Sprinkler irrigation distributes water uniformly over crops, making it suitable for various terrains but can result in higher evaporation and water runoff. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, maximizing water use efficiency and reducing waste by minimizing evaporation and deep percolation. Choosing between sprinkler and drip irrigation depends on crop type, soil conditions, and water availability, with drip irrigation often preferred for water conservation in arid regions.
Table of Comparison
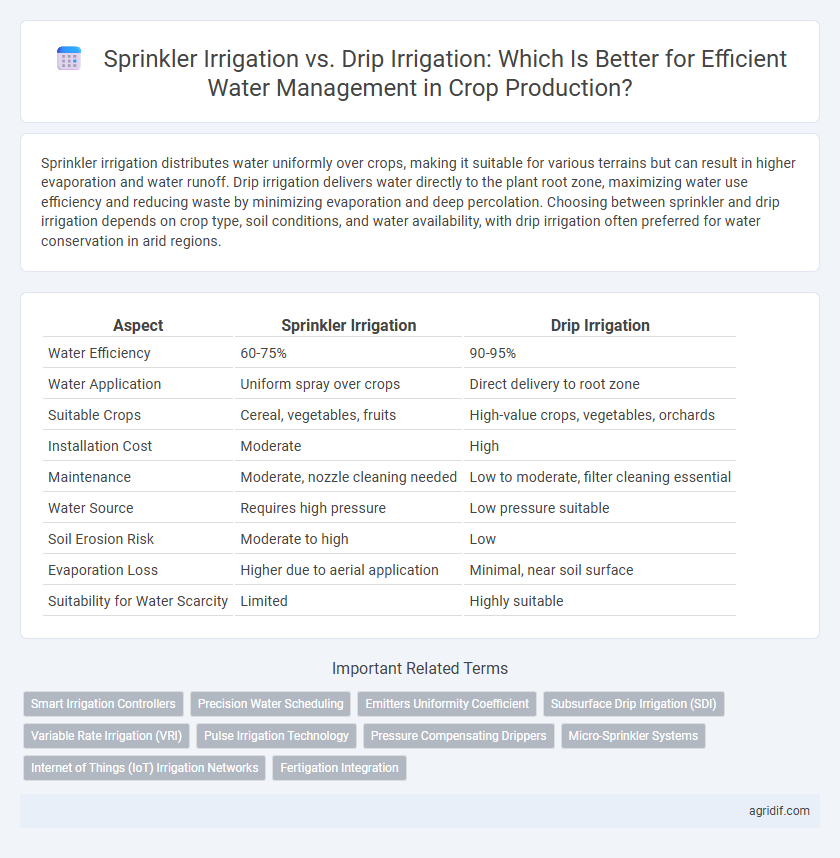
| Aspect | Sprinkler Irrigation | Drip Irrigation |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | 60-75% | 90-95% |
| Water Application | Uniform spray over crops | Direct delivery to root zone |
| Suitable Crops | Cereal, vegetables, fruits | High-value crops, vegetables, orchards |
| Installation Cost | Moderate | High |
| Maintenance | Moderate, nozzle cleaning needed | Low to moderate, filter cleaning essential |
| Water Source | Requires high pressure | Low pressure suitable |
| Soil Erosion Risk | Moderate to high | Low |
| Evaporation Loss | Higher due to aerial application | Minimal, near soil surface |
| Suitability for Water Scarcity | Limited | Highly suitable |
Introduction to Efficient Water Management in Crop Production
Sprinkler irrigation distributes water uniformly over crops, simulating natural rainfall and covering large areas efficiently. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it ideal for water-sensitive crops and arid regions. Efficient water management in crop production relies on selecting the appropriate irrigation method to maximize water use efficiency and crop yield.
Overview of Sprinkler and Drip Irrigation Systems
Sprinkler irrigation systems distribute water through overhead sprinklers, simulating natural rainfall, and are suitable for a wide range of crops and soil types, offering uniform water coverage over large areas. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone through a network of tubes and emitters, minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it highly efficient for water conservation in row crops, orchards, and vineyards. Both systems require proper design and maintenance, but drip irrigation typically achieves higher water-use efficiency and reduces weed growth compared to sprinkler systems.
Water Usage Efficiency: Sprinkler vs Drip Methods
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the plant root zone, resulting in water usage efficiency rates of up to 90%, significantly reducing evaporation and runoff compared to sprinkler irrigation, whose efficiency typically ranges between 60-75%. Sprinkler systems spread water over a large area, causing higher losses due to wind drift and surface evaporation, making them less efficient in water-scarce regions. Farmers aiming for precision water management often prefer drip irrigation as it optimizes water use, enhances crop yield, and conserves vital water resources.
Impact on Crop Yield and Quality
Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, enhancing moisture efficiency and significantly improving crop yield and quality by reducing water stress and nutrient leaching. Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over the canopy, which can lead to higher evaporation losses and potential disease incidence, often resulting in moderate yield improvements compared to drip systems. Optimizing irrigation methods based on crop type and soil conditions is crucial for maximizing both yield and produce quality in sustainable water management.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Sprinkler irrigation systems involve higher installation costs due to the need for pumps, pipes, and sprinkler heads, but they require less frequent maintenance compared to drip irrigation. Drip irrigation requires more precise installation with emitters placed near plant roots, which can increase setup time and complexity but offers water efficiency and targeted delivery. Regular inspection and cleaning of drip lines are necessary to prevent clogging, whereas sprinkler systems may face wear on sprinkler heads and piping leaks requiring periodic repairs.
Suitability for Different Crop Types and Soil Conditions
Sprinkler irrigation is ideal for cereal crops, vegetables, and fruits grown in loamy and sandy soils, offering uniform water distribution over large fields. Drip irrigation suits row crops, orchards, and high-value vegetables cultivated in clayey and saline soils, providing targeted water delivery that minimizes evaporation and runoff. Soil permeability and crop root depth are critical factors in choosing between these methods to enhance water use efficiency and crop yield.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operational Expenses
Sprinkler irrigation typically requires a lower initial investment compared to drip irrigation, making it more accessible for large-scale crop production with moderate budgets. Operational expenses for sprinkler systems tend to be higher due to increased energy consumption and water loss from evaporation, while drip irrigation minimizes water waste and reduces long-term costs through precise water delivery directly to plant roots. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors drip irrigation for water-efficient crop production despite its higher upfront expenses.
Water Loss and Evaporation Comparisons
Sprinkler irrigation experiences higher water loss due to evaporation and wind drift compared to drip irrigation, which delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing surface evaporation. Drip systems typically achieve water use efficiency rates of 90% or higher, while sprinkler systems often range between 65-75%. Reduced evaporation in drip irrigation is particularly critical in arid regions, promoting sustainable water management and enhancing crop yield.
Environmental and Sustainability Considerations
Sprinkler irrigation distributes water over crops uniformly but can lead to significant water loss through evaporation and runoff, impacting local water resources. Drip irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing water waste and reducing soil erosion, thereby enhancing water use efficiency and conserving groundwater. Sustainable crop production benefits from drip systems by lowering energy consumption and decreasing the carbon footprint associated with water pumping.
Choosing the Right Irrigation System for Your Farm
Sprinkler irrigation delivers water uniformly across the field, making it ideal for various crop types and larger acreage, while drip irrigation targets water directly to the plant roots, maximizing efficiency and reducing water waste. Farmers managing water resources in drought-prone areas often prefer drip systems to enhance crop yield and conserve moisture. Selecting the appropriate irrigation system depends on factors like crop type, soil conditions, water availability, and budget, with drip irrigation excelling in precision and sprinklers offering versatility.
Related Important Terms
Smart Irrigation Controllers
Smart irrigation controllers enhance water use efficiency in both sprinkler and drip irrigation systems by precisely adjusting schedules based on soil moisture, weather data, and crop needs. These controllers reduce water waste and improve crop yield by delivering optimal irrigation, with drip systems benefiting most through targeted water application directly to plant roots.
Precision Water Scheduling
Drip irrigation offers superior precision water scheduling by delivering water directly to the plant root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff losses compared to sprinkler irrigation. This targeted approach enhances water use efficiency, promoting optimal crop growth while conserving valuable water resources.
Emitters Uniformity Coefficient
Sprinkler irrigation systems typically exhibit an emitter uniformity coefficient (EUC) ranging from 75% to 85%, signifying moderate water distribution consistency. Drip irrigation, with EUC values often exceeding 90%, ensures precise and uniform water delivery directly to the root zone, enhancing water use efficiency and crop yield.
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) enhances crop production by delivering water directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to traditional sprinkler irrigation. This precise water management system improves water use efficiency, minimizes weed growth, and supports higher yields in water-scarce environments.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI)
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) technology enhances both sprinkler and drip irrigation systems by allowing precise water application tailored to specific soil and crop needs, improving water use efficiency and yield. Sprinkler irrigation with VRI is ideal for uniform crop canopies and larger fields, whereas drip irrigation with VRI provides targeted moisture directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff in heterogeneous or water-sensitive areas.
Pulse Irrigation Technology
Pulse irrigation technology in sprinkler systems delivers water in short, frequent bursts, enhancing soil moisture retention and reducing runoff compared to traditional continuous watering methods. Drip irrigation with pulse technology optimizes water use efficiency by providing precise water application directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and promoting healthier crop growth.
Pressure Compensating Drippers
Pressure compensating drippers in drip irrigation systems deliver a uniform water flow regardless of pressure variations, enhancing water use efficiency and promoting consistent crop growth. Compared to sprinkler irrigation, this method reduces water waste by minimizing evaporation and runoff, making it ideal for precise water management in diverse crop production settings.
Micro-Sprinkler Systems
Micro-sprinkler irrigation offers targeted water distribution with moderate flow rates, enhancing soil moisture uniformity compared to traditional sprinklers and minimizing runoff in crop production. This system balances water efficiency and coverage area, proving effective for diverse crop types while reducing water waste more than conventional sprinkler methods but less than drip irrigation.
Internet of Things (IoT) Irrigation Networks
IoT-enabled drip irrigation systems optimize water usage by delivering precise moisture levels directly to plant roots, reducing water waste by up to 40% compared to traditional sprinkler irrigation. These smart networks utilize sensors and real-time data analytics to adjust irrigation schedules, enhancing crop yield and conserving resources in diverse agricultural environments.
Fertigation Integration
Sprinkler irrigation delivers water uniformly over large crop areas but often results in higher evaporation losses compared to drip irrigation, which applies water directly to the root zone with greater efficiency. Drip irrigation systems facilitate precise fertigation integration, allowing optimized nutrient delivery and reducing fertilizer runoff, thereby enhancing crop yield and quality.
Sprinkler Irrigation vs Drip Irrigation for Water Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com