Drip line placement delivers water directly to the root zone, maximizing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead sprinklers. This targeted irrigation method minimizes leaf wetness, lowering the risk of disease in greenhouse crops while promoting uniform soil moisture. Overhead sprinklers, although simpler to install, often result in higher water loss and uneven distribution, potentially stressing plants and increasing resource waste.
Table of Comparison
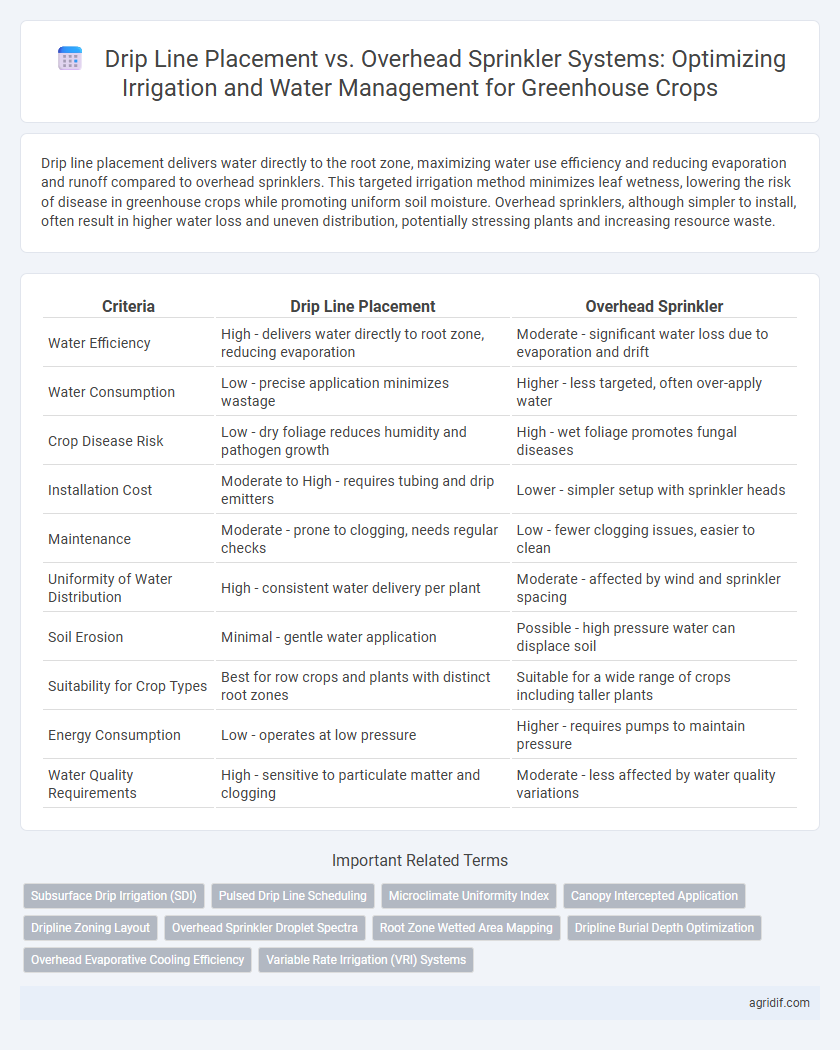
| Criteria | Drip Line Placement | Overhead Sprinkler |
|---|---|---|
| Water Efficiency | High - delivers water directly to root zone, reducing evaporation | Moderate - significant water loss due to evaporation and drift |
| Water Consumption | Low - precise application minimizes wastage | Higher - less targeted, often over-apply water |
| Crop Disease Risk | Low - dry foliage reduces humidity and pathogen growth | High - wet foliage promotes fungal diseases |
| Installation Cost | Moderate to High - requires tubing and drip emitters | Lower - simpler setup with sprinkler heads |
| Maintenance | Moderate - prone to clogging, needs regular checks | Low - fewer clogging issues, easier to clean |
| Uniformity of Water Distribution | High - consistent water delivery per plant | Moderate - affected by wind and sprinkler spacing |
| Soil Erosion | Minimal - gentle water application | Possible - high pressure water can displace soil |
| Suitability for Crop Types | Best for row crops and plants with distinct root zones | Suitable for a wide range of crops including taller plants |
| Energy Consumption | Low - operates at low pressure | Higher - requires pumps to maintain pressure |
| Water Quality Requirements | High - sensitive to particulate matter and clogging | Moderate - less affected by water quality variations |
Introduction to Greenhouse Irrigation Methods
Drip line placement delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which enhances water-use efficiency in greenhouse crops. Overhead sprinkler systems provide uniform coverage but often result in higher water loss through evaporation and leaf surface wetting, increasing the risk of disease. Choosing between drip line and overhead irrigation depends on crop type, greenhouse climate control, and water conservation goals.
Overview of Drip Line Systems in Greenhouse Agriculture
Drip line systems in greenhouse agriculture deliver water directly to the root zone through a network of tubes with emitters, optimizing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation losses compared to overhead sprinklers. These systems facilitate precise moisture control, minimize foliar diseases by keeping leaves dry, and conserve nutrients by limiting leaching and runoff. Drip irrigation's targeted delivery enhances crop growth uniformity, making it a preferred choice for water management in controlled environments.
Overhead Sprinkler Irrigation: Principles and Applications
Overhead sprinkler irrigation provides uniform water distribution by simulating natural rainfall, making it suitable for a wide range of greenhouse crops that require consistent moisture levels. The system operates by pressurized water delivery through nozzles, ensuring efficient coverage and reducing water runoff compared to surface irrigation methods. Proper sprinkler spacing and nozzle selection are critical to optimizing water use efficiency and minimizing leaf wetness, which helps prevent disease development in greenhouse environments.
Water Use Efficiency: Drip Line vs Overhead Sprinkler
Drip line irrigation delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which significantly enhances water use efficiency for greenhouse crops compared to overhead sprinklers. Overhead sprinkler systems tend to lose more water through evaporation and canopy wetting, increasing the risk of disease and reducing water efficiency. Precise drip line placement ensures uniform soil moisture, optimized nutrient uptake, and reduced water wastage, making it the preferred irrigation method for maximizing water use efficiency in controlled greenhouse environments.
Impact on Crop Health and Disease Management
Drip line placement delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing leaf wetness and reducing the risk of fungal diseases such as powdery mildew and botrytis in greenhouse crops. Overhead sprinklers increase humidity and wet foliage, creating an environment conducive to pathogen proliferation and negatively impacting crop health. Precise water management through drip irrigation enhances nutrient uptake efficiency and promotes stronger, disease-resistant plant growth.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Drip line placement in greenhouse crops offers precise water delivery at the root zone, minimizing evaporation and reducing fungal disease risk, while requiring careful layout to ensure even coverage and periodic flushing to prevent clogging. Overhead sprinkler systems provide broader coverage with simpler installation but demand frequent adjustments and maintenance to avoid water waste and leaf wetness that can promote diseases. Both systems necessitate regular monitoring, but drip irrigation benefits from targeted maintenance focused on emitters and filters, whereas overhead sprinklers require upkeep of nozzles, pipes, and pressure controls.
Cost Analysis: Drip Line and Overhead Sprinkler Systems
Drip line irrigation systems generally offer lower long-term costs due to reduced water usage and targeted delivery, minimizing waste and energy expenses. Overhead sprinkler systems tend to have higher initial installation costs and increased maintenance demands, especially with potential water loss from evaporation and wind drift. Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of drip lines versus overhead sprinklers requires considering factors such as greenhouse size, crop type, water availability, and energy pricing.
Environmental Sustainability and Resource Conservation
Drip line placement offers precise water delivery directly to the root zone, significantly reducing water waste and minimizing evaporation compared to overhead sprinkler systems in greenhouse crops. This method enhances environmental sustainability by promoting efficient water use, conserving energy associated with pumping and evaporation losses, and reducing nutrient runoff that can contaminate soil and water resources. Overhead sprinklers, while providing broader coverage, often lead to higher water consumption and increased potential for fungal diseases due to wet foliage, making drip irrigation a more resource-conserving and eco-friendly option for controlled environment agriculture.
Yield and Quality Outcomes for Greenhouse Crops
Drip line placement in greenhouse crop irrigation enhances yield by delivering water directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and promoting uniform moisture distribution. This method improves crop quality through better nutrient uptake and minimizes disease risks associated with foliar wetness common in overhead sprinkler systems. Overhead sprinklers often cause uneven water distribution and increased humidity, potentially leading to lower yield and compromised produce quality in greenhouse environments.
Choosing the Optimal Irrigation Method for Your Greenhouse
Drip line placement offers precise water delivery directly to plant roots, minimizing evaporation and runoff, which enhances water use efficiency for greenhouse crops. Overhead sprinklers provide broader coverage but can increase humidity and promote disease by wetting foliage, impacting crop health. Selecting the optimal irrigation method depends on crop type, growth stage, and greenhouse microclimate to balance water conservation and plant productivity.
Related Important Terms
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI)
Subsurface Drip Irrigation (SDI) delivers water directly to the root zone through buried drip lines, enhancing water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead sprinkler systems. This precise water placement promotes healthier greenhouse crops, reduces foliage wetting that can lead to disease, and optimizes nutrient uptake.
Pulsed Drip Line Scheduling
Pulsed drip line scheduling enhances water efficiency in greenhouse crops by delivering precise, targeted moisture directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead sprinklers. This method optimizes irrigation timing and frequency, promoting healthier plant growth and conserving water resources critical for sustainable greenhouse management.
Microclimate Uniformity Index
Drip line placement enhances microclimate uniformity index by delivering water directly to the root zone, minimizing evaporation and promoting consistent soil moisture distribution in greenhouse crops. Overhead sprinkler systems often lead to uneven humidity and temperature gradients, reducing microclimate uniformity and potentially stressing plants.
Canopy Intercepted Application
Drip line placement delivers water directly to the root zone, minimizing canopy intercepted application and reducing evaporation losses, which enhances water use efficiency in greenhouse crops. Overhead sprinklers increase canopy interception, leading to higher water runoff and potential disease risks due to prolonged leaf wetness.
Dripline Zoning Layout
Drip line placement in greenhouse irrigation enables precise water delivery directly to the root zone, enhancing water use efficiency and reducing evaporation compared to overhead sprinkler systems. Implementing a dripline zoning layout allows for tailored irrigation schedules based on specific crop water requirements, optimizing plant health and conserving water resources.
Overhead Sprinkler Droplet Spectra
Overhead sprinkler systems in greenhouse crops produce a droplet spectrum that enhances uniform water distribution and reduces soil surface crusting compared to drip line placement. This droplet size variation improves canopy coverage, promoting effective cooling and disease suppression while minimizing water runoff and evaporation losses.
Root Zone Wetted Area Mapping
Drip line placement delivers precise irrigation directly to the root zone, optimizing water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead sprinklers. Root zone wetted area mapping reveals that drip systems create a targeted moisture zone conducive to healthier root development, whereas overhead sprinklers distribute water less uniformly, potentially leading to water wastage and increased disease risk.
Dripline Burial Depth Optimization
Optimizing dripline burial depth in greenhouse crops enhances water use efficiency by delivering moisture directly to the root zone, reducing evaporation and runoff compared to overhead sprinklers. Research indicates maintaining a burial depth of 5-10 cm balances soil moisture retention and root access, improving crop yield and uniformity while minimizing fungal disease risk associated with surface wetting.
Overhead Evaporative Cooling Efficiency
Overhead sprinkler systems enhance evaporative cooling efficiency in greenhouses by uniformly distributing water droplets, which reduces air temperature and increases humidity, creating an optimal microclimate for crop growth. Drip line placement, while efficient for targeted irrigation and water conservation, does not contribute to evaporative cooling, making overhead sprinklers preferable for managing temperature and humidity in greenhouse environments.
Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) Systems
Drip line placement in greenhouses offers precise water delivery directly to the root zone, enhancing water use efficiency by minimizing evaporation and runoff, which is critical for Variable Rate Irrigation (VRI) systems that adjust water application based on crop and soil variability. Overhead sprinkler systems distribute water less uniformly and increase humidity levels, potentially leading to higher disease incidence, making them less compatible with the targeted, data-driven approach of VRI technologies in controlled environment agriculture.
Drip line placement vs Overhead sprinkler for greenhouse crops Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com