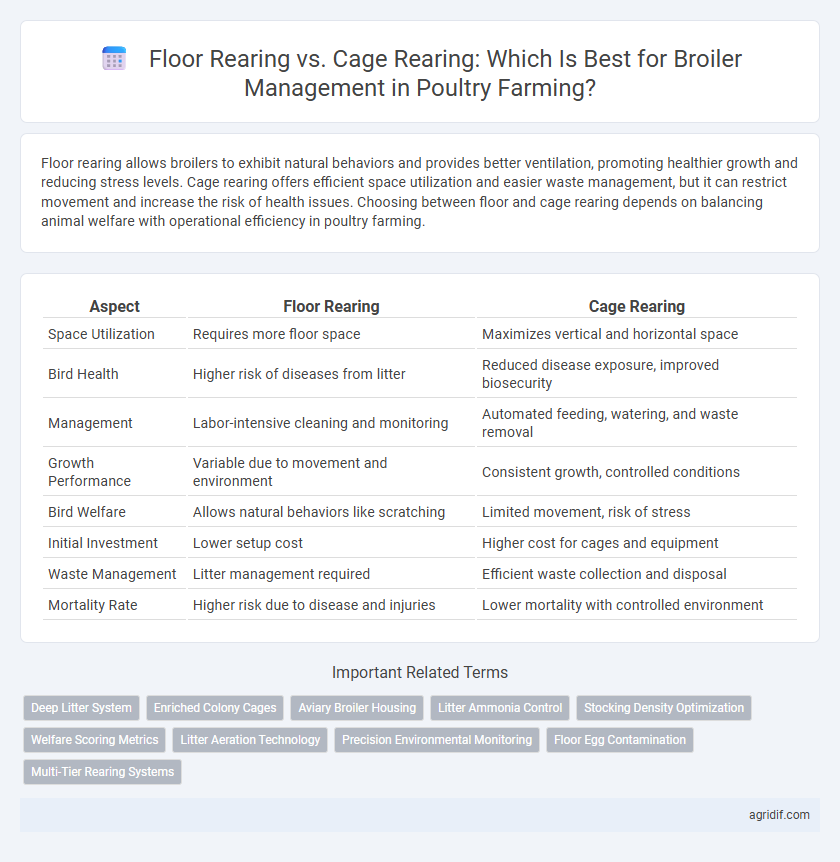
Floor rearing allows broilers to exhibit natural behaviors and provides better ventilation, promoting healthier growth and reducing stress levels. Cage rearing offers efficient space utilization and easier waste management, but it can restrict movement and increase the risk of health issues. Choosing between floor and cage rearing depends on balancing animal welfare with operational efficiency in poultry farming.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Floor Rearing | Cage Rearing |
|---|---|---|
| Space Utilization | Requires more floor space | Maximizes vertical and horizontal space |
| Bird Health | Higher risk of diseases from litter | Reduced disease exposure, improved biosecurity |
| Management | Labor-intensive cleaning and monitoring | Automated feeding, watering, and waste removal |
| Growth Performance | Variable due to movement and environment | Consistent growth, controlled conditions |
| Bird Welfare | Allows natural behaviors like scratching | Limited movement, risk of stress |
| Initial Investment | Lower setup cost | Higher cost for cages and equipment |
| Waste Management | Litter management required | Efficient waste collection and disposal |
| Mortality Rate | Higher risk due to disease and injuries | Lower mortality with controlled environment |
Introduction to Broiler Rearing Systems
Floor rearing and cage rearing represent the two primary systems for broiler management, each impacting growth performance and welfare differently. Floor rearing allows broilers to move freely, promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress but requires stringent litter management to prevent disease. Cage rearing offers space efficiency and facilitates better health monitoring but may limit movement, affecting muscle development and overall bird welfare.
Understanding Floor Rearing in Poultry Farming
Floor rearing in poultry farming involves raising broilers directly on a litter-covered floor, which provides them with more space for natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing. This method enhances bird welfare, reduces stress, and can lead to improved growth rates compared to cage rearing, where birds are confined in restrictive spaces. Proper management of litter quality, ventilation, and stocking density is critical to prevent disease outbreaks and optimize broiler performance under floor rearing systems.
Overview of Cage Rearing for Broilers
Cage rearing for broilers involves raising birds in confined wire cages, which enhances space utilization and simplifies manure management. This method improves biosecurity by limiting bird-to-bird contact and reducing disease transmission risks. However, cage rearing may restrict natural behaviors, requiring careful management to maintain bird welfare and growth performance.
Housing Design and Space Utilization
Floor rearing for broilers involves open housing designs with litter-based floors, allowing natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, which enhances welfare and uniform growth. Cage rearing utilizes tiered, confined spaces with optimized vertical stacking, improving space efficiency and ease of management but limiting movement and behavioral expression. Strategic housing design in floor systems requires ample area per bird, typically 1-1.5 square feet, while cage systems maximize density at around 0.5-0.7 square feet per bird, demanding precise ventilation and waste removal to maintain health.
Feed and Water Management in Both Systems
Floor rearing for broilers allows more natural feed consumption behavior, with feed and water distributed on the litter, promoting exercise but requiring frequent replenishment to prevent contamination. Cage rearing enables precise feed and water control through automated systems, improving feed conversion ratio and reducing waste, though it limits movement and natural foraging instincts. Optimal feed and water management in both systems depends on regular monitoring, sanitation, and adjustments to consumption patterns to maximize growth performance and health.
Health, Hygiene, and Disease Control
Floor rearing in broiler management promotes better exercise and natural behaviors, reducing stress-related illnesses, while cage rearing offers controlled hygiene conditions that limit pathogen exposure. Floor systems require rigorous litter management to prevent microbial buildup, whereas cage systems facilitate easier waste removal and biosecurity measures. Effective disease control depends on ventilation quality and sanitation protocols tailored to each rearing method's specific environmental challenges.
Growth Performance and Feed Conversion
Floor rearing in broiler management often promotes better growth performance due to increased space allowing natural behaviors and improved muscle development. Conversely, cage rearing provides controlled conditions that can lead to more efficient feed conversion ratios (FCR) by minimizing energy expenditure in movement. Optimizing these systems involves balancing welfare and productivity to enhance overall broiler growth and feed efficiency outcomes.
Animal Welfare and Behavioral Considerations
Floor rearing for broilers allows natural behaviors such as dust bathing, perching, and scratching, enhancing animal welfare by promoting physical activity and reducing stress. Cage rearing, although space-efficient, restricts movement and natural behaviors, potentially leading to feather pecking and leg disorders. Optimal broiler management balances welfare with production efficiency, favoring floor rearing systems for improved behavioral outcomes and health indicators.
Economic Comparison: Costs and Profits
Floor rearing in broiler management typically incurs higher initial costs due to litter materials and increased labor but offers better growth rates and lower mortality, enhancing overall profitability. Cage rearing reduces feed wastage and disease incidence through controlled environments, lowering operational expenses but may result in slower weight gain and higher equipment investment. Economic comparison reveals floor rearing generates greater net returns in markets valuing meat quality, while cage systems optimize cost-efficiency in high-volume, standardized production setups.
Choosing the Right Rearing System for Your Farm
Floor rearing offers birds more freedom to express natural behaviors, leading to improved welfare and potentially better meat quality, while cage rearing enables higher stocking densities and easier management of hygiene and disease control. Selecting the appropriate broiler rearing system depends on factors such as farm size, budget, labor availability, and specific production goals. Evaluating these parameters ensures optimal bird health, operational efficiency, and economic returns in broiler farming.
Related Important Terms
Deep Litter System
The deep litter system in floor rearing for broiler management offers improved bird welfare by allowing natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, resulting in better growth performance and reduced stress compared to cage rearing. This method also enhances manure management by promoting aerobic decomposition in the litter, lowering ammonia levels and minimizing respiratory issues in broilers.
Enriched Colony Cages
Enriched colony cages for broiler management offer improved animal welfare by providing enhanced space, perches, and nesting areas compared to traditional cage rearing, promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress. Floor rearing allows more freedom of movement but can increase disease risk and requires more space and labor, making enriched colony cages a balanced solution for efficient production and bird health.
Aviary Broiler Housing
Floor rearing and cage rearing represent two distinct poultry management systems, with aviary broiler housing in floor rearing offering enhanced space for natural behaviors, improved airflow, and better litter quality, leading to healthier, more robust birds. Aviary systems optimize broiler welfare by allowing movement and social interactions, reducing stress-related issues compared to the confined environment of cage rearing.
Litter Ammonia Control
Floor rearing in broiler management requires efficient litter ammonia control through regular dry litter maintenance and adequate ventilation to minimize respiratory health risks. Cage rearing significantly reduces ammonia exposure by isolating birds and facilitating easier waste removal, thus improving air quality and overall bird welfare.
Stocking Density Optimization
Floor rearing offers broilers more space for natural movement but requires precise stocking density control to prevent overcrowding and maintain optimal growth rates, typically around 10-12 birds per square meter. Cage rearing allows higher stocking densities of up to 15-18 birds per square meter, enhancing biosecurity and ease of management but may limit natural behaviors important for welfare and growth performance.
Welfare Scoring Metrics
Floor rearing for broilers typically enhances welfare scoring metrics by allowing natural behaviors such as dust bathing and scratching, which improves leg health and reduces stress indicators compared to cage rearing. Cage rearing often limits movement and increases contact dermatitis incidence, negatively impacting overall welfare scores and growth performance in broiler management.
Litter Aeration Technology
Floor rearing in broiler management benefits significantly from litter aeration technology, which enhances ammonia control and improves bird welfare by maintaining optimal moisture and oxygen levels in the bedding material. In contrast, cage rearing systems lack this advantage, often leading to increased respiratory issues and compromised growth rates due to poor air quality and limited natural behavior expression.
Precision Environmental Monitoring
Precision environmental monitoring in floor rearing allows for accurate control of temperature, humidity, and ammonia levels, promoting optimal broiler health and growth. In contrast, cage rearing benefits from localized sensor systems that ensure consistent microclimates, reducing disease risks and improving feed conversion efficiency.
Floor Egg Contamination
Floor rearing in broiler management presents a higher risk of floor egg contamination due to direct contact with litter, increasing exposure to pathogens like Salmonella and E. coli. Cage rearing minimizes this risk by restricting eggs from contacting the floor, thereby reducing contamination rates and improving overall flock health.
Multi-Tier Rearing Systems
Multi-tier rearing systems in poultry farming optimize space utilization by housing broilers in stacked layers, improving ventilation and manure management compared to traditional floor rearing. These systems enhance feed efficiency and reduce disease spread relative to cage rearing, promoting better growth rates and overall broiler health.
Floor Rearing vs Cage Rearing for Broiler Management Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com