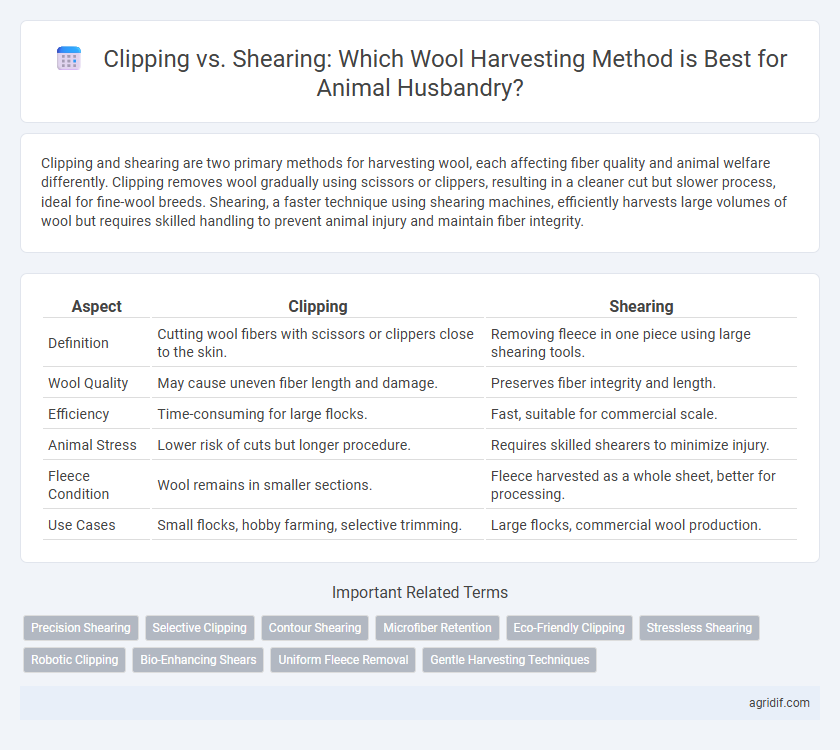
Clipping and shearing are two primary methods for harvesting wool, each affecting fiber quality and animal welfare differently. Clipping removes wool gradually using scissors or clippers, resulting in a cleaner cut but slower process, ideal for fine-wool breeds. Shearing, a faster technique using shearing machines, efficiently harvests large volumes of wool but requires skilled handling to prevent animal injury and maintain fiber integrity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clipping | Shearing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cutting wool fibers with scissors or clippers close to the skin. | Removing fleece in one piece using large shearing tools. |
| Wool Quality | May cause uneven fiber length and damage. | Preserves fiber integrity and length. |
| Efficiency | Time-consuming for large flocks. | Fast, suitable for commercial scale. |
| Animal Stress | Lower risk of cuts but longer procedure. | Requires skilled shearers to minimize injury. |
| Fleece Condition | Wool remains in smaller sections. | Fleece harvested as a whole sheet, better for processing. |
| Use Cases | Small flocks, hobby farming, selective trimming. | Large flocks, commercial wool production. |
Introduction to Wool Harvesting Methods
Clipping and shearing are primary wool harvesting methods that significantly impact fiber quality and animal welfare. Clipping involves trimming wool in sections using scissors or clippers, resulting in uneven cuts and potential stress to sheep, while shearing removes fleece in one continuous piece using shears or electric machines, preserving fiber integrity. Efficient wool harvesting techniques optimize yield, maintain fleece value, and ensure animal comfort during the process.
Understanding Clipping in Animal Husbandry
Clipping in animal husbandry involves carefully trimming the wool close to the skin using electric clippers or manual shears, allowing for controlled wool harvest without removing the fleece entirely. This method promotes animal comfort by reducing heat stress in warmer climates and minimizing skin injuries compared to full shearing. Understanding clipping techniques improves wool quality by targeting specific fleece areas, making it a strategic choice for selective wool production.
The Shearing Process Explained
Shearing is the process of cutting wool from sheep using specialized electric or hand shears, ensuring clean wool removal without harming the animal. Skilled shearers follow precise techniques that minimize stress and prevent injury, typically completing the task in under three minutes per sheep. This method yields high-quality fleece suitable for textile production while promoting animal welfare during the wool harvest.
Key Differences Between Clipping and Shearing
Clipping involves trimming wool using scissors or electric clippers, typically removing shorter, less uniform fibers and causing minimal stress to animals, while shearing uses large, specialized blades to remove an entire fleece in one continuous piece, providing longer, more uniform wool suitable for textile production. Shearing is more efficient for harvesting large quantities of wool and essential for maintaining animal health by preventing overheating and parasite buildup. Clipping is often used for smaller-scale operations or when selective wool removal is desired without fully exposing the animal.
Equipment Used for Clipping vs Shearing
Clipping for wool harvest typically uses electric clippers or manual hand shears designed for precision trimming of small areas, ideal for pet grooming or fine wool harvesting. Shearing involves specialized, larger electric or pneumatic shears that provide rapid, efficient removal of entire fleece in a single pass, essential for commercial sheep farming. The choice of equipment impacts fiber quality, animal comfort, and harvesting speed, with shearing tools optimized for high-volume wool production.
Impact on Animal Welfare and Stress
Clipping wool involves using electric clippers that trim the fleece close to the skin, resulting in a less invasive process that generally causes minimal distress and faster recovery for sheep. Shearing, which removes the fleece in one piece using specialized shears, can induce short-term stress and requires careful technique to avoid cuts and injuries, impacting animal welfare more significantly. Both methods demand skilled handlers to reduce handling time and stress, ensuring the overall well-being of the animals during wool harvest.
Wool Quality: Clipping vs Shearing Outcomes
Clipping preserves the outer fiber integrity by cutting wool close to the skin, reducing the risk of fiber damage and contamination compared to shearing. Shearing typically results in a cleaner fleece with minimal second cuts, enhancing the staple length and overall wool strength. Wool quality after shearing tends to be higher due to uniform fiber length and less matting, while clipped wool may require additional processing to remove burrs and vegetation.
Efficiency and Labor Requirements
Shearing wool is generally more efficient than clipping due to its ability to remove fleece in a single, continuous piece, saving time and reducing labor intensity. Clipping, which involves cutting wool in smaller sections, often requires more manual effort and prolongs the harvesting process. Shearing also minimizes stress on sheep and improves wool quality, making it the preferred method for large-scale animal husbandry operations.
Seasonal Considerations in Wool Harvesting
Seasonal considerations play a critical role in choosing between clipping and shearing for wool harvest, as shearing is typically performed during warmer months to prevent heat stress in sheep. Clipping, often used for finer wool or in less time-sensitive contexts, can be conducted with more flexibility but may not remove as much fiber as shearing. Optimal timing aligns with the sheep's natural wool growth cycles and environmental conditions to ensure animal welfare and maximize wool quality.
Choosing the Best Method for Your Flock
Choosing between clipping and shearing for wool harvest depends on the breed of sheep and wool quality goals. Shearing is faster and ensures a uniform fleece removal, ideal for large flocks with dense wool types like Merino. Clipping offers precision and reduces skin injury risk, making it suitable for finer or specialty wool breeds.
Related Important Terms
Precision Shearing
Precision shearing offers meticulous wool removal that minimizes fiber damage compared to traditional clipping, enhancing fleece quality and yield in sheep breeds like Merino. This method utilizes specialized shearing tools that contour closely to the animal's body, improving wool uniformity and reducing stress during harvest.
Selective Clipping
Selective clipping in wool harvest allows targeted removal of fleece from specific body areas, preserving the animal's comfort and promoting regrowth in high-quality wool zones. This technique minimizes stress and improves fleece uniformity compared to full-shearing methods often used in large-scale animal husbandry operations.
Contour Shearing
Contour shearing targets specific body areas of sheep to enhance wool quality by precisely removing wool around the face, belly, and legs while minimizing stress and skin damage. This method improves fleece uniformity and reduces contamination compared to traditional clipping, optimizing wool harvest efficiency in animal husbandry.
Microfiber Retention
Clipping wool involves trimming the fleece close to the skin, which can lead to higher microfiber retention by preserving the fiber integrity and reducing breakage. Shearing, while faster and suitable for large-scale operations, may cause more fiber damage and increased microfiber loss due to the mechanical action of the shearing blades.
Eco-Friendly Clipping
Eco-friendly clipping in wool harvest reduces energy consumption and minimizes environmental impact compared to traditional shearing methods, preserving animal welfare by causing less stress. This sustainable approach supports organic farming practices and promotes biodiversity by ensuring natural fiber quality without chemical treatments.
Stressless Shearing
Stressless shearing techniques minimize animal distress and improve wool quality by reducing physical strain and avoiding skin injuries compared to traditional clipping. Employing ergonomic tools and gentle handling during stressless shearing enhances animal welfare and promotes a more efficient and humane wool harvest.
Robotic Clipping
Robotic clipping in animal husbandry offers precise and efficient wool harvest by targeting specific fleece areas, reducing stress and injury compared to traditional shearing methods. Advanced AI sensors enable consistent wool removal with minimal animal discomfort, enhancing productivity and wool quality while supporting sustainable farm management.
Bio-Enhancing Shears
Bio-enhancing shears optimize wool harvest by improving fiber quality and minimizing animal stress compared to traditional clipping, which often results in uneven cuts and potential skin damage. These shears incorporate advanced technology to promote hair follicle health, enhancing fleece regeneration while ensuring efficient, sustainable animal husbandry practices.
Uniform Fleece Removal
Shearing ensures uniform fleece removal by cutting the wool close to the skin in a single, smooth motion, minimizing the risk of patchy or uneven wool lengths. Clipping, often performed with scissors or clippers, may result in inconsistent wool length and uneven fleece quality, affecting the overall value and processing efficiency.
Gentle Harvesting Techniques
Gentle harvesting techniques such as clipping involve carefully trimming wool close to the skin with scissors, minimizing stress and preventing skin injuries in sheep. Shearing, typically done with electric or manual shears, requires skillful handling to ensure clean wool removal while maintaining animal comfort and reducing the risk of cuts.
Clipping vs Shearing for Wool Harvest Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com