Traditional poultry breeds offer genetic diversity and adaptation to local environments, making them resilient and ideal for small-scale, sustainable farming. Hybrid breeds deliver rapid growth, higher egg production, and feed efficiency, suiting commercial poultry operations focused on maximizing yield. Selecting the right breed depends on balancing longevity, productivity, and environmental adaptability to match specific flock management goals.
Table of Comparison
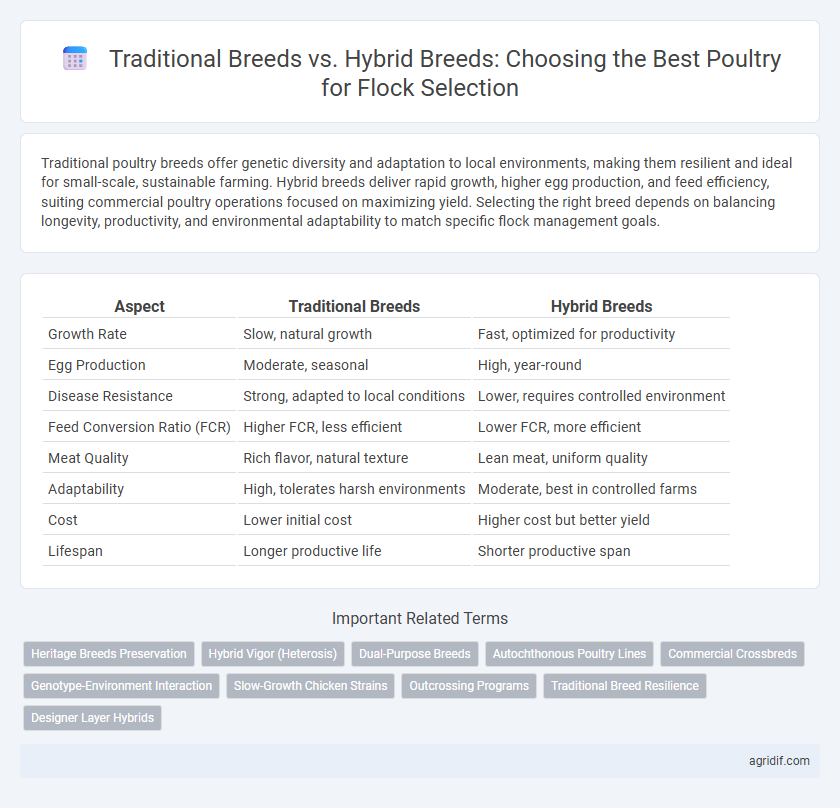
| Aspect | Traditional Breeds | Hybrid Breeds |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Slow, natural growth | Fast, optimized for productivity |
| Egg Production | Moderate, seasonal | High, year-round |
| Disease Resistance | Strong, adapted to local conditions | Lower, requires controlled environment |
| Feed Conversion Ratio (FCR) | Higher FCR, less efficient | Lower FCR, more efficient |
| Meat Quality | Rich flavor, natural texture | Lean meat, uniform quality |
| Adaptability | High, tolerates harsh environments | Moderate, best in controlled farms |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost but better yield |
| Lifespan | Longer productive life | Shorter productive span |
Introduction to Traditional and Hybrid Poultry Breeds
Traditional poultry breeds exhibit strong genetic diversity, adaptability to local environments, and resilience against diseases, making them ideal for sustainable and low-input farming systems. Hybrid breeds are developed through selective breeding for high productivity traits such as rapid growth, enhanced feed efficiency, and increased egg production, offering economic advantages for commercial poultry operations. Choosing between traditional and hybrid breeds depends on factors including farm resources, desired production goals, and market demand.
Genetic Background: Traditional vs Hybrid Breeds
Traditional breeds in poultry farming possess a rich genetic background characterized by high genetic diversity and resilience to local environmental conditions, often resulting in robust disease resistance and adaptability. Hybrid breeds are selectively bred using advanced genetic techniques, combining specific traits from different lines to optimize productivity factors such as growth rate, egg production, and feed efficiency. Understanding the genetic background differences between traditional and hybrid breeds is crucial for making informed decisions in flock selection aimed at balancing productivity with sustainability.
Growth Rate and Productivity Comparison
Traditional poultry breeds often exhibit slower growth rates but possess greater disease resistance and adaptability to local environments, making them suitable for sustainable farming practices. Hybrid breeds, engineered for rapid growth and higher productivity, typically reach market weight faster and yield increased egg production, contributing to enhanced commercial efficiency. Selection between these breeds depends on balancing growth rate benefits with long-term productivity and resilience factors in flock management.
Egg Production: Yield and Quality
Traditional poultry breeds often produce fewer eggs compared to hybrid breeds but offer superior egg quality with richer yolks and robust shell strength. Hybrid breeds are genetically optimized for high egg yield, consistently delivering larger quantities with uniform size and color, making them ideal for commercial production. Choosing between traditional and hybrid breeds depends on balancing the demand for egg quantity against the preference for natural egg attributes in flock selection.
Disease Resistance and Adaptability
Traditional poultry breeds exhibit superior disease resistance and adaptability to local environmental conditions due to their long-term natural selection and genetic diversity. Hybrid breeds, while optimized for rapid growth and higher productivity, often show increased vulnerability to diseases and require controlled, optimal environments to thrive. Selecting appropriate breeds for flock management involves balancing the robustness of traditional strains with the efficiency of hybrids to ensure sustainable poultry farming.
Feed Conversion Efficiency
Traditional poultry breeds often exhibit lower feed conversion efficiency compared to hybrid breeds, consuming more feed for the same or less meat or egg output. Hybrid breeds are selectively bred for optimized growth rates and superior feed conversion ratios, resulting in reduced feed costs and higher productivity. However, traditional breeds can offer resilience and adaptability benefits in low-input or specialty farming systems despite their less efficient feed utilization.
Lifespan and Hardiness
Traditional poultry breeds typically exhibit longer lifespans and greater hardiness, making them well-suited for sustainable flock management in diverse environmental conditions. Hybrid breeds, while often optimized for rapid growth and high production, usually have shorter lifespans and reduced disease resistance, requiring more intensive care and controlled environments. Selecting between traditional and hybrid breeds depends on balancing longevity and resilience against production efficiency in poultry farming operations.
Economic Considerations in Breed Selection
Traditional poultry breeds offer lower initial investment and resilience to local environmental conditions, reducing ongoing costs related to disease management and feed requirements. Hybrid breeds provide higher productivity with faster growth rates and improved feed conversion ratios, which often results in increased short-term profits. Economic considerations in flock selection must balance the higher upfront costs and management needs of hybrids against the long-term sustainability and lower input expenses associated with traditional breeds.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Traditional poultry breeds exhibit greater resilience to local environmental conditions, requiring fewer inputs such as feed and water, which reduces their ecological footprint. Hybrid breeds, while offering higher productivity and faster growth rates, often rely on intensive resource use and specialized management practices that can increase environmental strain. Sustainable flock selection prioritizes traditional breeds for their adaptability and lower resource demands, promoting biodiversity and long-term environmental balance in poultry farming.
Choosing the Right Breed for Your Poultry Farm
Traditional breeds offer resilience, adaptability to local climates, and disease resistance, making them ideal for sustainable and low-input poultry farming systems. Hybrid breeds deliver higher productivity with rapid growth rates and improved feed conversion, suited for commercial operations aiming for maximum egg or meat output. Selecting the right breed depends on balancing production goals, management capacity, and environmental conditions specific to the poultry farm.
Related Important Terms
Heritage Breeds Preservation
Heritage breeds in poultry farming offer genetic diversity and resilience essential for long-term flock sustainability, contrasting with hybrid breeds that prioritize rapid growth and uniformity. Preserving traditional breeds supports biodiversity and adaptability in changing environmental conditions, ensuring valuable traits are not lost.
Hybrid Vigor (Heterosis)
Hybrid breeds in poultry farming exhibit hybrid vigor (heterosis), resulting in enhanced growth rates, higher egg production, and improved disease resistance compared to traditional breeds. This genetic advantage makes hybrids more efficient and cost-effective for commercial flock selection, optimizing overall productivity and profitability.
Dual-Purpose Breeds
Dual-purpose breeds in poultry farming offer balanced advantages by providing both meat and egg production, making them a practical choice for small to medium-scale operations. These traditional breeds exhibit better adaptability, disease resistance, and foraging ability compared to hybrid breeds, which are often optimized solely for high egg yield or rapid growth.
Autochthonous Poultry Lines
Autochthonous poultry lines offer unique genetic traits such as disease resistance and adaptability to local climates, making them valuable for sustainable flock selection compared to hybrid breeds that prioritize rapid growth and high yield. Maintaining traditional breeds supports biodiversity and preserves heritage genetics crucial for long-term resilience in poultry farming.
Commercial Crossbreds
Commercial crossbred chickens combine the hardiness and adaptability of traditional breeds with the rapid growth and high yield of hybrid breeds, optimizing flock productivity for diverse farming conditions. These crossbreds exhibit enhanced disease resistance and improved feed conversion ratios, making them ideal for commercial poultry operations aiming for sustainable and cost-effective meat or egg production.
Genotype-Environment Interaction
Traditional poultry breeds exhibit strong genotype-environment interactions, thriving in local conditions with resilience to climate stressors and endemic diseases, ensuring sustainable flock performance. Hybrid breeds, while genetically optimized for rapid growth and high productivity, often require controlled environments to express their full potential, making their performance highly sensitive to environmental fluctuations.
Slow-Growth Chicken Strains
Traditional poultry breeds, known for their slow-growth chicken strains, offer enhanced flavor profiles and better adaptability to free-range environments compared to hybrid breeds, which are optimized for rapid weight gain and high production efficiency. Slow-growth strains from traditional breeds also demonstrate stronger immune responses and greater resilience to local diseases, making them ideal for sustainable and organic poultry farming.
Outcrossing Programs
Outcrossing programs in poultry farming enhance genetic diversity by crossing traditional breeds with hybrid breeds, improving disease resistance and productivity traits in the flock; traditional breeds contribute robust adaptability and unique resilience, while hybrid breeds offer superior growth rates and egg production. Strategic selection within these programs balances maintaining heritage genetics with achieving commercial performance goals.
Traditional Breed Resilience
Traditional poultry breeds exhibit greater resilience to local diseases and climatic variations compared to hybrid breeds, making them advantageous for sustainable flock selection in diverse environmental conditions. Their innate adaptability supports lower mortality rates and reduces dependency on veterinary interventions, enhancing long-term flock stability.
Designer Layer Hybrids
Designer layer hybrids combine the genetic advantages of both traditional and hybrid breeds, offering enhanced egg production, disease resistance, and adaptability to varied environmental conditions. These specialized hybrids optimize flock performance and profitability by delivering consistent quality and higher yield compared to conventional poultry breeds.
Traditional Breeds vs Hybrid Breeds for Flock Selection Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com