On-farm pasteurization ensures milk safety by eliminating harmful pathogens directly at the source, preserving freshness and quality for dairy pets. Bulk tank sale offers convenience and efficiency for large-scale operations but may increase the risk of contamination during transport and storage. Choosing between these methods depends on balancing control over milk hygiene with operational scalability in dairy farming.
Table of Comparison
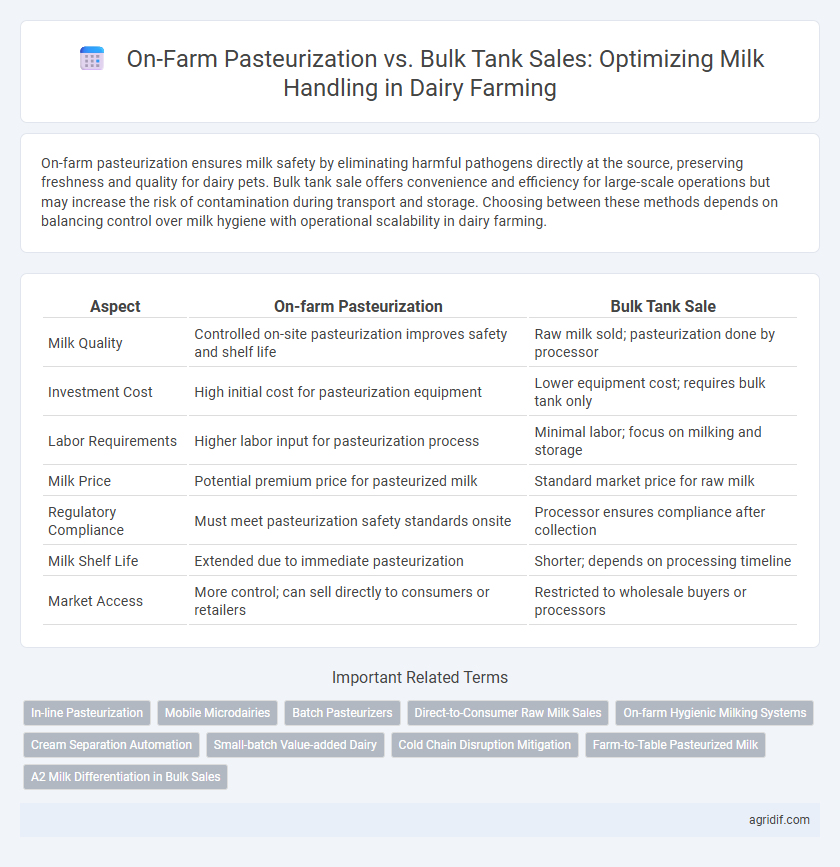
| Aspect | On-farm Pasteurization | Bulk Tank Sale |
|---|---|---|
| Milk Quality | Controlled on-site pasteurization improves safety and shelf life | Raw milk sold; pasteurization done by processor |
| Investment Cost | High initial cost for pasteurization equipment | Lower equipment cost; requires bulk tank only |
| Labor Requirements | Higher labor input for pasteurization process | Minimal labor; focus on milking and storage |
| Milk Price | Potential premium price for pasteurized milk | Standard market price for raw milk |
| Regulatory Compliance | Must meet pasteurization safety standards onsite | Processor ensures compliance after collection |
| Milk Shelf Life | Extended due to immediate pasteurization | Shorter; depends on processing timeline |
| Market Access | More control; can sell directly to consumers or retailers | Restricted to wholesale buyers or processors |
Introduction to Milk Handling Methods in Dairy Farming
On-farm pasteurization involves heating raw milk to a specific temperature to eliminate pathogens before packaging, enhancing milk safety directly at the dairy farm. Bulk tank sale refers to collecting raw milk in large refrigerated tanks, where it is stored and cooled for transportation to processing facilities. Both methods impact milk quality, shelf life, and biosecurity, influencing dairy farm operational efficiency and compliance with food safety regulations.
What is On-farm Pasteurization?
On-farm pasteurization is the process of heating raw milk to a specific temperature to eliminate harmful pathogens while preserving nutritional quality, performed directly at the dairy farm before distribution. This method ensures immediate control over milk safety, reducing contamination risks associated with bulk tank storage and transport. By implementing on-farm pasteurization, farmers can deliver safer milk products, meeting regulatory standards and enhancing consumer trust.
Understanding Bulk Tank Milk Sales
Bulk tank milk sales allow dairy farmers to store large volumes of milk at regulated temperatures, ensuring freshness and safety before distribution. This method reduces labor and processing costs by eliminating on-farm pasteurization while maintaining compliance with industry standards for bacterial count and somatic cell levels. Efficient milk cooling and frequent bulk tank cleaning are critical to preserving milk quality and meeting buyer requirements in bulk sales.
Food Safety: Pasteurized vs Raw Milk
On-farm pasteurization significantly reduces the risk of pathogens such as Salmonella, Listeria, and E. coli, ensuring milk safety before it reaches consumers, unlike raw milk stored in bulk tanks that carries higher contamination risks. Regulatory standards often mandate pasteurization to prevent foodborne illnesses, making on-farm processes critical for compliance and public health. This method enhances traceability and control over microbial hazards compared to raw bulk tank sales, which may lack stringent safety monitoring.
Economic Implications: Profit Margins and Costs
On-farm pasteurization requires significant upfront investment in equipment and ongoing operational costs, impacting short-term profit margins but allowing for direct sales at premium prices. Bulk tank sales minimize processing expenses and labor but often result in lower profit margins due to reliance on intermediaries and fluctuating commodity milk prices. Economic success depends on balancing capital expenditures and market pricing strategies associated with each milk handling method.
Quality Control and Milk Shelf Life
On-farm pasteurization significantly enhances milk quality control by eliminating pathogens immediately after milking, reducing contamination risks and extending milk shelf life up to 14 days under optimal refrigeration. In contrast, bulk tank sales rely on centralized pasteurization which can introduce delays, increasing potential bacterial growth and shortening shelf life to about 7-10 days. Implementing on-farm pasteurization supports dairy farmers in maintaining higher microbial standards and delivering fresher milk products to consumers.
Equipment and Infrastructure Requirements
On-farm pasteurization requires specialized pasteurizers, temperature control systems, and strict sanitation protocols to ensure milk safety before packaging, demanding significant initial investment and maintenance. Bulk tank sale relies on large refrigerated storage tanks and seamless milk transport systems, emphasizing capacity and cooling efficiency over pasteurization equipment. Both methods necessitate robust infrastructure but differ in complexity, with on-farm pasteurization integrating processing equipment while bulk tank sale focuses on storage and distribution logistics.
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
On-farm pasteurization requires strict adherence to state and federal regulations, including regular inspections, record-keeping, and verification of pasteurization processes to ensure milk safety. Bulk tank sales are subject to stringent dairy industry standards and must comply with sanitary requirements, frequent microbial testing, and temperature control mandates set by the FDA and USDA. Non-compliance in either method can result in fines, product recalls, or suspension of the dairy operation's license, emphasizing the importance of rigorous regulatory oversight in milk handling.
Market Access and Consumer Demand
On-farm pasteurization enhances market access by meeting stringent local regulations and consumer demand for fresher, minimally processed milk, often allowing direct sales to retailers and farmers markets. Bulk tank sales facilitate large-volume distribution to processors but may limit opportunities for producers to cater to niche markets seeking high-quality or artisanal products. Consumer preferences increasingly favor transparency and traceability, which on-farm pasteurization can provide, driving demand for locally produced dairy with verified safety standards.
Choosing the Right Milk Handling Method for Your Dairy Farm
Selecting the ideal milk handling method depends on factors like farm size, infrastructure, and target market requirements. On-farm pasteurization offers control over milk quality and can meet direct consumer sales standards, while bulk tank sales streamline large-scale distribution to processors. Evaluating cost, regulatory compliance, and desired product freshness ensures optimal operational efficiency and profitability.
Related Important Terms
In-line Pasteurization
In-line pasteurization offers precise temperature control and immediate heat treatment during milk flow, reducing bacterial contamination risks compared to bulk tank sale systems that rely on post-collection pasteurization. This method enhances milk safety, extends shelf life, and maintains nutritional quality directly on-farm, optimizing dairy farm operational efficiency and product integrity.
Mobile Microdairies
Mobile microdairies enhance on-farm pasteurization by enabling immediate milk treatment, reducing contamination risks and preserving milk quality more effectively than bulk tank sales. This approach supports small-scale dairy farmers in meeting local safety standards while maximizing freshness and consumer trust through direct farm-to-table distribution.
Batch Pasteurizers
Batch pasteurizers on dairy farms provide precise temperature control and effective pathogen reduction, enhancing milk safety directly at the source compared to bulk tank sale methods. This on-farm pasteurization minimizes contamination risks during transport and storage, ensuring higher quality milk for processing or direct consumption.
Direct-to-Consumer Raw Milk Sales
On-farm pasteurization ensures microbial safety and extends shelf life, enabling compliance with health regulations while preserving milk quality for direct-to-consumer raw milk sales. Bulk tank sales bypass on-site processing, relying on centralized pasteurization facilities but reducing farmer control over product freshness and traceability in raw milk distribution.
On-farm Hygienic Milking Systems
On-farm hygienic milking systems enhance milk quality by minimizing contamination through immediate pasteurization, ensuring pathogen reduction at the source before storage or sale. This practice reduces the risk of spoilage compared to bulk tank sale methods, where milk remains untreated longer, increasing vulnerability to bacterial growth and quality degradation.
Cream Separation Automation
Automated cream separation during on-farm pasteurization improves milk quality by efficiently removing fat, enhancing product consistency and extending shelf life compared to bulk tank sale systems. This automation reduces labor costs and minimizes contamination risks, optimizing overall dairy farm milk handling processes.
Small-batch Value-added Dairy
On-farm pasteurization enables small-batch, value-added dairy producers to maintain product freshness and safety while capturing higher market premiums compared to bulk tank sales that prioritize volume over quality. This method supports artisanal branding and compliance with health regulations, enhancing consumer trust and profitability in niche markets.
Cold Chain Disruption Mitigation
On-farm pasteurization minimizes cold chain disruption by immediately heating milk, reducing microbial load before chilling and storage, which ensures higher milk safety and quality. In contrast, bulk tank sales rely heavily on continuous refrigeration during transport and handling, increasing the risk of temperature fluctuations and potential spoilage.
Farm-to-Table Pasteurized Milk
On-farm pasteurization ensures milk undergoes immediate heat treatment at controlled temperatures, significantly reducing pathogen risks and preserving freshness from the farm-to-table supply chain. This method offers enhanced quality control and traceability compared to bulk tank sales, where raw milk is pooled and transported, increasing contamination potential and reducing direct farm oversight.
A2 Milk Differentiation in Bulk Sales
On-farm pasteurization maintains A2 milk's unique beta-casein protein integrity, enhancing consumer trust in product quality, while bulk tank sales streamline distribution but risk diluting A2 milk differentiation due to mixed milk sources. Prioritizing A2 milk certification in bulk sales requires stringent segregation and testing protocols to preserve its market value and meet premium consumer demand.
On-farm Pasteurization vs Bulk Tank Sale for Milk Handling Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com