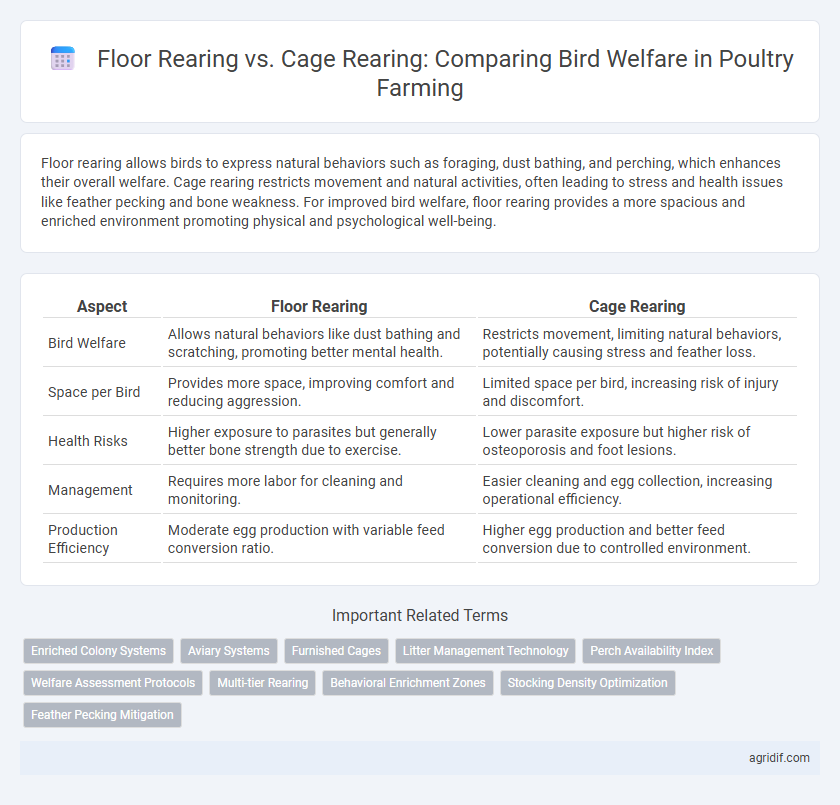
Floor rearing allows birds to express natural behaviors such as foraging, dust bathing, and perching, which enhances their overall welfare. Cage rearing restricts movement and natural activities, often leading to stress and health issues like feather pecking and bone weakness. For improved bird welfare, floor rearing provides a more spacious and enriched environment promoting physical and psychological well-being.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Floor Rearing | Cage Rearing |
|---|---|---|
| Bird Welfare | Allows natural behaviors like dust bathing and scratching, promoting better mental health. | Restricts movement, limiting natural behaviors, potentially causing stress and feather loss. |
| Space per Bird | Provides more space, improving comfort and reducing aggression. | Limited space per bird, increasing risk of injury and discomfort. |
| Health Risks | Higher exposure to parasites but generally better bone strength due to exercise. | Lower parasite exposure but higher risk of osteoporosis and foot lesions. |
| Management | Requires more labor for cleaning and monitoring. | Easier cleaning and egg collection, increasing operational efficiency. |
| Production Efficiency | Moderate egg production with variable feed conversion ratio. | Higher egg production and better feed conversion due to controlled environment. |
Introduction to Poultry Rearing Systems
Floor rearing and cage rearing represent two primary poultry farming systems, each influencing bird welfare differently. Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors such as scratching and dust bathing, promoting better physical and psychological health, whereas cage rearing restricts movement, often leading to stress and higher susceptibility to diseases. Understanding the welfare implications of these systems is crucial for optimizing poultry productivity and ethical farming practices.
Defining Floor Rearing and Cage Rearing
Floor rearing involves raising poultry on a litter-covered floor where birds can move freely, exhibit natural behaviors like dust bathing, and access feeders and waterers at ground level, promoting better welfare through environmental enrichment. Cage rearing confines birds in individual or group cages with limited space, restricting movement and natural behaviors but allowing easier management and disease control. Understanding the differences between floor and cage rearing is crucial for assessing their impact on poultry welfare, health, and productivity.
Space Allowance and Bird Mobility
Floor rearing provides greater space allowance per bird, allowing natural behaviors such as dust bathing, stretching, and wing flapping, which promote better welfare and reduce stress. Cage rearing typically restricts bird mobility due to confined space, limiting movement and often leading to higher risks of skeletal and muscular issues. Enhanced mobility in floor systems supports improved physical health and reduces negative behaviors associated with confinement.
Natural Behaviors and Environmental Enrichment
Floor rearing allows birds to express natural behaviors such as scratching, dust bathing, and foraging, which are essential for their welfare and psychological health. Environmental enrichment in floor systems includes litter material, perches, and pecking objects that stimulate exploratory activities and reduce stress. In contrast, cage rearing restricts movement and natural behaviors, often leading to increased frustration and welfare concerns despite controlled environments.
Health and Hygiene Considerations
Floor rearing in poultry farming promotes better natural behaviors and reduces stress, enhancing overall bird welfare through increased movement and interaction with the environment. Cage rearing, while efficient for space utilization, often restricts mobility, increasing risks of foot lesions and respiratory issues due to limited ventilation and waste accumulation. Maintaining stringent hygiene practices in floor systems is crucial to prevent disease spread, whereas regular cleaning protocols and proper cage design are essential in cage systems to mitigate health risks.
Impact on Mortality and Injury Rates
Floor rearing in poultry farming generally results in lower injury rates compared to cage rearing due to increased space and natural movement, which reduces stress and aggressive behavior among birds. Mortality rates tend to be higher in cage systems because restricted movement can cause skeletal problems and exacerbated aggression, leading to more frequent injuries and fatalities. Studies show that floor-reared birds exhibit improved welfare indicators, including better bone strength and reduced bruising, ultimately contributing to lower mortality and injury incidences.
Stress Levels and Behavioral Indicators
Floor rearing allows birds to exhibit natural behaviors such as dust bathing and foraging, which significantly reduces stress levels compared to cage rearing. Cage rearing often restricts movement, leading to increased corticosterone levels, feather pecking, and stereotypic behaviors indicative of chronic stress. Behavioral indicators like increased vocalizations and aggression are more prevalent in caged birds, highlighting the welfare benefits of floor systems.
Egg Quality and Production Outcomes
Floor rearing provides poultry with more natural movement, often leading to improved egg shell strength and reduced incidence of cracked eggs compared to cage systems. Cage rearing optimizes space and feed efficiency, typically resulting in higher egg production rates, but may increase stress-related defects in egg quality such as thinner shells. Balancing bird welfare with production outcomes requires considering the trade-offs between enhanced behavioral opportunities in floor systems and the productivity advantages of cages.
Welfare Standards and Legal Regulations
Floor rearing in poultry farming generally allows birds to express natural behaviors such as dust bathing and perching, which aligns with higher welfare standards set by organizations like the RSPCA and the Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. Cage rearing, often subject to strict legal regulations including the EU Council Directive 1999/74/EC, limits movement and behavioral expression, raising concerns over welfare that has led to bans or phase-outs of conventional battery cages in many regions. Compliance with welfare standards and legal frameworks is critical for poultry producers to ensure ethical treatment, reduce stress-induced health issues, and maintain market access in countries with stringent animal welfare laws.
Consumer Perception and Market Demand
Consumer perception increasingly favors floor rearing over cage rearing due to concerns about bird welfare and natural behaviors. Market demand reflects this shift, with higher sales for products labeled as cage-free or free-range, often associated with floor-reared poultry. Studies indicate that ethically conscious consumers are willing to pay premium prices, driving producers to adopt floor rearing systems to align with welfare standards and market trends.
Related Important Terms
Enriched Colony Systems
Enriched colony systems enhance bird welfare by providing more space, perches, nesting areas, and environmental enrichment compared to traditional cage rearing, promoting natural behaviors and reducing stress. These systems balance the benefits of floor rearing, such as freedom of movement, with the health and management advantages of cage housing, resulting in improved physical and psychological well-being.
Aviary Systems
Aviary systems in poultry farming enhance bird welfare by providing greater freedom of movement and natural behaviors compared to traditional floor rearing and cage rearing methods. These systems reduce stress and improve physical health by allowing hens to perch, nest, and forage in a multi-tiered environment that mimics natural habitats.
Furnished Cages
Furnished cages in poultry farming offer enhanced bird welfare compared to traditional battery cages by providing perches, nesting areas, and scratching pads that encourage natural behaviors and reduce stress. Floor rearing allows greater movement and social interaction but may increase risks of disease and feather pecking, making furnished cages a balanced solution for improving hen welfare while maintaining efficient production.
Litter Management Technology
Litter management technology in floor rearing systems significantly enhances bird welfare by maintaining optimal moisture levels and reducing ammonia emissions, promoting healthier respiratory conditions and natural behaviors. Cage rearing often limits natural movement and increases stress, whereas advanced litter systems in floor rearing support better hygiene and comfort for poultry.
Perch Availability Index
Floor rearing offers a higher Perch Availability Index, promoting natural behaviors and enhanced welfare by allowing birds unrestricted access to perches. In contrast, cage rearing typically limits perch space, restricting movement and negatively impacting bird welfare.
Welfare Assessment Protocols
Welfare assessment protocols in poultry farming emphasize behavioral expression, physical health, and environmental conditions, showing floor rearing allows birds more freedom for natural behaviors like foraging and dust bathing compared to cage rearing, which often restricts movement and increases stress indicators. Objective measures such as feather condition, gait scores, and corticosterone levels consistently indicate better overall welfare in floor-reared birds due to enhanced space and environmental enrichment opportunities.
Multi-tier Rearing
Multi-tier rearing systems in poultry farming offer enhanced space utilization and improved bird welfare by allowing natural behaviors like perching and dust bathing, unlike traditional cage rearing that restricts movement. Compared to floor rearing, multi-tier systems reduce ground contact, lowering disease risks and promoting better air quality, which contributes to healthier and less stressed birds.
Behavioral Enrichment Zones
Floor rearing provides birds with behavioral enrichment zones such as perches, dust bathing areas, and scratch pads, promoting natural behaviors and better welfare outcomes. Cage rearing often limits movement and access to enrichment, leading to increased stress and reduced expression of innate behaviors in poultry.
Stocking Density Optimization
Floor rearing allows birds more freedom of movement and natural behaviors but requires careful management of stocking density to prevent overcrowding and stress. Cage rearing offers controlled space allocation to optimize stocking density, reducing aggression and injury while supporting bird welfare through regulated environmental conditions.
Feather Pecking Mitigation
Floor rearing in poultry farming allows birds more natural behaviors and movement, which significantly reduces stress-induced feather pecking compared to cage rearing, where confinement often leads to higher aggression and feather damage. Implementing environmental enrichments and adequate space in floor systems further mitigates feather pecking by promoting foraging and social interaction.
Floor rearing vs Cage rearing for bird welfare Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com