Choosing between heirloom and hybrid seeds significantly impacts crop production outcomes, with heirloom varieties offering genetic diversity, rich flavors, and adaptability to local conditions, while hybrids provide higher yields, disease resistance, and uniformity. Farmers prioritizing seed selection must balance the preservation of traditional traits against the demand for consistent productivity and resilience. Understanding the specific goals and environmental factors is essential to optimize seed choice and maximize crop performance.
Table of Comparison
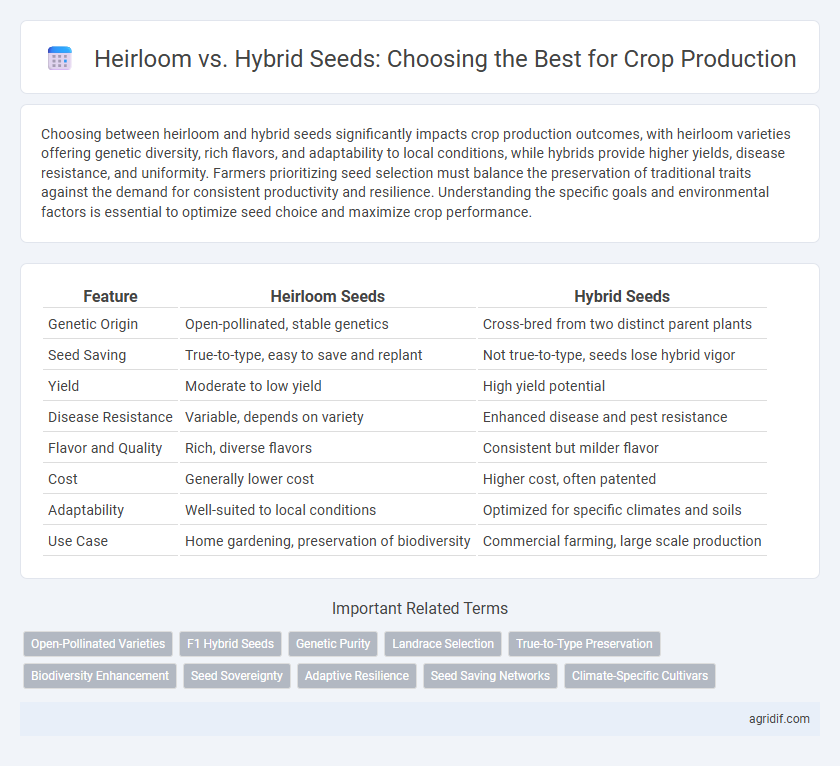
| Feature | Heirloom Seeds | Hybrid Seeds |
|---|---|---|
| Genetic Origin | Open-pollinated, stable genetics | Cross-bred from two distinct parent plants |
| Seed Saving | True-to-type, easy to save and replant | Not true-to-type, seeds lose hybrid vigor |
| Yield | Moderate to low yield | High yield potential |
| Disease Resistance | Variable, depends on variety | Enhanced disease and pest resistance |
| Flavor and Quality | Rich, diverse flavors | Consistent but milder flavor |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost, often patented |
| Adaptability | Well-suited to local conditions | Optimized for specific climates and soils |
| Use Case | Home gardening, preservation of biodiversity | Commercial farming, large scale production |
Understanding Heirloom Seeds: Definition and Characteristics
Heirloom seeds are open-pollinated varieties passed down through generations, prized for their genetic diversity and adaptability to local growing conditions. These seeds retain their original traits without genetic modification, ensuring authentic flavor profiles and resilience. Farmers favor heirloom seeds for preserving agricultural heritage and promoting biodiversity in crop production.
What Makes Hybrid Seeds Different?
Hybrid seeds result from crossbreeding two genetically distinct parent plants to combine desirable traits such as higher yield, disease resistance, and uniformity. Unlike heirloom seeds that preserve genetic diversity and traditional qualities, hybrids offer enhanced performance but often produce sterile or less stable offspring. This genetic uniformity in hybrids supports consistent crop production but limits saving seeds for future planting compared to heirlooms.
Genetic Diversity: Heirloom vs Hybrid
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity by maintaining traditional, open-pollinated varieties that adapt to local environments over generations, offering resilience against pests and climate changes. Hybrid seeds, created through controlled crossbreeding, typically focus on uniformity and high yield but often lack the genetic variety that supports long-term crop adaptability. Prioritizing heirloom varieties in crop production helps sustain biodiversity and safeguards agricultural ecosystems against future uncertainties.
Yield and Productivity Comparisons
Heirloom seeds generally produce lower yields compared to hybrid seeds, which are bred specifically for higher productivity and resilience to pests and environmental stress. Hybrid varieties often outperform heirlooms in both total crop yield and consistency across different growing conditions, making them preferable for commercial farming. However, heirloom seeds retain genetic diversity and unique flavors but typically require more attentive cultivation to achieve optimal yields.
Disease Resistance: Choosing the Right Seeds
Heirloom seeds often lack modern disease resistance, making them more vulnerable to common crop pathogens, while hybrid seeds are bred specifically for enhanced resistance to diseases like blight and wilt. Selecting hybrid seeds can significantly reduce crop losses and decrease the need for chemical treatments, promoting a healthier and more productive harvest. Understanding the trade-offs between genetic diversity in heirlooms and the targeted protection in hybrids is crucial for sustainable disease management in crop production.
Flavor and Nutritional Value Differences
Heirloom seeds typically offer superior flavor and richer nutritional profiles due to their genetic diversity and open-pollination, preserving unique taste characteristics and higher antioxidant levels. Hybrid seeds, bred for yield and disease resistance, often compromise on flavor intensity and nutrient density despite improved crop uniformity and productivity. Selecting heirloom varieties enhances crop quality focused on taste and health benefits, while hybrids prioritize agricultural efficiency.
Seed Saving and Sustainability Considerations
Heirloom seeds offer superior seed saving potential due to their open-pollinated nature, allowing farmers to sustainably preserve genetic diversity and adapt crops to local conditions over time. In contrast, hybrid seeds often produce sterile or less vigorous offspring, limiting effective seed saving and increasing dependence on seed suppliers. Prioritizing heirloom varieties supports sustainability by fostering resilience in crop production systems and reducing reliance on commercial seed markets.
Cost and Accessibility of Heirloom and Hybrid Seeds
Heirloom seeds are generally more affordable and accessible through local seed exchanges and community gardens, promoting biodiversity and preserving traditional varieties. Hybrid seeds often incur higher costs due to proprietary technology and are primarily distributed by commercial seed companies, offering uniformity and higher yield potential. Farmers seeking cost-effective and readily available seeds may prefer heirlooms, while those prioritizing productivity and pest resistance often choose hybrids despite higher prices.
Adaptability to Local Growing Conditions
Heirloom seeds often exhibit superior adaptability to local growing conditions due to their long history of cultivation in specific regions, preserving traits such as climate tolerance and soil preference. Hybrid seeds, while engineered for high yield and disease resistance, may lack the same level of environmental resilience found in heirloom varieties. Selecting seeds based on local adaptability improves crop sustainability and productivity in variable agroecological zones.
Making the Best Choice for Your Farm or Garden
Selecting between heirloom and hybrid seeds hinges on balancing genetic diversity with yield potential. Heirloom seeds offer unique flavors and adaptability suited for small-scale gardens seeking biodiversity, while hybrid seeds provide disease resistance and higher uniformity, ideal for commercial farms aiming for consistent production. Evaluating soil conditions, climate, and market goals ensures the best seed choice to maximize crop health and productivity.
Related Important Terms
Open-Pollinated Varieties
Open-pollinated varieties, often referred to as heirloom seeds, allow farmers to save seeds from year to year, preserving genetic diversity and adapting crops to specific local conditions, unlike hybrid seeds which are bred for consistency but do not produce reliable offspring. Choosing open-pollinated seeds supports sustainable agriculture by maintaining crop heritage and resilience against pests and diseases in crop production.
F1 Hybrid Seeds
F1 hybrid seeds combine the genetic traits of two distinct parent plants to produce offspring with enhanced vigor, yield, and disease resistance, making them a preferred choice for commercial crop production. While heirloom seeds retain traditional qualities and diverse genetics, F1 hybrids offer uniformity and predictable performance critical for large-scale agricultural efficiency.
Genetic Purity
Heirloom seeds maintain genetic purity by preserving traditional plant varieties passed down through generations, ensuring stable traits and authentic flavor profiles. Hybrid seeds result from cross-pollinating distinct parent plants to enhance specific qualities, but their genetic mixture leads to variability and reduced purity in subsequent generations.
Landrace Selection
Landrace selection preserves genetic diversity by favoring seeds adapted to local environments, enhancing resilience and flavor profiles in crop production. Compared to hybrid seeds, landraces offer stable yields and greater resistance to pests and diseases, supporting sustainable agriculture practices.
True-to-Type Preservation
Heirloom seeds guarantee true-to-type preservation, maintaining genetic purity and consistent traits across generations, unlike hybrid seeds that often produce variable offspring due to genetic segregation. Choosing heirloom varieties supports biodiversity and ensures stable crop characteristics essential for sustainable farming and seed saving.
Biodiversity Enhancement
Heirloom seeds promote biodiversity by preserving genetic diversity and traditional varieties that adapt to specific local environments, supporting ecosystem resilience and long-term sustainability. Hybrid seeds offer higher yields and disease resistance but often reduce genetic variation, potentially compromising biodiversity and ecological balance in agricultural systems.
Seed Sovereignty
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and empower farmers with seed sovereignty by enabling them to save and exchange seeds each season, while hybrid seeds often limit this freedom due to controlled germination traits. Choosing heirloom varieties supports sustainable agriculture and resilient crop systems by maintaining traditional knowledge and adapting to local environmental conditions.
Adaptive Resilience
Heirloom seeds offer greater genetic diversity, enhancing adaptive resilience by supporting crops that withstand local environmental stresses and climate variations. Hybrid seeds provide uniformity and higher immediate yields but may lack long-term adaptability to evolving conditions, making heirlooms crucial for sustainable crop production.
Seed Saving Networks
Heirloom seeds preserve genetic diversity and are favored in seed saving networks for their adaptability and unique traits, ensuring long-term crop resilience. Hybrid seeds offer higher initial yields but often fail to breed true, limiting their usefulness in community-based seed saving and sharing initiatives.
Climate-Specific Cultivars
Heirloom seeds offer genetic diversity and adaptability to local microclimates, making them ideal for traditional farming in stable environments, while hybrid seeds are engineered for higher yields and disease resistance tailored to specific climate conditions. Selecting climate-specific cultivars from hybrid varieties enhances crop resilience and productivity, especially in regions facing variable weather patterns and extreme temperatures.
Heirloom vs Hybrid for seed selection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com