Free-range poultry farming promotes natural behaviors and improves animal welfare by allowing birds access to outdoor spaces, leading to healthier and more resilient flocks. Battery-cage systems, while efficient and cost-effective, often restrict movement, increase stress, and raise ethical concerns regarding bird well-being. Selecting free-range methods supports sustainable farming practices and meets growing consumer demand for ethically produced poultry products.
Table of Comparison
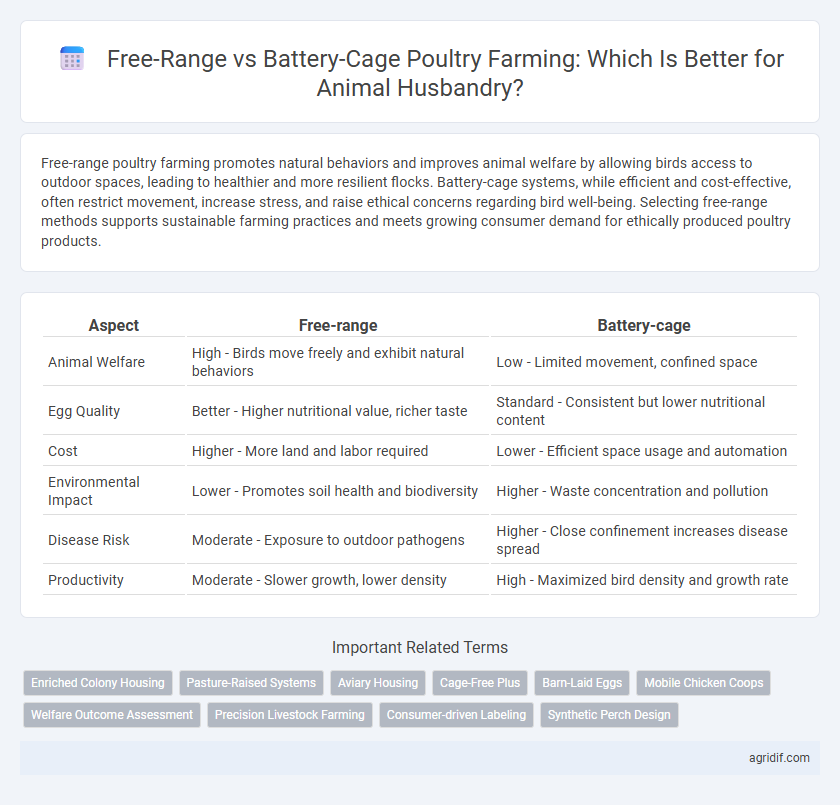
| Aspect | Free-range | Battery-cage |
|---|---|---|
| Animal Welfare | High - Birds move freely and exhibit natural behaviors | Low - Limited movement, confined space |
| Egg Quality | Better - Higher nutritional value, richer taste | Standard - Consistent but lower nutritional content |
| Cost | Higher - More land and labor required | Lower - Efficient space usage and automation |
| Environmental Impact | Lower - Promotes soil health and biodiversity | Higher - Waste concentration and pollution |
| Disease Risk | Moderate - Exposure to outdoor pathogens | Higher - Close confinement increases disease spread |
| Productivity | Moderate - Slower growth, lower density | High - Maximized bird density and growth rate |
Understanding Free-Range and Battery-Cage Systems
Free-range poultry farming allows birds to roam outdoors, promoting natural behaviors and improving animal welfare, while battery-cage systems confine birds in small, restricted cages designed for high-density production. Free-range systems often result in higher costs and lower production efficiency, contrasted with battery-cage systems that maximize space and egg output but raise welfare concerns due to limited mobility and increased stress. Understanding these systems requires balancing economic efficiency with animal welfare priorities in modern poultry farming.
Key Differences Between Free-Range and Battery-Cage Poultry
Free-range poultry farming allows birds to roam outdoors, facilitating natural behaviors and improving animal welfare, while battery-cage systems confine hens in restricted cages, limiting movement and often increasing stress levels. Free-range eggs typically have higher nutritional value, including increased omega-3 fatty acids and vitamins, contrasting with battery-cage eggs that may lack these benefits due to limited hen diet diversity. Environmental impact varies, with free-range systems promoting biodiversity and soil health, whereas battery-cage farms concentrate waste, posing higher pollution risks.
Animal Welfare: Comfort and Health Comparisons
Free-range poultry farming promotes better animal welfare by allowing birds to engage in natural behaviors such as foraging, dust bathing, and stretching their wings, which reduces stress and enhances overall comfort. In contrast, battery-cage systems confine birds in cramped spaces, often leading to physical ailments like osteoporosis, feather loss, and increased susceptibility to disease due to limited movement and poor air quality. Studies consistently show that free-range environments improve immune function and reduce mortality rates compared to the restricted conditions of battery cages.
Productivity and Egg Yield Analysis
Free-range poultry farming enhances egg quality and bird welfare, often resulting in higher consumer demand but may produce slightly lower egg yield per hen compared to battery-cage systems. Battery-cage systems maximize space efficiency and egg production rates, achieving up to 300 eggs per hen annually, but raise concerns over animal welfare and reduced bird activity. Productivity analysis reveals a trade-off between yield optimization in battery cages and improved health and egg marketability in free-range setups, influencing farm management decisions.
Environmental Impact of Poultry Farming Methods
Free-range poultry farming typically reduces environmental impact through enhanced soil health and lower ammonia emissions compared to battery-cage systems, which often concentrate waste and increase pollution risks. Battery-cage methods generate higher levels of nitrogen runoff and require significant energy inputs for ventilation and waste management, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable poultry production benefits from free-range practices that promote biodiversity and reduce reliance on synthetic inputs.
Cost and Economic Considerations for Farmers
Free-range poultry farming typically involves higher initial investments and operational costs due to larger land requirements and increased labor for animal welfare management. Battery-cage systems offer lower production costs per bird by maximizing space efficiency and automating feeding and egg collection, leading to higher short-term profitability. However, consumer demand for ethically produced eggs often allows free-range farmers to command premium prices, balancing higher expenses with potential market advantages.
Nutrition and Egg Quality Differences
Free-range poultry farming enhances egg nutritional profiles by increasing omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and carotenoids due to birds' natural foraging activities. In contrast, battery-cage systems typically yield eggs with lower nutrient diversity, often lacking the beneficial fatty acid composition found in free-range eggs. Studies show that free-range eggs possess superior shell strength and yolk color intensity, reflecting improved overall egg quality compared to battery-cage counterparts.
Disease Management and Biosecurity
Free-range poultry farming reduces the risk of airborne diseases due to increased ventilation and lower stocking densities but requires rigorous monitoring to prevent exposure to wild birds and parasites that can introduce pathogens. Battery-cage systems simplify biosecurity measures by restricting bird movement and minimizing contact with external contaminants, yet the high density and stress levels often increase susceptibility to disease outbreaks like avian influenza. Effective disease management in both systems hinges on tailored vaccination programs, regular health screenings, and strict sanitation protocols to control pathogen transmission and maintain flock health.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Consumer preferences increasingly favor free-range poultry products due to perceived animal welfare benefits and higher nutritional value, driving market growth in this segment. Battery-cage systems, while cost-effective and efficient for large-scale production, face declining demand as ethical concerns and stricter regulations prompt retailers to prioritize cage-free options. Market trends highlight a shift towards transparency and sustainability, with free-range poultry commanding premium prices and expanding in organic and specialty food markets.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Poultry Farming
Free-range poultry farming supports sustainable agriculture through improved animal welfare, reduced disease risk, and enhanced biodiversity, aligning with growing consumer demand for ethically produced meat and eggs. Innovations in pasture management and rotational grazing increase nutrient recycling and soil health, positioning free-range systems as a viable long-term solution. In contrast, battery-cage systems face regulatory restrictions and market pressure due to animal welfare concerns, driving the industry toward more humane and environmentally friendly practices.
Related Important Terms
Enriched Colony Housing
Enriched colony housing combines elements of free-range and battery-cage systems by providing hens with more space, perches, nesting areas, and scratching pads within a controlled environment, enhancing animal welfare and productivity. This system reduces stress and aggressive behaviors while maintaining efficient space utilization compared to traditional battery cages, promoting sustainable poultry farming practices.
Pasture-Raised Systems
Pasture-raised poultry systems promote natural behaviors and improved animal welfare by allowing birds access to outdoor environments with ample space, fresh air, and sunlight, leading to healthier growth and better-quality meat and eggs. Compared to battery-cage systems, pasture-raised methods reduce stress and disease incidence while enhancing nutrient content and environmental sustainability through rotational grazing and soil enrichment.
Aviary Housing
Aviary housing in poultry farming combines the welfare benefits of free-range systems with the space efficiency of battery-cage setups, allowing hens to express natural behaviors while optimizing flock density. This system enhances animal health and productivity through enriched environments and improved air quality compared to traditional battery cages.
Cage-Free Plus
Cage-Free Plus poultry farming enhances animal welfare by providing more space, natural light, and perching opportunities compared to traditional battery-cage systems, reducing stress and improving egg quality. Studies indicate that Cage-Free Plus environments promote better bone health and lower mortality rates, aligning with growing consumer demand for ethically raised poultry products.
Barn-Laid Eggs
Barn-laid eggs come from hens raised in spacious indoor environments with bedding, offering better animal welfare than battery-cage systems where birds are confined to small cages with limited movement. These conditions improve hen health and egg quality by reducing stress and the risk of disease, making barn-laid eggs a preferred choice over battery-cage alternatives in poultry farming.
Mobile Chicken Coops
Mobile chicken coops optimize free-range poultry farming by enhancing animal welfare, promoting natural behaviors, and reducing disease risks compared to battery-cage systems. These movable shelters improve soil health through natural fertilization and allow flexible pasture rotation, ultimately increasing bird productivity and sustainability.
Welfare Outcome Assessment
Free-range poultry farming promotes better welfare outcomes by allowing natural behaviors such as perching, foraging, and dust bathing, leading to reduced stress and improved physical health. Battery-cage systems restrict movement and natural activities, often resulting in higher incidence of bone fractures, feather loss, and increased mortality rates.
Precision Livestock Farming
Precision livestock farming integrates advanced sensors and real-time monitoring to optimize welfare and productivity in both free-range and battery-cage poultry systems. Free-range setups benefit from environmental data tracking for outdoor behavior, while battery-cage systems utilize controlled conditions monitoring to enhance health and feed efficiency.
Consumer-driven Labeling
Consumer-driven labeling in poultry farming highlights the growing preference for free-range systems over battery-cage methods, emphasizing animal welfare, product quality, and ethical sourcing. Labels such as "free-range," "cage-free," and "organic" influence purchasing decisions by providing transparency about the living conditions and treatment of poultry.
Synthetic Perch Design
Synthetic perch designs in free-range poultry farming enhance bird welfare by mimicking natural roosting behaviors and reducing stress compared to battery-cage systems. These durable, easy-to-clean materials improve hygiene while supporting efficient space utilization and lung health in poultry environments.
Free-range vs Battery-cage for Poultry Farming Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com