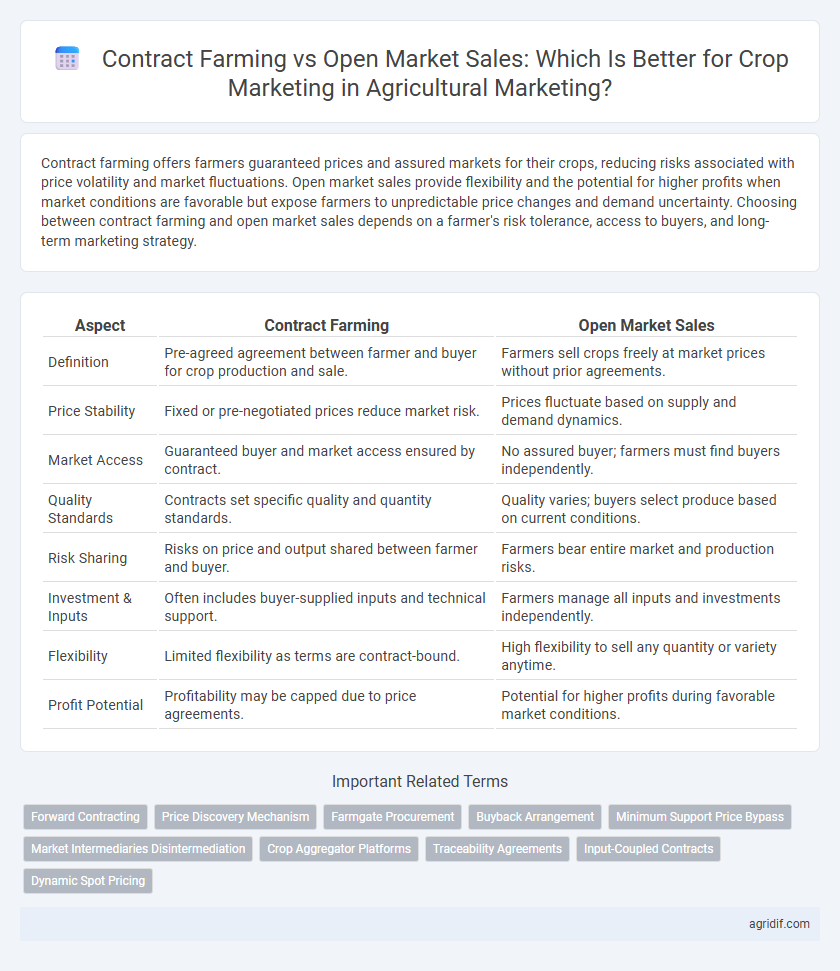
Contract farming offers farmers guaranteed prices and assured markets for their crops, reducing risks associated with price volatility and market fluctuations. Open market sales provide flexibility and the potential for higher profits when market conditions are favorable but expose farmers to unpredictable price changes and demand uncertainty. Choosing between contract farming and open market sales depends on a farmer's risk tolerance, access to buyers, and long-term marketing strategy.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Contract Farming | Open Market Sales |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pre-agreed agreement between farmer and buyer for crop production and sale. | Farmers sell crops freely at market prices without prior agreements. |
| Price Stability | Fixed or pre-negotiated prices reduce market risk. | Prices fluctuate based on supply and demand dynamics. |
| Market Access | Guaranteed buyer and market access ensured by contract. | No assured buyer; farmers must find buyers independently. |
| Quality Standards | Contracts set specific quality and quantity standards. | Quality varies; buyers select produce based on current conditions. |
| Risk Sharing | Risks on price and output shared between farmer and buyer. | Farmers bear entire market and production risks. |
| Investment & Inputs | Often includes buyer-supplied inputs and technical support. | Farmers manage all inputs and investments independently. |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility as terms are contract-bound. | High flexibility to sell any quantity or variety anytime. |
| Profit Potential | Profitability may be capped due to price agreements. | Potential for higher profits during favorable market conditions. |
Understanding Contract Farming in Crop Marketing
Contract farming in crop marketing establishes a direct agreement between farmers and buyers, ensuring fixed prices and guaranteed sales, which reduces market risks and income volatility for farmers. This system often provides access to quality inputs, technical assistance, and timely payments, enhancing crop quality and productivity. Compared to open market sales, contract farming fosters stronger supply chain integration and market stability for both producers and agribusinesses.
Key Features of Open Market Sales
Open market sales in agricultural marketing involve direct transactions between farmers and buyers without predetermined agreements, allowing flexible pricing based on real-time supply and demand. This method provides farmers the freedom to choose buyers, negotiate prices, and sell crops at market-driven rates, fostering competitive environments. However, it exposes farmers to price volatility and uncertain income due to fluctuating market conditions and lack of guaranteed sales.
Price Stability: Contract vs Open Market
Contract farming offers greater price stability by pre-establishing prices and reducing exposure to volatile market fluctuations, ensuring predictable income for farmers. In contrast, open market sales expose farmers to the risks of price volatility due to supply-demand dynamics, weather conditions, and market speculation. Price stability in contract farming enhances financial planning and reduces uncertainty compared to the unpredictable nature of open market pricing.
Risk Management in Crop Marketing Approaches
Contract farming offers farmers risk mitigation through guaranteed prices and assured markets, reducing exposure to price volatility common in open market sales. Open market sales, while providing price flexibility, expose growers to unpredictable demand and price fluctuations, increasing financial risk. Strategic use of contract agreements facilitates more stable income streams and improved access to inputs and technical support, enhancing overall risk management in crop marketing.
Farmer-Buyer Relationships in Both Systems
Contract farming establishes a structured, long-term relationship between farmers and buyers, ensuring price stability and input support, which reduces market risks for farmers. In contrast, open market sales offer farmers flexibility to sell crops to multiple buyers but expose them to price volatility and limited access to resources. Trust and coordination in contract farming enhance production planning and quality control, whereas open market transactions often rely on spot negotiations with minimal ongoing collaboration.
Quality Standards and Compliance
Contract farming ensures strict adherence to quality standards and compliance through predefined agreements between farmers and buyers, guaranteeing crop specifications and timely delivery. Open market sales often lack standardized quality control, leading to variability in crop grades and compliance challenges with market regulations. Prioritizing contract farming enhances traceability and consistency, supporting higher market value and consumer trust in agricultural products.
Flexibility and Autonomy for Farmers
Contract farming offers farmers assured markets and fixed prices but often limits their flexibility and autonomy in crop selection and management. Open market sales provide greater freedom for farmers to decide crop variety, timing, and buyers, enhancing their control over marketing decisions. This autonomy in open markets can lead to higher profits but also exposes farmers to price volatility and marketing risks.
Income Potential and Profitability Comparison
Contract farming offers farmers guaranteed prices and reduced market risks, often leading to more stable income streams compared to open market sales. Open market sales can provide higher profitability during peak demand periods but expose farmers to price volatility and bargaining challenges. Evaluating income potential, contract farming tends to deliver consistent returns, while open market sales may yield higher profits sporadically but with increased financial uncertainty.
Legal and Policy Implications
Contract farming offers legal advantages by establishing clear agreements on price, quality, and delivery terms, reducing disputes and ensuring farmer protection under statutory frameworks. Open market sales expose farmers to price volatility and lack formal legal safeguards, increasing risks and limiting policy-driven support mechanisms. Policy implications favor contract farming through regulatory measures promoting transparency, dispute resolution, and farmer rights enforcement, while open markets often face challenges in implementing consistent legal oversight.
Choosing the Right Marketing Strategy for Your Farm
Contract farming provides farmers with guaranteed prices, access to inputs, and technical support, reducing market risks and ensuring stable income. Open market sales offer flexibility and potentially higher profits but expose farmers to price volatility and lack of assured buyers. Evaluating factors such as crop type, market demand, risk tolerance, and resource availability is crucial for selecting the optimal marketing strategy tailored to your farm's goals.
Related Important Terms
Forward Contracting
Forward contracting in contract farming provides farmers with guaranteed prices and assured buyers before harvesting, reducing market risk and price volatility compared to open market sales. This method enhances financial stability and planning efficiency by locking in terms, whereas open market sales expose farmers to unpredictable price fluctuations and demand uncertainty.
Price Discovery Mechanism
Contract farming ensures predetermined prices agreed upon before production, reducing price volatility and risk for farmers by securing guaranteed payment terms. Open market sales rely on real-time supply-demand dynamics for price discovery, leading to potentially higher volatility but offering farmers the chance to capitalize on favorable market conditions.
Farmgate Procurement
Farmgate procurement in contract farming ensures fixed prices and guaranteed sales for farmers, reducing market risk and enhancing income stability. Open market sales offer flexibility and potential for higher profits but expose farmers to price volatility and limited bargaining power at the farmgate level.
Buyback Arrangement
Contract farming offers farmers guaranteed buyback arrangements that secure predetermined prices and quantities, reducing market risk and ensuring steady income. Open market sales lack such assurances, exposing farmers to price volatility and demand fluctuations that can impact profitability.
Minimum Support Price Bypass
Contract farming ensures price stability and guaranteed market access by pre-defining prices, effectively bypassing the uncertainties of Minimum Support Price (MSP) fluctuations, while open market sales expose farmers to volatile prices and potential MSP bypass risks due to intermediary exploitation. By securing contractual agreements, farmers mitigate risks associated with MSP bypass, enhancing income predictability compared to the open market's price-driven vulnerabilities.
Market Intermediaries Disintermediation
Contract farming reduces reliance on market intermediaries by establishing direct agreements between farmers and buyers, ensuring predictable prices and supply chains. Open market sales involve multiple intermediaries that can increase transaction costs and diminish farmers' profit margins due to price volatility and asymmetric information.
Crop Aggregator Platforms
Crop aggregator platforms streamline contract farming by connecting farmers with buyers through pre-agreed terms, ensuring price stability and reducing market risks compared to open market sales. These platforms enhance supply chain efficiency by aggregating produce, providing better market access, and enabling data-driven demand forecasting for crops.
Traceability Agreements
Contract farming ensures traceability agreements by specifying crop quality, quantity, and delivery timelines, enhancing accountability between farmers and buyers. Open market sales lack standardized traceability protocols, making it difficult to verify product origin and maintain consistent quality assurance.
Input-Coupled Contracts
Input-coupled contracts in contract farming secure timely access to quality seeds, fertilizers, and technical support, enhancing crop yield predictability compared to open market sales where farmers face price volatility and input uncertainties. This model strengthens supply chain integration by aligning input provision with guaranteed crop purchase agreements, reducing marketing risks and improving farmer income stability.
Dynamic Spot Pricing
Contract farming provides farmers with price stability and guaranteed market access, enabling better planning and risk management, while open market sales leverage dynamic spot pricing, allowing farmers to maximize profits by responding to real-time supply and demand fluctuations. Dynamic spot pricing in open markets fosters competitive pricing signals but exposes farmers to price volatility and market unpredictability.
Contract Farming vs Open Market Sales for crop marketing Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com