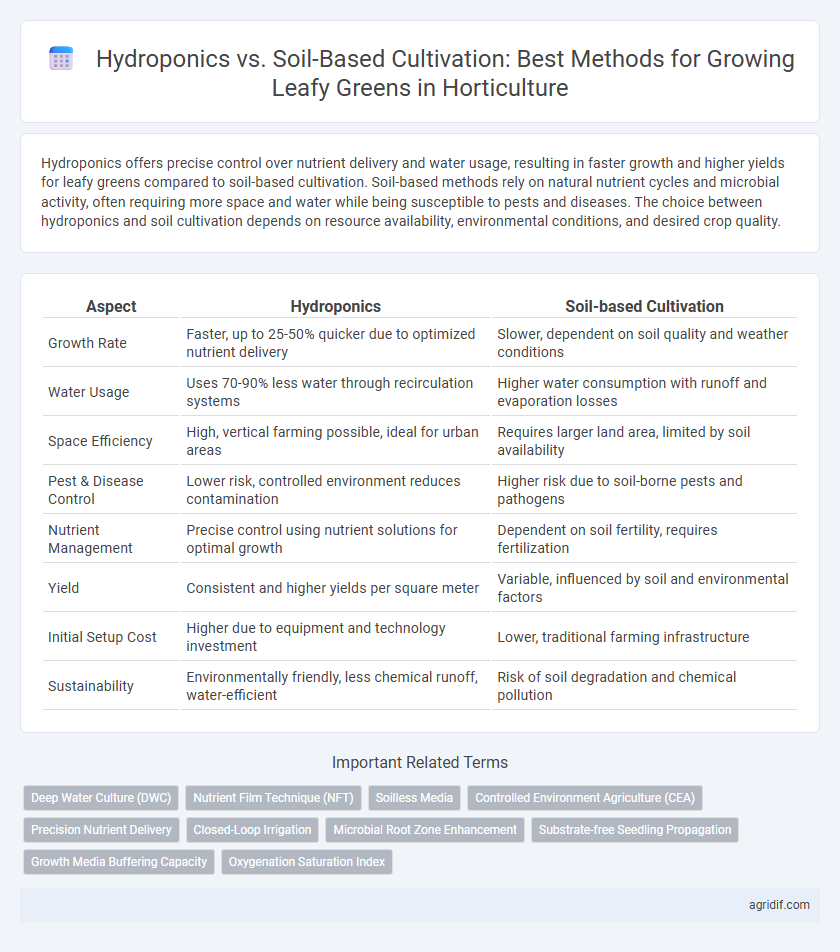
Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and water usage, resulting in faster growth and higher yields for leafy greens compared to soil-based cultivation. Soil-based methods rely on natural nutrient cycles and microbial activity, often requiring more space and water while being susceptible to pests and diseases. The choice between hydroponics and soil cultivation depends on resource availability, environmental conditions, and desired crop quality.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Hydroponics | Soil-based Cultivation |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Faster, up to 25-50% quicker due to optimized nutrient delivery | Slower, dependent on soil quality and weather conditions |
| Water Usage | Uses 70-90% less water through recirculation systems | Higher water consumption with runoff and evaporation losses |
| Space Efficiency | High, vertical farming possible, ideal for urban areas | Requires larger land area, limited by soil availability |
| Pest & Disease Control | Lower risk, controlled environment reduces contamination | Higher risk due to soil-borne pests and pathogens |
| Nutrient Management | Precise control using nutrient solutions for optimal growth | Dependent on soil fertility, requires fertilization |
| Yield | Consistent and higher yields per square meter | Variable, influenced by soil and environmental factors |
| Initial Setup Cost | Higher due to equipment and technology investment | Lower, traditional farming infrastructure |
| Sustainability | Environmentally friendly, less chemical runoff, water-efficient | Risk of soil degradation and chemical pollution |
Introduction to Leafy Green Cultivation Methods
Hydroponics and soil-based cultivation represent two primary methods for growing leafy greens, each offering distinct advantages in nutrient delivery and growth control. Hydroponic systems utilize nutrient-rich water solutions, enabling faster growth rates and higher yields by precisely managing environmental factors, while soil-based cultivation relies on natural soil fertility and microbial activity to support plant development. Selecting the appropriate cultivation method depends on factors such as space availability, resource efficiency, and desired crop quality in leafy green production.
Fundamentals of Hydroponics for Leafy Greens
Hydroponics for leafy greens involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil, enabling precise control over nutrient delivery and environmental conditions. This soilless method enhances growth rates and yields by optimizing oxygen levels and minimizing soil-borne diseases. Key factors include maintaining pH balance between 5.5 and 6.5, ensuring adequate dissolved oxygen, and supplying essential macronutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for optimal leaf development.
Overview of Soil-based Cultivation Techniques
Soil-based cultivation of leafy greens relies on nutrient-rich, well-drained soils, often enhanced with organic matter such as compost or manure to improve fertility and structure. Traditional techniques emphasize crop rotation, mulching, and integrated pest management to maintain soil health and optimize plant growth while minimizing disease risks. Proper soil preparation and moisture management ensure consistent nutrient availability, which supports healthy leaf development and higher yields in soil-grown leafy greens.
Growth Rate Comparison: Hydroponics vs Soil
Hydroponic systems accelerate the growth rate of leafy greens by providing a precise nutrient delivery directly to roots, resulting in up to 50% faster maturation compared to soil-based cultivation. Soil cultivation relies on natural nutrient cycles and microbial activity, which can lead to slower nutrient uptake and growth variability depending on soil quality. Controlled environment agriculture with hydroponics ensures consistent optimal conditions, enhancing leaf biomass and reducing time to harvest significantly versus traditional soil methods.
Nutrient Management in Hydroponics and Soil Systems
Hydroponics enables precise control over nutrient delivery through water-soluble solutions tailored to the specific requirements of leafy greens, leading to optimized growth and higher nutrient uptake efficiency compared to traditional soil-based systems. Soil cultivation relies on the natural nutrient cycling and organic matter content, which can vary significantly and affect nutrient availability, often resulting in less consistent nutrient management. The ability of hydroponic systems to maintain stable pH and nutrient concentrations promotes rapid growth and reduces the risk of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that are more common in soil environments.
Water Usage Efficiency: Hydroponics vs Soil-based Methods
Hydroponics systems use up to 90% less water than soil-based cultivation by recycling nutrient solutions and minimizing evaporation losses. Soil-based methods rely on natural water infiltration and often require frequent irrigation due to runoff and evaporation, leading to higher overall water consumption. The water usage efficiency of hydroponics makes it a sustainable choice for leafy green production in water-scarce regions.
Pest and Disease Control in Both Systems
Hydroponics offers enhanced pest and disease control for leafy greens by reducing soil-borne pathogens and allowing precise monitoring of nutrient and water conditions. Soil-based cultivation faces challenges from soil pests and diseases such as root rot and fungal infections, often requiring chemical treatments or crop rotation to manage. Integrated pest management and proper sanitation are critical in both systems to minimize outbreaks and ensure healthy plant growth.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Resource Use
Hydroponics systems use up to 90% less water than soil-based cultivation, significantly reducing water consumption in leafy green production. These soilless methods minimize land use and prevent soil degradation, enhancing sustainability by recycling nutrient solutions and reducing chemical runoff. In contrast, soil-based cultivation often requires more water, fertilizers, and pesticides, leading to higher environmental footprints and potential soil erosion.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Operational Expenses
Hydroponics systems for leafy greens typically require a higher initial investment due to the costs of specialized equipment, nutrient solutions, and controlled environment infrastructure compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. Operational expenses for hydroponics include energy consumption for lighting and climate control, along with regular nutrient replenishment, which can exceed costs associated with soil-based inputs such as fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation. Despite higher upfront and operational costs, hydroponics offers potential for greater yield efficiency and space optimization, which can offset expenses over time in commercial production.
Yield Quality and Nutritional Value Differences
Hydroponics offers higher yield efficiency for leafy greens by providing precise nutrient control and optimal growing conditions, resulting in faster growth cycles and consistent quality. Soil-based cultivation delivers complex flavor profiles due to natural soil microbiomes but may exhibit greater variability in nutrient content and crop quality. Nutritional analysis shows hydroponic leafy greens often contain comparable or higher levels of essential vitamins and minerals, while soil-grown greens can have diverse antioxidant profiles influenced by soil composition.
Related Important Terms
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponics enables faster growth rates and higher yields of leafy greens by providing constant oxygen and nutrient availability directly to the roots, reducing disease risk compared to soil-based cultivation. The controlled environment in DWC systems minimizes pest exposure and water usage, enhancing sustainability and crop quality in commercial horticulture.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) in hydroponics delivers a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water over leafy green roots, ensuring precise nutrient uptake and faster growth compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. This method reduces water usage by up to 90% and minimizes pest and disease risks associated with soil, enhancing crop yield and quality.
Soilless Media
Soilless media in hydroponics provide optimal nutrient delivery and water retention for leafy greens, enabling faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. These inert substrates, such as coconut coir and perlite, reduce pest-related issues and enhance root aeration, promoting healthier plants with consistent quality.
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)
Hydroponics in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) enables precise nutrient management and water efficiency, accelerating leafy green growth with minimal pest exposure compared to soil-based cultivation. Soil-based methods offer natural microbiome interactions that enhance flavor and resilience but require more space, water, and are prone to environmental variability affecting yield consistency.
Precision Nutrient Delivery
Hydroponics enables precision nutrient delivery by supplying water-soluble minerals directly to the root zone, optimizing nutrient uptake and promoting faster growth in leafy greens compared to soil-based cultivation. Soil-based methods often face variability in nutrient availability due to soil composition and microbial activity, which can lead to inconsistent crop quality and slower development.
Closed-Loop Irrigation
Closed-loop irrigation in hydroponics for leafy greens maximizes water efficiency by recirculating nutrient solutions, reducing waste compared to soil-based cultivation that often loses water through runoff and evaporation. This system enhances nutrient uptake precision, promoting faster growth and higher yields while minimizing environmental impact.
Microbial Root Zone Enhancement
Hydroponics offers precise control over nutrient delivery and significantly reduces soil-borne pathogens, promoting a more stable microbial root zone environment for leafy greens. Soil-based cultivation supports diverse microbial communities that enhance nutrient cycling and plant immunity, but may experience inconsistent microbial root zone interactions due to variable soil conditions and pathogen presence.
Substrate-free Seedling Propagation
Hydroponics enables substrate-free seedling propagation for leafy greens by using nutrient-rich water solutions that deliver precise nutrition and oxygen directly to roots, enhancing growth rates and reducing disease risk compared to traditional soil-based cultivation. This method eliminates soil-borne pathogens and supports consistent, sustainable production in controlled environments, optimizing yield and resource efficiency.
Growth Media Buffering Capacity
Hydroponic systems utilize inert growth media with minimal buffering capacity, requiring precise nutrient solution control to maintain pH stability for optimal leafy green growth, whereas soil-based cultivation benefits from the natural buffering capacity of organic matter and clay minerals that stabilize pH fluctuations and nutrient availability. Understanding the differences in growth media buffering capacity is critical for managing nutrient uptake efficiency and maximizing yield quality in hydroponics versus soil cultivation.
Oxygenation Saturation Index
Hydroponics systems maintain a higher Oxygenation Saturation Index (OSI) compared to soil-based cultivation, enhancing root respiration and nutrient uptake for leafy greens. Elevated OSI in hydroponic setups leads to faster growth rates and increased biomass accumulation by ensuring optimal oxygen availability directly in the nutrient solution.
Hydroponics vs Soil-based cultivation for leafy greens Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com