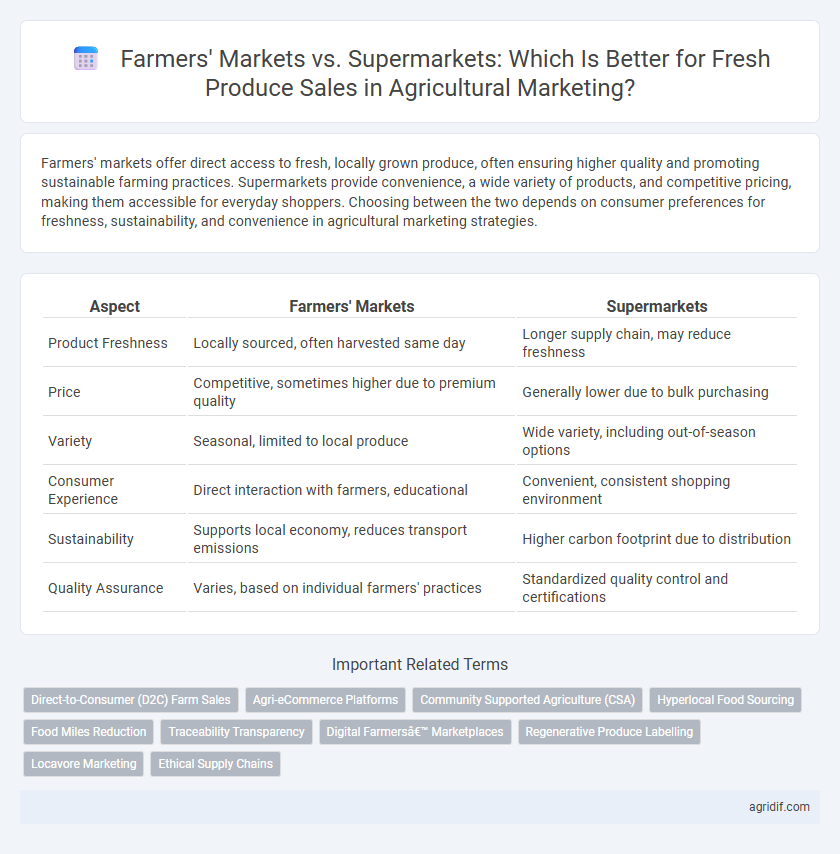
Farmers' markets offer direct access to fresh, locally grown produce, often ensuring higher quality and promoting sustainable farming practices. Supermarkets provide convenience, a wide variety of products, and competitive pricing, making them accessible for everyday shoppers. Choosing between the two depends on consumer preferences for freshness, sustainability, and convenience in agricultural marketing strategies.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Farmers' Markets | Supermarkets |
|---|---|---|
| Product Freshness | Locally sourced, often harvested same day | Longer supply chain, may reduce freshness |
| Price | Competitive, sometimes higher due to premium quality | Generally lower due to bulk purchasing |
| Variety | Seasonal, limited to local produce | Wide variety, including out-of-season options |
| Consumer Experience | Direct interaction with farmers, educational | Convenient, consistent shopping environment |
| Sustainability | Supports local economy, reduces transport emissions | Higher carbon footprint due to distribution |
| Quality Assurance | Varies, based on individual farmers' practices | Standardized quality control and certifications |
Overview of Fresh Produce Distribution Channels
Farmers' markets provide direct-to-consumer sales, emphasizing local, seasonal, and often organic fresh produce, which supports regional economies and reduces supply chain complexity. Supermarkets dominate mass distribution with extensive logistics networks, offering year-round availability of a wide variety of fresh produce sourced nationally and internationally. The choice between these channels impacts pricing, freshness, consumer trust, and the environmental footprint of produce distribution.
Role of Farmers’ Markets in Supporting Local Agriculture
Farmers' markets play a crucial role in supporting local agriculture by providing direct access for farmers to sell fresh produce, enhancing farmers' income and promoting sustainable farming practices. These markets reduce the supply chain length, ensuring fresher products with higher nutritional value compared to supermarkets. Consumer preference for locally grown fruits and vegetables at farmers' markets boosts regional economies and encourages agricultural diversity.
Supermarkets: Scale, Convenience, and Variety
Supermarkets dominate fresh produce sales due to their large-scale operations, offering extensive product variety that meets diverse consumer preferences in one location. Their supply chain efficiency ensures year-round availability and consistent quality of fruits and vegetables, appealing to convenience-seeking shoppers. Advanced inventory management and strategic sourcing enable supermarkets to maintain competitive pricing and freshness standards, attracting a broad customer base for agricultural products.
Pricing Strategies: Farmers’ Markets vs Supermarkets
Farmers' markets often employ transparent, flexible pricing strategies that allow direct negotiation between producers and consumers, leading to competitive prices based on freshness and local supply. Supermarkets implement dynamic pricing models driven by bulk purchasing, supply chain efficiencies, and promotional discounts to attract a broader customer base and maximize volume sales. Pricing at farmers' markets reflects seasonal availability and quality premiums, whereas supermarkets focus on price consistency and variety through standardized pricing algorithms.
Quality and Freshness of Produce Compared
Farmers' markets consistently offer fresher produce compared to supermarkets due to direct sourcing from local farms, ensuring minimal time between harvest and sale. The quality of products at farmers' markets often reflects seasonal availability and organic or sustainable farming practices, enhancing nutritional value and flavor. Supermarkets may stock produce with longer shelf lives but often rely on extended supply chains, which can reduce freshness and quality by the time consumers purchase items.
Consumer Trust and Transparency in Sourcing
Farmers' markets often foster higher consumer trust due to direct interaction with growers, ensuring transparency in sourcing and product origins. Supermarkets, despite widespread availability, may face skepticism regarding the provenance and handling of fresh produce due to complex supply chains. Transparent sourcing practices at farmers' markets enhance consumer confidence and support sustainable agricultural marketing.
Economic Impact on Local Farmers
Farmers' markets generate higher profit margins for local farmers by eliminating intermediary costs and allowing direct sales to consumers, boosting rural economies and enhancing farmers' financial stability. Supermarkets often offer lower prices due to bulk purchasing and centralized distribution, which can undercut local producers' earnings and reduce their market share. Local farmers benefit economically from farmers' markets through increased community engagement and consumer loyalty, driving sustainable agricultural development.
Environmental Sustainability Considerations
Farmers' markets significantly reduce carbon emissions by minimizing transportation distance and packaging waste compared to supermarkets, which rely on extensive supply chains. Locally sourced fresh produce at farmers' markets supports biodiversity and soil health through sustainable farming practices, while large-scale supermarket suppliers often prioritize yield over environmental impact. Choosing farmers' markets promotes a circular economy and lowers the carbon footprint of fresh produce consumption.
Accessibility and Community Engagement
Farmers' markets offer greater accessibility for local consumers by providing fresh produce directly from nearby growers, fostering stronger community engagement through personal interactions and support for local economies. Supermarkets provide convenience with extended hours and a wide variety of produce, but often lack the localized connection that encourages community involvement. The unique social experience at farmers' markets promotes trust and transparency, enhancing consumer loyalty and awareness about sustainable agriculture.
The Future of Fresh Produce Sales in the Digital Age
Farmers' markets offer direct-to-consumer freshness and traceability, appealing to niche markets valuing local and organic produce, while supermarkets provide convenience, variety, and digital integration through e-commerce platforms. The future of fresh produce sales hinges on hybrid models combining face-to-face farmer interactions with advanced digital supply chain management and online sales channels. Innovations like blockchain for food traceability, AI-driven demand forecasting, and augmented reality shopping experiences are transforming consumer engagement and operational efficiency in fresh produce marketing.
Related Important Terms
Direct-to-Consumer (D2C) Farm Sales
Farmers' markets enable direct-to-consumer (D2C) sales, allowing producers to capture higher profit margins and foster stronger community relationships compared to supermarkets, where fresh produce often passes through multiple intermediaries. These markets enhance transparency in product origin and freshness, supporting local economies and increasing consumer trust in farm-to-table quality.
Agri-eCommerce Platforms
Farmers' markets offer direct-to-consumer sales of fresh, locally-grown produce, enhancing transparency and supporting small-scale growers, while supermarkets provide broader product variety with large-scale supply chains but often less freshness and traceability. Agri-eCommerce platforms bridge these models by enabling farmers to reach wider markets online, ensuring freshness through optimized logistics and promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
Farmers' markets and supermarkets differ significantly in fresh produce sales, with Community Supported Agriculture (CSA) programs strengthening local economies by connecting consumers directly to regional farms, ensuring fresher products and seasonal variety. CSA models enhance consumer trust and sustainability by offering subscription-based access to fresh, organically grown produce, contrasting with supermarkets' broader but less locally sourced inventory.
Hyperlocal Food Sourcing
Farmers' markets offer hyperlocal food sourcing with fresh produce grown within the community, reducing transportation emissions and supporting local economies. Supermarkets provide convenience and variety but often rely on long supply chains that diminish freshness and increase carbon footprints.
Food Miles Reduction
Farmers' markets significantly reduce food miles by sourcing produce directly from local farms, ensuring fresher products and lower carbon emissions compared to supermarkets that often rely on long-distance transportation. This localized supply chain not only minimizes environmental impact but also supports regional economies and promotes sustainable agricultural practices.
Traceability Transparency
Farmers' markets offer superior traceability and transparency by enabling direct interactions between consumers and producers, allowing buyers to verify the origin and cultivation practices of fresh produce. Supermarkets rely on complex supply chains and third-party certifications, which can obscure detailed product provenance and reduce consumer confidence in transparency.
Digital Farmers’ Marketplaces
Digital farmers' marketplaces leverage advanced e-commerce platforms to provide farmers direct access to consumers, enhancing freshness and transparency compared to traditional supermarkets. These online platforms optimize supply chains, reduce intermediary costs, and offer real-time inventory updates, boosting efficiency in fresh produce sales.
Regenerative Produce Labelling
Farmers' markets offer direct access to regenerative produce labelling, enhancing consumer trust through transparency about sustainable farming practices, contrasting with supermarkets where regenerative claims often lack traceability and verification. This growing preference for certified regenerative produce at farmers' markets supports eco-friendly agriculture by promoting soil health and biodiversity while providing farmers with fairer profit margins.
Locavore Marketing
Farmers' markets offer fresh produce directly sourced from local farms, emphasizing seasonal and regional varieties that appeal to locavores seeking sustainability and reduced carbon footprints. Supermarkets provide convenience and variety but often stock produce grown in distant regions, diminishing the emphasis on local provenance crucial to locavore marketing strategies.
Ethical Supply Chains
Farmers' markets support ethical supply chains by promoting transparency, local sourcing, and fair compensation for producers, fostering direct relationships between farmers and consumers. Supermarkets often rely on complex, global supply chains with less visibility, which can obscure labor conditions and environmental impacts associated with fresh produce.
Farmers’ markets vs Supermarkets for fresh produce sales Infographic
 agridif.com
agridif.com