Electronic trading platforms offer increased transparency, faster transactions, and broader market access compared to traditional physical mandis, enhancing efficiency in crop trading. Farmers benefit from real-time price discovery and reduced middlemen interference, which can lead to better profit margins. Physical mandis, while providing direct personal interactions and immediate payment methods, often face challenges like limited market reach and slower transaction processes.
Table of Comparison
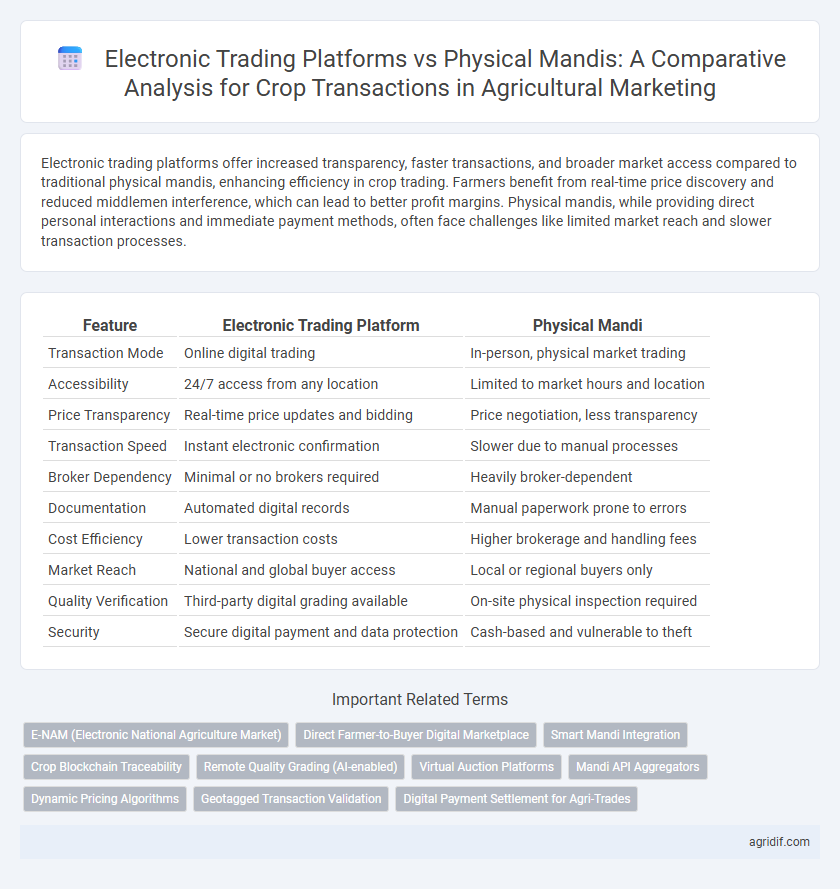
| Feature | Electronic Trading Platform | Physical Mandi |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Mode | Online digital trading | In-person, physical market trading |
| Accessibility | 24/7 access from any location | Limited to market hours and location |
| Price Transparency | Real-time price updates and bidding | Price negotiation, less transparency |
| Transaction Speed | Instant electronic confirmation | Slower due to manual processes |
| Broker Dependency | Minimal or no brokers required | Heavily broker-dependent |
| Documentation | Automated digital records | Manual paperwork prone to errors |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower transaction costs | Higher brokerage and handling fees |
| Market Reach | National and global buyer access | Local or regional buyers only |
| Quality Verification | Third-party digital grading available | On-site physical inspection required |
| Security | Secure digital payment and data protection | Cash-based and vulnerable to theft |
Introduction to Crop Marketing Channels
Electronic Trading Platforms streamline crop marketing by providing farmers direct access to buyers, reducing intermediaries and increasing price transparency. Physical Mandis remain traditional hubs for crop transactions, offering localized market presence and immediate goods inspection but often involve higher transaction costs and delayed payments. Digital platforms enhance efficiency and traceability, crucial for modern agricultural supply chains.
Overview of Electronic Trading Platforms
Electronic trading platforms revolutionize agricultural marketing by enabling seamless crop transactions through digital interfaces, increasing transparency and efficiency compared to traditional physical mandis. These platforms provide real-time price discovery, reduce intermediaries, and facilitate direct interaction between farmers and buyers, enhancing market accessibility and reducing transaction costs. Integration of data analytics and secure payment systems further optimizes supply chain management and ensures timely settlements in crop trading.
Understanding Physical Mandis in Agriculture
Physical Mandis serve as traditional marketplaces where farmers and traders conduct crop transactions through face-to-face interactions, enabling price discovery based on local demand and supply. These mandis provide essential services such as quality assessment, weighing, and storage, ensuring transparency and trust among participants. Despite the rise of electronic trading platforms, physical mandis remain crucial for many farmers due to their accessibility and established market networks.
Accessibility and Reach: Digital vs Traditional
Electronic trading platforms in agricultural marketing provide far-reaching accessibility, enabling farmers from remote areas to connect with multiple buyers without geographical constraints. Traditional physical mandis, while offering direct inspection of crops, are limited by location and operating hours, often restricting the number of participants. Digital platforms enhance market reach and transaction efficiency through real-time price discovery and wider buyer options, significantly expanding market access compared to conventional mandis.
Pricing Transparency for Farmers
Electronic trading platforms enhance pricing transparency for farmers by providing real-time market data and competitive bid prices, reducing information asymmetry commonly found in physical mandis. These platforms enable direct access to multiple buyers, ensuring farmers receive fairer and more accurate price signals based on current demand and quality parameters. In contrast, physical mandis often involve intermediaries whose opaque pricing mechanisms can limit farmers' ability to gauge true market value.
Transaction Efficiency and Speed
Electronic trading platforms significantly enhance transaction efficiency and speed by enabling real-time bidding and automated payment processing, reducing the time farmers spend waiting for buyers. Physical mandis often involve manual processes and face logistical delays, resulting in slower deal closures and increased transaction costs. The digitization of crop transactions on electronic platforms minimizes intermediaries and accelerates market access, providing farmers with faster revenue realization.
Quality Assessment and Dispute Resolution
Electronic trading platforms in agricultural marketing enable standardized digital quality assessment through image recognition and sensor data, enhancing transparency and reducing subjectivity compared to physical mandi inspections. These platforms incorporate automated dispute resolution mechanisms such as smart contracts and real-time data verification, expediting conflict management and minimizing transaction delays. Traditional physical mandis rely heavily on manual inspection and local adjudicators, often leading to inconsistent quality evaluations and prolonged dispute settlements.
Costs and Commissions Involved
Electronic trading platforms for agricultural crops significantly reduce transaction costs by eliminating middlemen and providing direct access to buyers and sellers, often resulting in lower commissions compared to traditional physical mandis. Physical mandis involve higher overhead costs such as transportation, storage, and commission agents' fees, which can increase the overall cost of crop transactions. Farmers benefit from electronic platforms through transparent pricing and minimal service charges, enhancing profitability and market efficiency.
Farmer Empowerment and Market Linkages
Electronic trading platforms enhance farmer empowerment by providing direct access to market prices and reducing dependence on intermediaries, thereby increasing transparency and fair pricing. These digital platforms strengthen market linkages through real-time data and broader buyer access, enabling farmers to reach diverse markets beyond local physical mandis. Physical mandis remain vital for traditional interactions but often limit farmers due to geographic constraints and variable price information, making electronic platforms a transformative tool in agricultural marketing.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Electronic trading platforms face challenges such as digital divide, limited internet access in rural areas, and the need for robust cybersecurity frameworks to protect farmer data during crop transactions. Physical mandis struggle with inefficiencies like middlemen exploitation, price opacity, and logistical constraints affecting timely crop sales and fair pricing. Future prospects indicate integration of blockchain for transparent transactions, AI-driven price forecasting, and hybrid models combining electronic platforms with traditional mandis to enhance accessibility and trust among farmers.
Related Important Terms
E-NAM (Electronic National Agriculture Market)
E-NAM (Electronic National Agriculture Market) revolutionizes crop transactions by providing a digital platform that enhances transparency, reduces intermediaries, and offers farmers real-time price discovery and wider market access compared to traditional physical mandis. This electronic trading platform integrates multiple agricultural markets nationwide, promoting competitive bidding and ensuring better price realization for farmers while streamlining the supply chain.
Direct Farmer-to-Buyer Digital Marketplace
Electronic trading platforms enable direct farmer-to-buyer transactions, reducing intermediaries and enhancing price transparency in agricultural markets. These digital marketplaces facilitate real-time bidding, secure payments, and access to wider markets, outperforming traditional physical mandis in efficiency and inclusivity.
Smart Mandi Integration
Smart Mandi integration enhances electronic trading platforms by enabling real-time price discovery, transparent transactions, and efficient crop procurement compared to traditional physical mandis. These platforms leverage digital infrastructure to streamline supply chains, reduce intermediaries, and provide farmers with direct market access, boosting agricultural marketing efficiency.
Crop Blockchain Traceability
Electronic trading platforms enhance crop transactions by integrating blockchain traceability, ensuring transparent, immutable records of crop origin, quality, and supply chain history. Physical mandis lack this high level of data security and real-time verification, making blockchain-enabled platforms a superior choice for traceable and efficient agricultural marketing.
Remote Quality Grading (AI-enabled)
AI-enabled remote quality grading on electronic trading platforms enhances crop transaction accuracy by providing real-time, standardized assessments that minimize human bias and delay compared to traditional physical mandis. This technology streamlines supply chains, improves price transparency, and expands market access for farmers in remote areas, fostering efficient agricultural marketing ecosystems.
Virtual Auction Platforms
Virtual auction platforms streamline crop transactions by enabling real-time bidding among farmers, buyers, and middlemen without the constraints of physical mandi boundaries, increasing market transparency and price discovery. These electronic trading platforms reduce transaction costs and logistical challenges, fostering wider participation and quicker settlement compared to traditional physical mandis.
Mandi API Aggregators
Mandi API aggregators streamline crop transactions by integrating multiple physical mandis into a unified electronic trading platform, enhancing price transparency and reducing transaction costs for farmers. This hybrid approach leverages real-time market data and digital access, facilitating efficient crop trading while maintaining the trusted mandi ecosystem.
Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
Electronic trading platforms utilize dynamic pricing algorithms that analyze real-time data such as supply fluctuations, demand trends, and market conditions to optimize crop prices efficiently. Physical mandis, limited by manual price discovery processes, often lack the responsiveness and transparency provided by algorithm-driven dynamic pricing in digital platforms.
Geotagged Transaction Validation
Electronic trading platforms leverage geotagged transaction validation to ensure precise location verification and authenticity of crop sales, reducing fraud and enhancing transparency in agricultural marketing. Physical mandis lack this real-time geospatial tracking capability, often resulting in less accurate transaction records and increased disputes over crop provenance and delivery.
Digital Payment Settlement for Agri-Trades
Electronic trading platforms enable seamless digital payment settlements for crop transactions, reducing delays and minimizing risks associated with cash handling in traditional physical mandis. These platforms offer enhanced transparency and traceability in agri-trades, streamlining transaction records and facilitating quicker fund transfers between farmers, traders, and buyers.
Electronic Trading Platform vs Physical Mandi for crop transactions Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com