise control over nutrient distribution compared to precision granular dispersion systems, which enable uniform application and reduce wastage by targeting specific soil zones. Precision granular dispersion optimizes nutrient efficiency and supports sustained plant growth by ensuring controlled release and enhanced root zone absorption.
Solubility-Driven Nutrient Uptake
Water-soluble fertilizers provide rapid nutrient availability and uniform distribution, enhancing immediate solubility-driven nutrient uptake by plant roots. Granular fertilizers release nutrients gradually through dissolution, supporting sustained nutrient supply but with slower initial solubility compared to water-soluble formulations.
Micronutrient Fortified Solubles
Micronutrient fortified water-soluble fertilizers offer precise nutrient delivery and rapid absorption, enhancing crop uptake efficiency compared to traditional granular fertilizers that release nutrients slowly and less uniformly. These soluble formulations improve micronutrient availability in soil solution, promoting quicker correction of deficiencies and better overall plant health in precision agriculture.
Polymer-Coated Granular Fertilizers
Polymer-coated granular fertilizers provide controlled nutrient release, reducing leaching and enhancing nutrient-use efficiency compared to water-soluble fertilizers, which offer immediate but short-lived nutrient availability. Their encapsulating polymer layer enables sustained nutrient delivery, making them ideal for precision nutrient management in various cropping systems.
High-Analysis Water-Soluble Mixes
High-analysis water-soluble fertilizers provide precise nutrient delivery with rapid uptake, boosting crop yield efficiency compared to slower-dissolving granular fertilizers. These water-soluble mixes enhance nutrient availability in fertigation and foliar feeding, optimizing plant growth under varying soil conditions.
Dual-Stage Application Protocols
Water-soluble fertilizers enable rapid nutrient uptake during the initial growth phase, enhancing early root development, while granular fertilizers provide a slow-release nutrient supply for sustained plant growth in the later stage. Dual-stage application protocols leverage the solubility and release rates of each fertilizer type to optimize nutrient efficiency, improve crop yield, and reduce environmental runoff.
Water-soluble Fertilizers vs Granular Fertilizers for Nutrient Application Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com