Seed treatment offers targeted protection by coating seeds with fungicides or insecticides, ensuring early disease control and promoting healthy seedling growth. Foliar application provides direct protection to leaves and stems, effectively managing diseases throughout the growing season, especially during critical growth stages. Combining both methods can enhance crop resilience, reduce disease pressure, and improve overall yield quality.
Table of Comparison
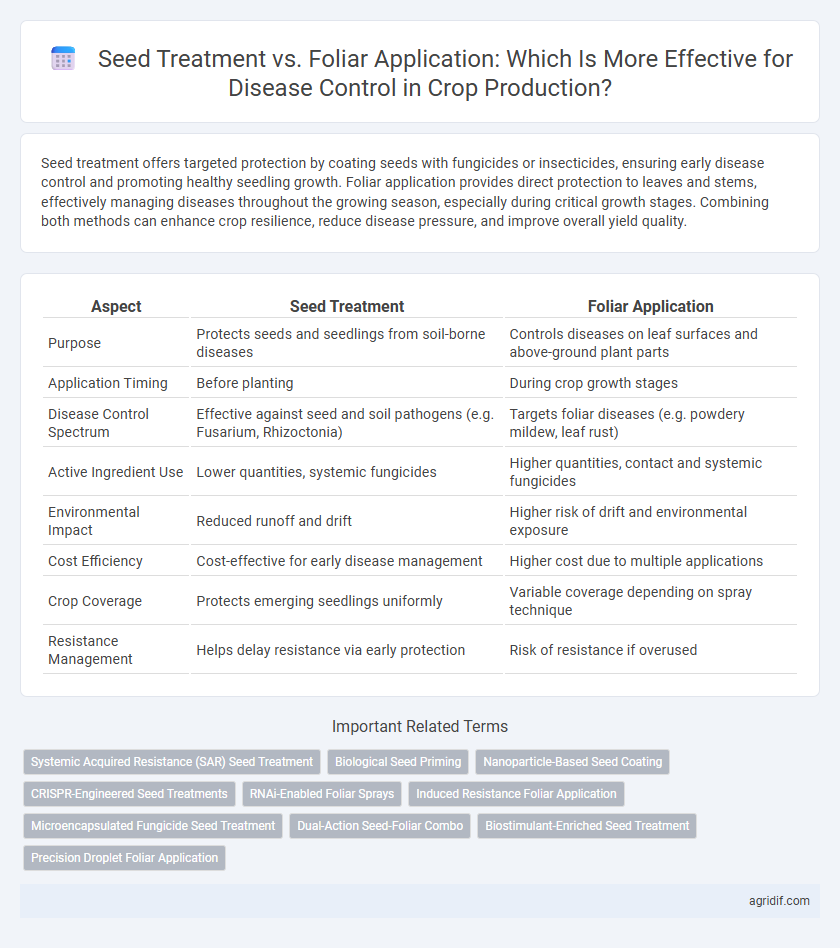
| Aspect | Seed Treatment | Foliar Application |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Protects seeds and seedlings from soil-borne diseases | Controls diseases on leaf surfaces and above-ground plant parts |
| Application Timing | Before planting | During crop growth stages |
| Disease Control Spectrum | Effective against seed and soil pathogens (e.g. Fusarium, Rhizoctonia) | Targets foliar diseases (e.g. powdery mildew, leaf rust) |
| Active Ingredient Use | Lower quantities, systemic fungicides | Higher quantities, contact and systemic fungicides |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced runoff and drift | Higher risk of drift and environmental exposure |
| Cost Efficiency | Cost-effective for early disease management | Higher cost due to multiple applications |
| Crop Coverage | Protects emerging seedlings uniformly | Variable coverage depending on spray technique |
| Resistance Management | Helps delay resistance via early protection | Risk of resistance if overused |
Understanding Seed Treatment in Crop Disease Management
Seed treatment uses fungicides and insecticides applied directly to seeds to protect emerging seedlings from soil-borne pathogens and pests, enhancing early plant vigor and reducing disease incidence. This method provides targeted, systemic protection that supports root health and minimizes the need for repeated chemical applications during crop growth. Compared to foliar application, seed treatment offers a preventive approach with prolonged efficacy and reduced environmental impact in crop disease management.
Foliar Application: Method and Mechanism
Foliar application involves spraying fungicides or biocontrol agents directly onto plant leaves, enabling rapid absorption and targeted disease control. This method allows for precise dosage and quick action against foliar pathogens such as powdery mildew and rust, improving overall crop health and yield. The mechanism relies on the active ingredient penetrating the leaf surface, disrupting pathogen development and enhancing plant resistance.
Key Differences Between Seed Treatment and Foliar Application
Seed treatment involves coating seeds with fungicides or insecticides before planting to protect young plants from soil-borne pathogens and improve germination rates, providing early-stage disease control. Foliar application delivers pesticides or nutrients directly to the crop leaves, targeting above-ground diseases and allowing for rapid action against pathogens during the growth cycle. The primary difference lies in timing and target area: seed treatment offers preventive protection at the root and initial growth stage, while foliar application is a reactive measure for controlling diseases affecting mature plant tissues.
Effectiveness of Seed Treatment Against Major Crop Diseases
Seed treatment provides systemic protection by delivering fungicides or insecticides directly to the emerging seedling, effectively controlling soil-borne diseases such as damping-off, root rot, and seedling blights. Compared to foliar applications, seed treatment targets pathogens early in the plant's development, reducing infection rates and improving establishment and yield potential. Data show that crops like wheat, maize, and soybean exhibit significant disease suppression and enhanced vigor following seed treatment, underscoring its critical role in integrated disease management strategies.
Foliar Applications for In-Season Disease Control
Foliar applications provide targeted in-season disease control by delivering fungicides directly to the affected leaf surfaces, enabling rapid action against pathogens such as powdery mildew and rust. This method enhances nutrient uptake and reduces disease spread during critical crop growth stages, improving yield and crop quality. Compared to seed treatment, foliar sprays offer flexibility to manage multiple diseases as they arise, allowing timely intervention based on field conditions.
Environmental Impact: Seed Treatment vs. Foliar Application
Seed treatment minimizes environmental impact by delivering precise doses of pesticides directly to the seed, reducing chemical runoff and non-target exposure. Foliar application can lead to higher pesticide drift and contamination of surrounding ecosystems due to spray drift and runoff. Selecting seed treatment over foliar sprays enhances sustainable crop protection by limiting environmental pollution and preserving beneficial insect populations.
Cost Analysis: Seed Treatment Compared to Foliar Sprays
Seed treatment often provides a cost-effective disease control method by protecting seedlings early, reducing the need for multiple foliar spray applications throughout the growing season. Foliar sprays typically incur higher expenses due to repeated applications, labor, and equipment costs, increasing overall disease management budgets. Economic analyses show that seed treatment can lower input costs while maintaining crop health, making it a preferred choice for sustainable disease control in high-value crops.
Timing and Application Strategies for Maximum Efficacy
Seed treatment provides early disease protection by targeting pathogens at the germination stage, ensuring healthier seedling development. Foliar application is most effective when timed to coincide with critical growth stages or disease outbreak periods, delivering direct protection to foliage and reducing pathogen spread. Optimizing timing by integrating seed treatment with foliar sprays enhances overall disease control and maximizes crop yield potential.
Integrated Disease Management: Combining Both Approaches
Integrating seed treatment and foliar application enhances disease control by targeting pathogens at multiple crop growth stages, improving overall plant health and yield. Seed treatment provides early protection against soil-borne diseases, while foliar applications address foliar pathogens during the growing season, creating a comprehensive defense system. Combining both methods supports sustainable crop production by reducing disease pressure and minimizing reliance on chemical inputs.
Future Trends in Disease Control Methods for Crop Production
Emerging trends in crop disease control emphasize integrating advanced seed treatment technologies with precision foliar applications to enhance efficacy and reduce chemical usage. Innovations such as nanotechnology-based seed coatings and drone-assisted foliar sprays enable targeted delivery of biocontrol agents and systemic fungicides, improving disease resistance while minimizing environmental impact. Future crop protection strategies prioritize sustainable methods combining genetic seed enhancements with smart foliar treatments to ensure resilient production systems under climate variability.
Related Important Terms
Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR) Seed Treatment
Systemic Acquired Resistance (SAR) seed treatment enhances crop defense by activating the plant's immune system from the root stage, providing long-lasting protection against pathogens compared to foliar applications that offer more localized, short-term disease control. SAR seed treatments improve overall plant health and yield by inducing systemic resistance throughout the plant, reducing the reliance on repeated foliar fungicide applications.
Biological Seed Priming
Biological seed priming enhances crop resilience by promoting beneficial microbial colonization on seeds, offering targeted disease control and improved germination compared to foliar applications that provide surface-level protection with limited systemic effects. This method reduces dependency on chemical fungicides by enabling early biochemical defenses and sustained pathogen resistance throughout crop development.
Nanoparticle-Based Seed Coating
Nanoparticle-based seed coating enhances disease control by delivering targeted antimicrobial agents directly to the seed surface, promoting early seedling protection compared to foliar application that treats above-ground plant parts later in the growth cycle. This method improves seed germination rates and crop vigor while reducing pathogen load in the rhizosphere, offering prolonged and efficient disease suppression in crop production.
CRISPR-Engineered Seed Treatments
CRISPR-engineered seed treatments offer precise disease resistance by directly modifying genetic traits, enhancing early-stage crop immunity more effectively than foliar applications, which provide temporary surface protection against pathogens. This genetic approach reduces reliance on chemical sprays, promoting sustainable crop production and long-term disease control.
RNAi-Enabled Foliar Sprays
RNAi-enabled foliar sprays offer targeted disease control by silencing specific pathogen genes directly on plant surfaces, enhancing crop protection with minimal environmental impact compared to traditional seed treatments. This technology provides rapid, customizable defense without altering seed genetics, promoting sustainable crop production and integrated pest management strategies.
Induced Resistance Foliar Application
Induced resistance foliar application enhances crop defense by activating the plant's innate immune system against pathogens, providing targeted and systemic disease control compared to seed treatment, which primarily protects seedlings during early growth. Foliar application ensures timely delivery of elicitors directly to vulnerable leaf tissues, promoting stronger and longer-lasting resistance in crop production.
Microencapsulated Fungicide Seed Treatment
Microencapsulated fungicide seed treatments provide targeted, long-lasting protection by releasing active ingredients gradually, reducing pathogen impact from germination onward and minimizing environmental runoff compared to foliar applications. Foliar application offers immediate disease control but requires frequent application and higher chemical doses, increasing resistance risk and environmental exposure.
Dual-Action Seed-Foliar Combo
Dual-action seed-foliar combinations enhance disease control by integrating systemic protection from seed treatment with targeted application of foliar sprays, ensuring early and sustained defense against pathogens in crops. This synergistic approach improves crop health, maximizes yield potential, and reduces the reliance on high chemical doses by optimizing fungicide efficacy throughout critical growth stages.
Biostimulant-Enriched Seed Treatment
Biostimulant-enriched seed treatment enhances early crop vigor and disease resistance by delivering targeted microbial and nutrient formulations directly to the seed, fostering robust root development and systemic protection against soil-borne pathogens. Foliar application, while effective for controlling foliar diseases, often lacks the early-stage penetration and sustained disease resistance provided by seed treatments enriched with biostimulants, resulting in comparatively lower disease suppression during critical growth phases.
Precision Droplet Foliar Application
Precision Droplet Foliar Application enhances disease control in crop production by delivering targeted treatment directly onto plant foliage, improving efficacy over traditional seed treatment methods that primarily protect early root development. This method reduces chemical usage and environmental impact by optimizing droplet size and application timing, leading to higher crop yield and sustainable disease management.
Seed treatment vs Foliar application for disease control Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com