Organic feed for animal nutrition is derived from natural sources without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, promoting healthier livestock and reducing exposure to harmful chemicals. Conventional feed often contains genetically modified ingredients and synthetic additives, which may impact animal health and product quality. Choosing organic feed supports sustainable farming practices and enhances the nutritional value of animal products.
Table of Comparison
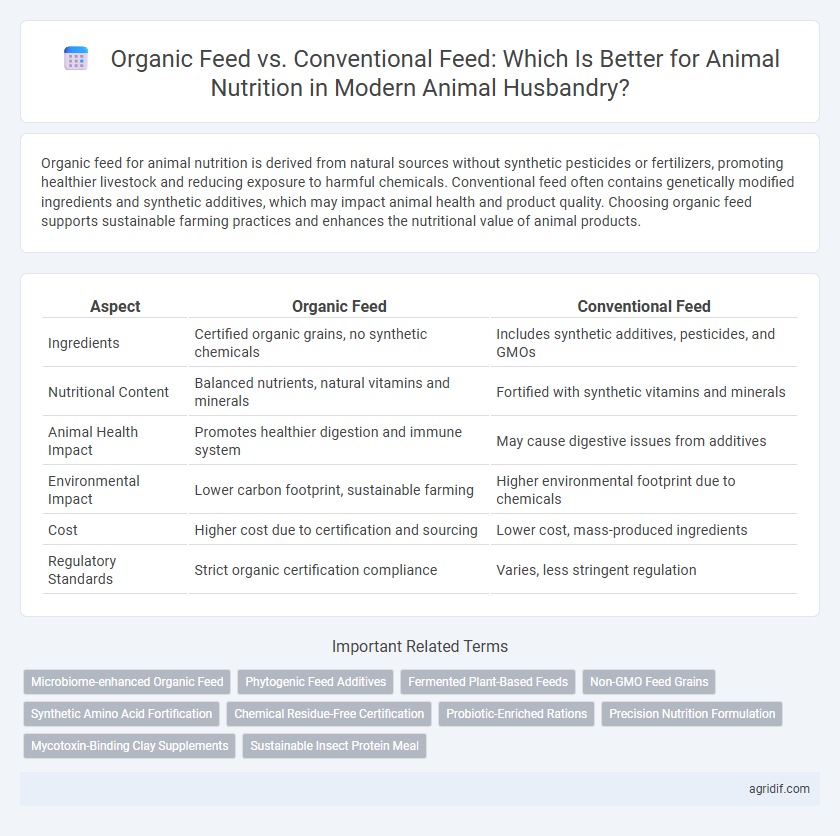
| Aspect | Organic Feed | Conventional Feed |
|---|---|---|
| Ingredients | Certified organic grains, no synthetic chemicals | Includes synthetic additives, pesticides, and GMOs |
| Nutritional Content | Balanced nutrients, natural vitamins and minerals | Fortified with synthetic vitamins and minerals |
| Animal Health Impact | Promotes healthier digestion and immune system | May cause digestive issues from additives |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint, sustainable farming | Higher environmental footprint due to chemicals |
| Cost | Higher cost due to certification and sourcing | Lower cost, mass-produced ingredients |
| Regulatory Standards | Strict organic certification compliance | Varies, less stringent regulation |
Understanding Organic and Conventional Animal Feeds
Organic animal feed consists of ingredients grown without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms, ensuring a natural nutrient profile and reduced chemical residues in livestock products. Conventional feed typically includes grains and supplements produced with synthetic chemicals and genetically modified crops, potentially impacting animal health and product safety through pesticide residues and antibiotic use. Understanding these differences helps farmers optimize animal nutrition strategies, improve animal welfare, and meet regulatory standards for organic certification.
Key Nutritional Differences: Organic vs Conventional Feed
Organic feed for animal nutrition emphasizes natural growth without synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms, resulting in higher levels of omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants compared to conventional feed. Conventional feed often contains higher concentrations of protein and energy due to synthetic additives and fortified supplements, but may include residues of antibiotics and growth hormones. These nutritional differences impact animal health, product quality, and consumer preferences in animal husbandry.
Ingredient Sourcing: Organic Feed vs Conventional Feed
Organic feed ingredients are sourced from crops grown without synthetic pesticides, herbicides, or genetically modified organisms, ensuring compliance with strict organic certification standards. Conventional feed ingredients often include conventionally grown grains and by-products that may contain chemical residues and genetically modified components. The purity and sustainability of organic ingredient sourcing contribute to improved animal health and reduce environmental impact compared to conventional feed.
Impact on Animal Health and Growth
Organic feed, free from synthetic pesticides and genetically modified organisms, enhances animal immune function and reduces exposure to harmful residues, promoting better overall health. Conventional feed often contains antibiotics and chemical additives which can lead to antibiotic resistance and potential health issues in livestock. Studies show animals fed organic diets exhibit improved growth rates and lower disease incidence compared to those on conventional feed regimes.
Feed Safety and Residue Concerns
Organic feed in animal nutrition prioritizes safety by eliminating synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, and genetically modified organisms, thereby reducing the risk of harmful chemical residues in animal products. Conventional feed, often containing synthetic additives and pesticides, poses higher concerns regarding residue accumulation, potentially impacting both animal health and food safety for consumers. Rigorous testing and certification processes in organic feed production ensure minimal contamination, enhancing the overall safety profile of organic animal-derived foods.
Environmental Effects of Feed Choices
Organic feed reduces chemical runoff and soil degradation by avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting sustainable farming practices. Conventional feed often relies on intensive monoculture crops, contributing to higher greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity loss. Choosing organic feed supports ecological balance and mitigates negative environmental impacts associated with animal nutrition.
Cost Comparisons: Organic and Conventional Feeds
Organic feed for animal nutrition typically incurs higher costs due to more expensive raw materials, certification fees, and stricter production standards, resulting in prices that can be 30% to 50% above conventional feed. Conventional feed benefits from large-scale industrial production, lower input costs, and widespread availability, making it more economical for many farmers. Despite higher upfront costs, organic feed may offer benefits such as improved animal health and premium product pricing that can offset increased expenses in the long term.
Regulatory Standards for Organic and Conventional Feed
Regulatory standards for organic feed require strict adherence to natural ingredients, prohibiting synthetic pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and synthetic growth promoters, ensuring animal diets meet organic certification criteria. Conventional feed regulations allow broader use of synthetic additives, fertilizers, and genetically engineered crops, subject to safety evaluations by authorities such as the FDA or EFSA. Compliance with these regulatory frameworks impacts animal health, product labeling, and market access for organic versus conventional animal nutrition sources.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences in animal nutrition increasingly favor organic feed due to rising demand for natural, chemical-free livestock products and perceptions of enhanced animal welfare. Market trends indicate a significant growth in organic feed sales, driven by regulatory support and premium pricing strategies that appeal to health-conscious and environmentally aware consumers. Conventional feed remains dominant due to cost efficiency and established supply chains but faces challenges from sustainability concerns and shifting consumer values.
Future Perspectives in Animal Feed Innovation
Emerging trends in animal feed innovation emphasize the integration of organic feed sources enriched with probiotics, prebiotics, and natural antioxidants to enhance animal health and productivity. Advanced research in precision nutrition and microbial fermentation techniques aims to optimize nutrient bioavailability while minimizing environmental impact. Future perspectives prioritize sustainable feed formulations that support animal welfare, reduce antibiotic reliance, and promote carbon-neutral livestock systems.
Related Important Terms
Microbiome-enhanced Organic Feed
Microbiome-enhanced organic feed improves animal nutrition by promoting beneficial gut bacteria, leading to better digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune function compared to conventional feed. This advancement supports sustainable animal husbandry by reducing reliance on antibiotics and synthetic additives while enhancing overall animal health and productivity.
Phytogenic Feed Additives
Phytogenic feed additives derived from herbs, spices, and plants enhance organic feed by improving digestion, immune response, and growth performance in livestock compared to conventional feed. These natural compounds offer antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory benefits that support sustainable animal nutrition and reduce reliance on synthetic antibiotics.
Fermented Plant-Based Feeds
Fermented plant-based feeds in organic animal husbandry enhance nutrient bioavailability, improve gut health, and reduce pathogen load compared to conventional feeds. This organic approach supports sustainable farming by minimizing synthetic additives and promoting natural probiotic benefits for livestock nutrition.
Non-GMO Feed Grains
Non-GMO feed grains in organic animal nutrition promote enhanced animal health and consumer safety by eliminating genetically modified organisms commonly found in conventional feed. Studies reveal that organic feed supports better nutrient absorption and lowers exposure to synthetic pesticides and herbicides, distinguishing it from conventional feed grains that often contain GMO variants.
Synthetic Amino Acid Fortification
Organic feed excludes synthetic amino acid fortification, relying instead on natural protein sources, which may limit precise nutritional balance compared to conventional feed. Conventional feed incorporates synthetic amino acids to optimize animal growth and health by ensuring tailored amino acid profiles that enhance protein synthesis and feed efficiency.
Chemical Residue-Free Certification
Organic feed in animal husbandry is certified chemical residue-free, ensuring the absence of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers commonly found in conventional feed. This certification guarantees safer animal nutrition, promoting healthier livestock and reducing the risk of chemical contaminants entering the human food chain.
Probiotic-Enriched Rations
Probiotic-enriched rations in organic feed enhance gut health and nutrient absorption in livestock more effectively than conventional feed, supporting immune function and growth performance. These rations promote beneficial microbial populations, reducing reliance on antibiotics and improving overall animal welfare and productivity in organic animal husbandry systems.
Precision Nutrition Formulation
Precision nutrition formulation in animal husbandry emphasizes tailoring organic feed to meet specific nutrient requirements, enhancing animal health and productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Conventional feed, often relying on standardized nutrient profiles, may lack the adaptability and bioavailability benefits inherent in organic feed ingredients optimized through precision techniques.
Mycotoxin-Binding Clay Supplements
Mycotoxin-binding clay supplements in organic feed improve animal health by reducing toxin absorption, enhancing nutrient bioavailability, and supporting gut integrity more effectively than conventional feed additives. Studies show that these natural clays help mitigate mycotoxin risks without synthetic chemicals, aligning with organic farming standards and promoting safer animal nutrition.
Sustainable Insect Protein Meal
Sustainable insect protein meal offers a high-quality, eco-friendly alternative to conventional feed in animal nutrition, improving nutrient digestibility and reducing the environmental footprint associated with traditional feed sources. Integrating organic insect protein into animal husbandry promotes circular agriculture by utilizing organic waste streams and supporting biodiversity, enhancing overall farm sustainability.
Organic Feed vs Conventional Feed for Animal Nutrition Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com